1. Introduction
2. Mechanobiological structural basis for cell-matrix interaction
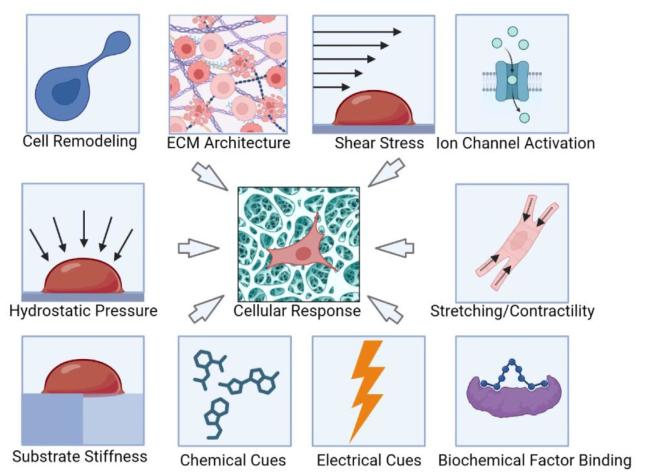
Fig. 1. The scheme for mechanobiology microenvironment influences the cellular response under loading conditions [12]. Microenvironment factors include cell remodeling, ECM architecture, shear stress, ion channel activation, hydrostatic pressure, stretching contractility, substrate stiffness, chemical cues, electrical cues and biochemical factors binding. All these Multiphysics would have an impact at cell level with biochemical cell response [12]. |
2.1. Extracellular matrix component and architecture
2.2. Matrix stiffness and porosity
2.3. Primary cilium
2.4. Membrane-bound proteins
2.5. Membrane ion channel
2.6. Motor protein
2.7. LINC complex
2.8. Clathrins and vesicles
3. The construction of matrix mechanobiological structure by TPL
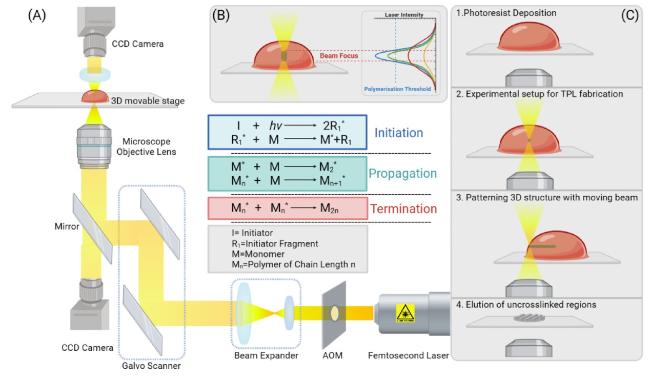
Fig. 2. (A). Schematic picture of an example TPL consisting of a femtosecond laser, acousto-optic modulator (AOM), beam expander, galvo scanner, CCD camera, 3D movable stage and controlling system (B). In TPL, the polymerization processes only occur in the focus of a femtosecond-pulsed laser voxel (volume pixel). But in one-photon direct laser writing, instead, the laser beam is absorbed all along the focalization cone, making it hard to realize complex 3D structures [27] (C). The generation mechanism of the procedure of TPL sample fabrication. controllable relative movement between the laser focus would cause the polymerization in a designed shape to form customized graphics [27]. |
4. The polymerization mechanism for the TPL
Table 1. Photoinitiators with corresponding cross-linked hydrogels and the applications. |
| Name | Structure | Hydrogel Type | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzophenone dimer | 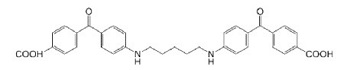 | BSA, Collagen | Drug Delivery, Scaffold | [39,40] |
| Flavin adenine dinucleotide | 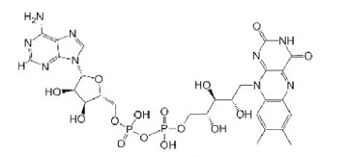 | BSA, Avidin, PMMA | Cell Delivery | [39,40,41,42] |
| G2CK(a) | 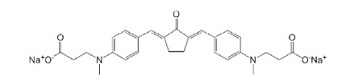 | GelMOD | Drug Delivery, Scaffold | [43,44] |
| Irgacure 369 | 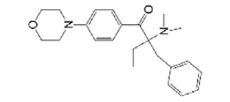 | PEGDA | Scaffold | [45] |
| Irgacure 651 | 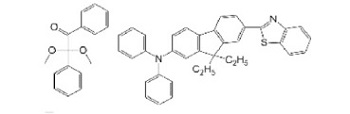 | PEGDA/HEMA | Scaffold | [46] |
