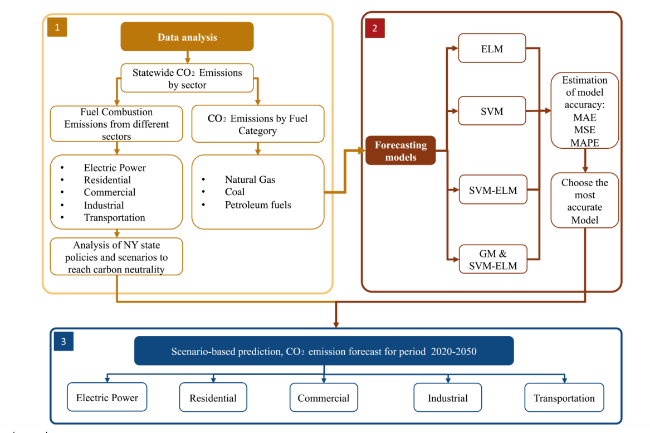
1 Introduction
Fig. 1 Research roadmap |
2 Literature review
2.1 Literature on Carbon emission studies and reports
2.2 Literature on machine learning algorithms
3 Methodology and data collection
3.1 Data collection
3.2 Description of the implementation of the four algorithms and the hyperparameters used
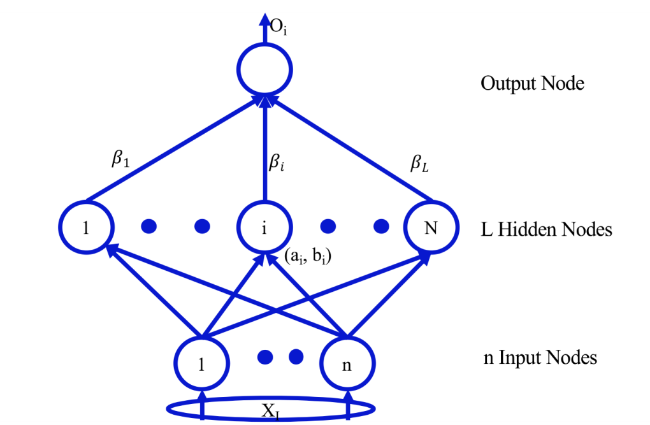
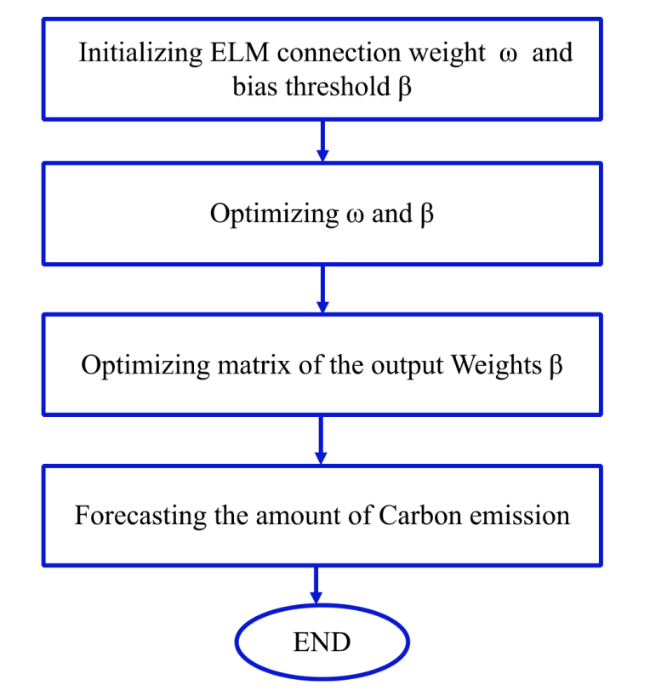
3.2.1 Basic methodology of extreme learning machine algorithm
Fig. 2 The topological structure of the ELM algorithm |
Fig. 3 Flow chart of the model ELM |
3.2.2 Basic methodology of support vector machines
Fig. 4 Flow chart of the model SVM |
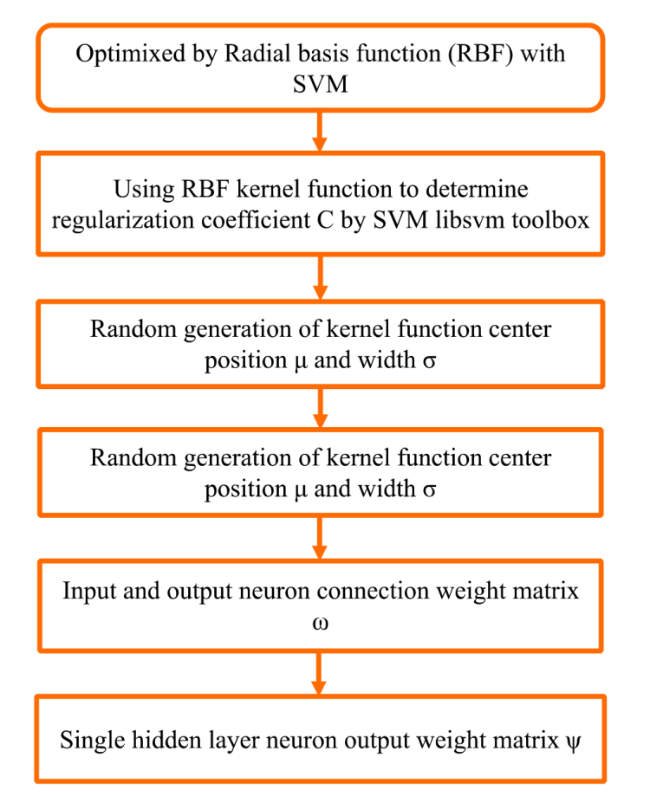
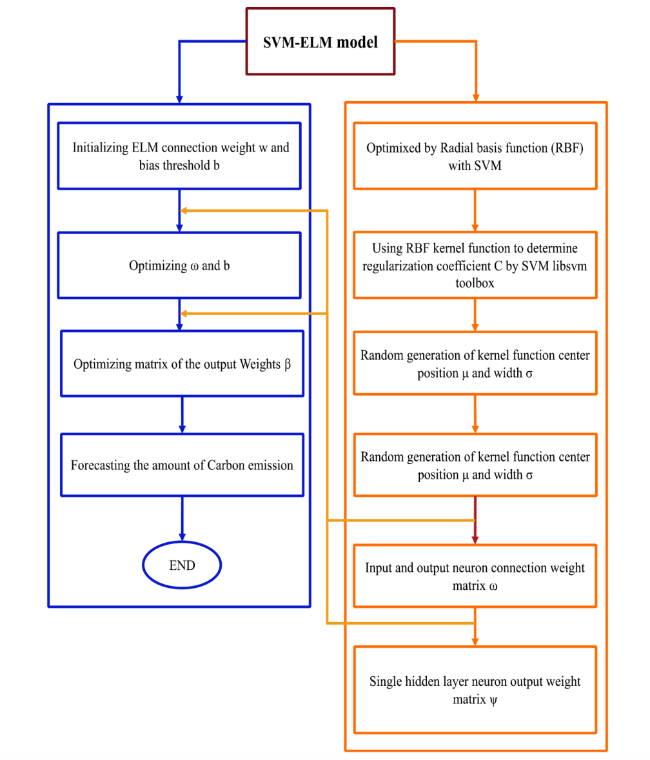
3.2.3 Principal of the SVM-ELM model
