1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Fabrication and characterization of GelMA hydrogel
2.2. Cell culture and encapsulation
2.3. Cell proliferation, cytotoxicity and IC50 assay
2.4. qPCR assay
2.5. Western blotting and immunoprecipitation
2.6. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Encapsulation of MDA-MB-231 cells in GelMA hydrogels
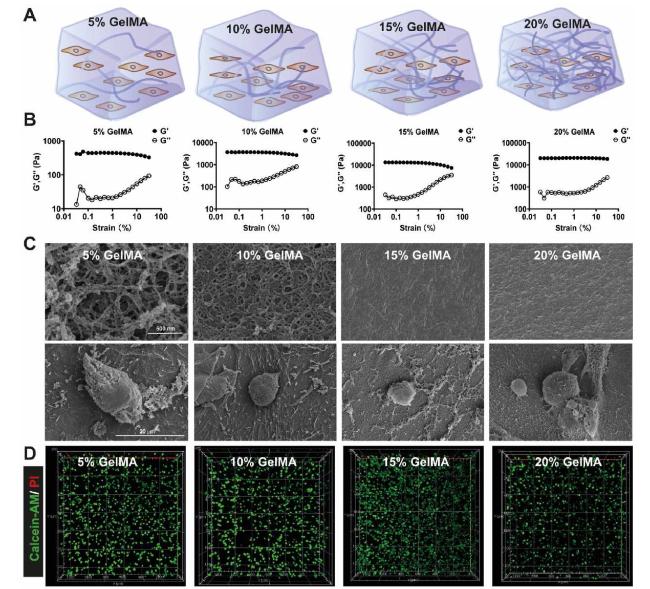
Fig. 1. Characterization of GelMA hydrogel (A) The schematic illustration of GelMA hydrogel with different concentrations (B) Rheological testing of GelMA hydrogels, variation in the storage modulus (G′) and loss modulus (G″) of hydrogels at different strain (C) Representative SEM images of GelMA hydrogels and MDA-MB-231 cells laden in the hydrogels (D) Calcein-AM/PI was used for live/dead staining of MDA-MB-231 cells in hydrogels cultured for 3 days. |
3.2. The drug response ability of cells encapsulated in GelMA hydrogels
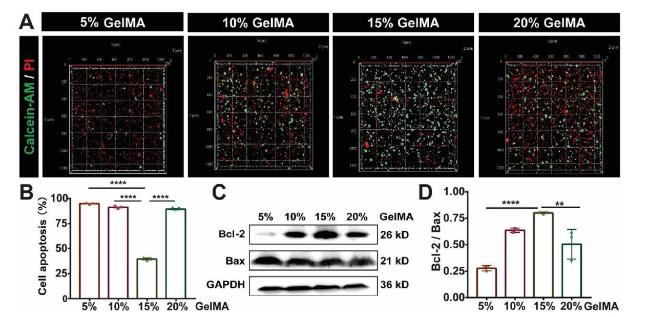
Fig. 2. Cytotoxic efficacy of DOX in MDA-MB-231cells cultured in GelMA hydrogels with different concentrations (A) Fluorescence images represent live/dead cell staining of MDA-MB-231 cells treated with 8 μM DOX for 48 h in GelMA hydrogels with different concentrations, live cells (Calcein-AM, green), dead cells (PI, red cells) (B) The quantitative fluorescence intensity of Calcein-AM/PI staining indicated cell apoptosis, n = 3, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001 with one-way ANOVA and post hoc Dunnett test (C) Representative Western blotting showing bands for Bcl-2 and Bax in MDA-MB-231 cells cultured in GelMA hydrogels after 8 μM DOX treatment (D) Bar graph showing the Western blotting quantifications of the ratio of Bcl-2 to Bax by pixel density, n = 3, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗P < 0.01 with one-way ANOVA and post hoc Dunnett test. |
3.3. ECM stiffness dependent EGFR activity is necessary for drug resistance
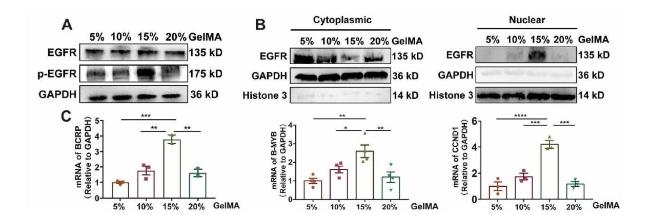
Fig. 3. EGFR is activated in 15% GelMA group (A) Western blot showing bands for EGFR and phosphorylated EGFR (p-EGFR) in MDA-MB-231 cells cultured in GelMA hydrogels (B) Western blot showing bands for EGFR and p-EGFR in cytoplasm or nucleus of MDA-MB-231 cells cultured in GelMA hydrogels (C) q-PCR analysis of the mRNA expression of EGFR targeted gene (BCRP, B-MYB, CCND1), n ≥ 3, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗P < 0.05 with one-way ANOVA and post hoc Dunnett test. |