| Irgacure 2959 | 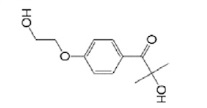 | GelMOD, HA | Scaffold | [47,48,49] |
| P2CK(a) |  | GelMOD | Drug Delivery, Scaffold | [43,44] |
| Rose Bengal |  | BSA, Fibrinogen, Collagen, Fibronectin, Concanavalin A | Drug Delivery, Scaffold | [39,40,50,51] |
| WSPI(a) | 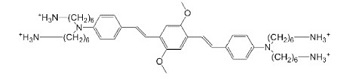 | PEGDA, Gelatin Derivative | Scaffold | [43,52] |
BSA: Bovine serum albumin; PMMA: Poly(methyl methacrylate); GelMOD: Methacrylamide-modified gelatin; PEGDA: Polyethylene Glycol Diacrylate; HEMA (Hydroxyethyl) methacrylate; HA: Hyaluronic acid. |
5. Recent mechanobiology studies made by TPL
Table 2. Materials list for TPL techniques Realized for Mechanobiological Studies. |
| Materials | Photoinitiators | Structures | Cell Type | Resolution | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDDA | Irgacure 819 | Star Shape | Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cell (OPC) | 5 μm | [68]R |
| Gelma; PEGDA; PEGOA | N/A | Vessel | Human Breast Cancer Cells (MCF-7); HUVECs | 500 μm | [67]R |
| Acrylamide; Bis-Acrylamide | LAP | Strips | Rat Kidney Epithelial Cells (Nrk-52e) | 100 μm | [69]R |
| PEGDA | Irgacure 369 | Scaffold | Cardiomyocyte | 0.6 μm | [54]R |
| PEGDA | Irgacure 369 | Scaffold | Chicken Fibroblasts | 1 μm | [55]R |
| PEGDA | Irgacure 369 | Ridges | Rat Adrenal Pheochromocytoma Cell Line (Pc12); Human Neuroblastoma Derived Cell Line (Sh-Sy5y) | 0.3 μm | [20]R |
| IP-L 780 | N/A | Woodpile Structure | Mature Human Dendritic Cells (Dcs) | 1.3 μm | [58]R |
| IP-L 780 | N/A | Hexagonal Grid | Osteosarcoma Cells (Saos-2, MG-63, U-2 OS) | 0.45 μm | [56]R |
| PETTA | Irgacure 379 | Scaffold | Human Lung Carcinoma Cells (A549); Wildtype Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEF) | 0.75 μm | [64]R |
| TPETA | Irgacure 369 | Scaffold | Epithelial (A549); Fibroblast (3T3) | 1 μm | [57]R |
| IP-Dip | N/A | Tetrakaidecahedral Scaffold | Saos-2 Cell | 1 μm | [63]R |
| SZ2080 | Irgacure 369 | Nichoid Structure | Rat BMSCs | 2 μm | [70]R |
HDDA: Hexanediol Diacrylate, GelMA: Gelatin-Methacryloyl; PEGDA: Poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate; PEGOA: 8-arm polyethylene glycol-octaacrylate; IP-L 780: Acrylatebased Resin; PETTA: Trimethylolpropane Ethoxylate Triacrylate; TPETA: Trimethylolpropane Ethoxylate Triacrylate. |