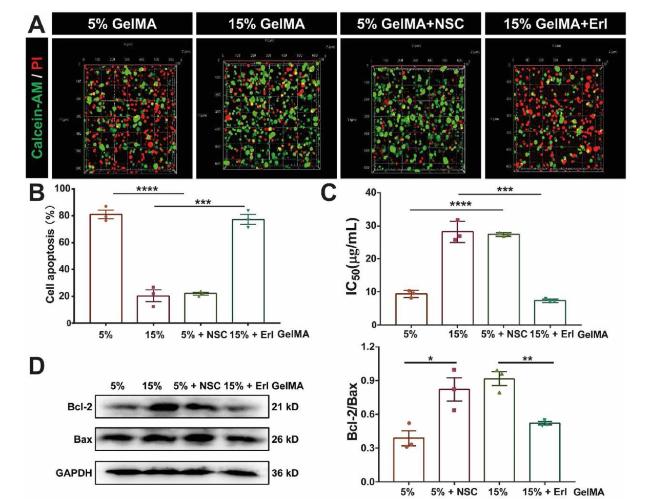
Fig. 4. EGFR promotes ECM stiffness-dependent drug resistance (A) Fluorescence images represent live/dead cell staining of MDA-MB-231 cells cultured in 5% GelMA with or without NSC treatment and 15% GelMA hydrogel with or without Erl treatment, live cells (Calcein-AM, green), dead cells (PI, red cells) (B) The quantitative fluorescence intensity of Calcein-AM/PI staining in (A) indicated cell apoptosis, n = 3, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 with unpaired t-test (C) IC50 values for MDA-MB-231 cells cultured in 5% GelMA with or without NSC treatment and 15% GelMA hydrogel with or without Erl treatment, n = 3, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 with unpaired t-test (D) Western blot showing bands for Bcl-2 and Bax in MDA-MB-231 cells cultured in 5% GelMA with or without NSC treatment and 15% GelMA hydrogel with or without Erl treatment. Bar graph showing the Western blotting quantifications of the ratio of Bcl-2 to Bax by pixel density in (D) (bottom right corner), ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗P < 0.05 with t-test. |
3.4. ECM stiffness inhibits the Hippo pathway by the activation of EGFR to facilitate YAP enter into nucleus, leading to drug resistance
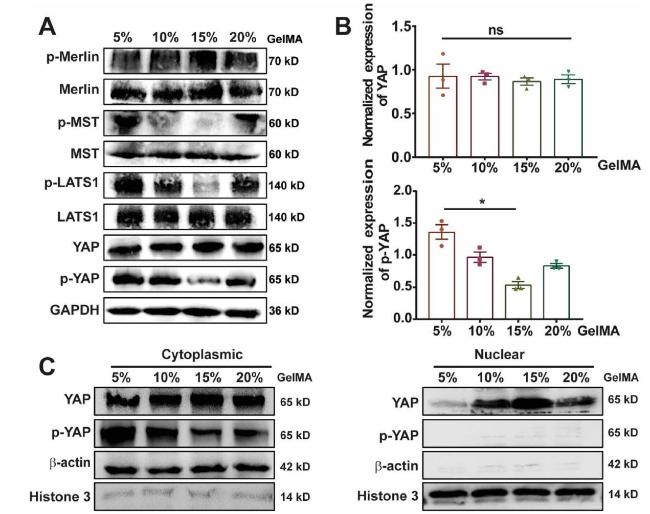
Fig. 5. ECM stiffness regulates the expression and distribution of YAP (A) Western blot showing bands for the protein expression in Hippo signaling pathway (B) Bar graph showing Western blotting quantifications of YAP and p-YAP by pixel density normalized to GAPDH loading control in (A), n = 3, ns, no significant, ∗P < 0.05 with unpaired t-test (C) Western blot showing bands for YAP and phosphorylated YAP (p-YAP) in cytoplasm or nucleus of MDA-MB-231 cells cultured in GelMA hydrogels. |
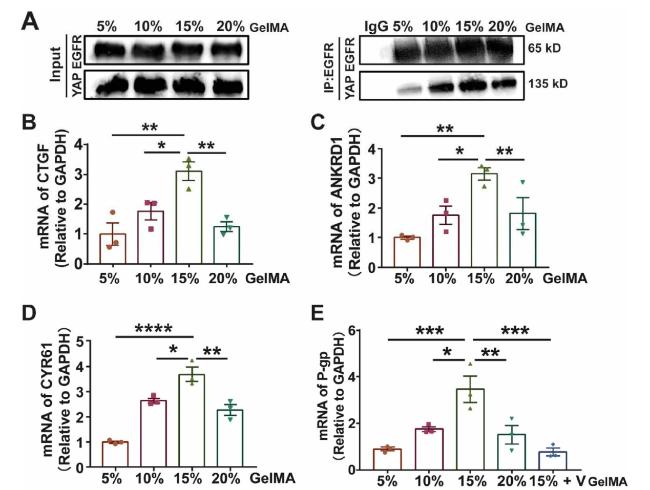
Fig. 6. Interaction of YAP and EGFR facilitates EGFR translocate into the nucleus and active the target genes (A) Immunocoprecipitation analysis showing the binding ability of EGFR and YAP in MDA-MB-231 cells cultured in GelMA hydrogel (B-D) qPCR analysis of the mRNA expression of YAP targeted gene (CTGF, ANKRD1, CYR61) (E) qPCR analysis of the mRNA expression of P-gp, MDA-MB-231 cells cultured in GelMA hydrogels, YAP inhibitor Verteporfin was added when indicated. n = 3, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗P < 0.05 one-way ANOVA and post hoc Dunnett test. |