Fig. 5 Flow chart of the model SVM-ELM |
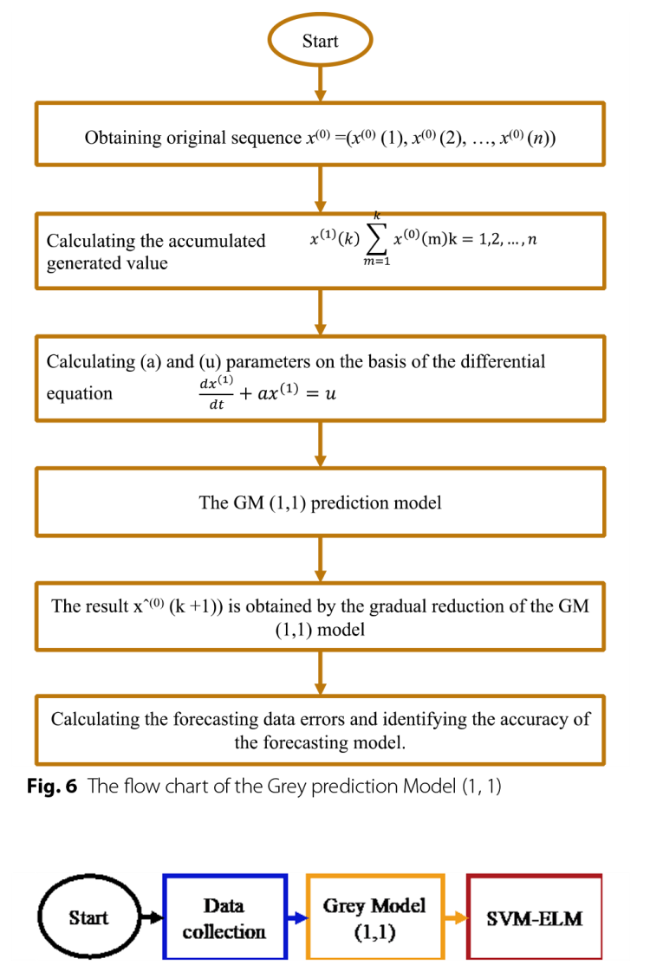
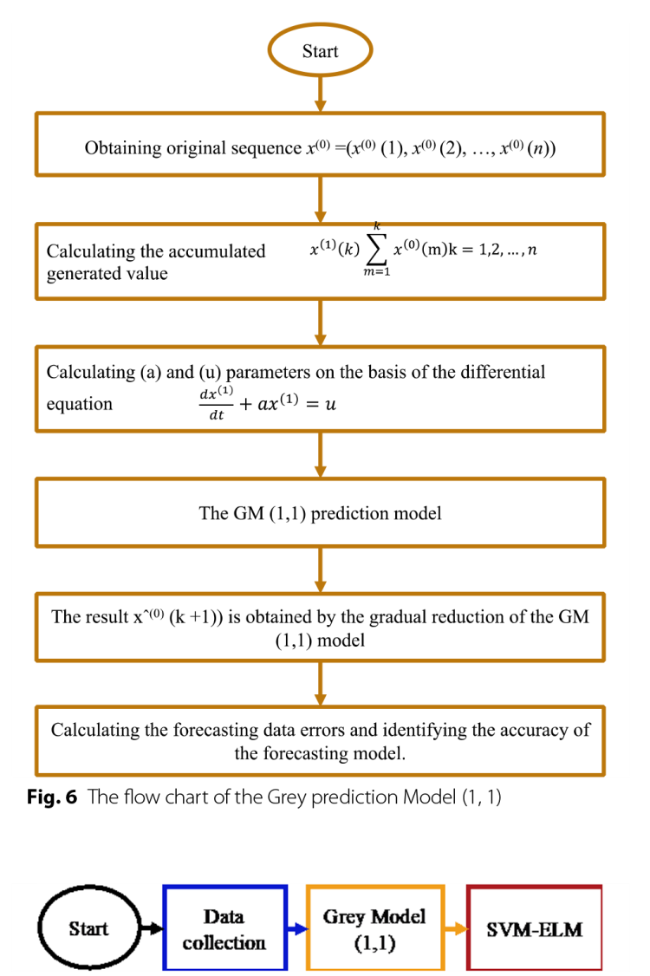
3.2.4 Hybrid GM (1,1) optimized by SVM -ELM algorithm
Fig. 6 The flow chart of the Grey prediction Model (1, 1) |
Fig. 7 The flow chart of the Grey prediction Model (1, 1) optimized by the SVM-ELM model |
3.3 Performance metrics used for evaluating the accuracy of the models
Table 1 Interpretation of typical MAPE |
| MAPE (%) | Model accuracy |
|---|---|
| < 10 | EXCELLENT |
| 10-20 | GOOD |
| 20-50 | QUALIFIED |
| > 50 | UNQUALIFIED |
Source; Lewis (1982, p. 40) [24] |
3.4 Experimental setup and implementation
3.5 New York State decarbonization pathways analysis
Table 2 Strategy for economic sectors to develope pathways, key assumptions |
| Strategy | Pathway 1: High Technology Availability | Pathway 2: Integrated Pathway | Pathway 3 (Reference Case Pathway) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Power | Clean Electricity Generation: Technology-specific targets | Share of renewable/zero- emission generation: 70% renewable by 2030, 100% zero- emission by 2040 Offshore wind capacity: 9 GW by 2035 Behind-the-meter solar PV: 6 GW by 2025 Energy storage: 3 GW by 2030 | Share of renewable/zero- emission generation:50% renewable by 2030 Offshore wind capacity: 2.4 GW by 2030 Behind-the-meter solar PV: 3 GW by 2023 Energy storage: 3 GW by 2030 | |
| Residential and Commercial sector | Building Electrification Appliance Efficiency (non-HVAC) | Electric heat pump sales share: 50% by 2030, 95% by 2050 Appliance Efficiency (non-HVAC): 90% by 2023, 100% by 2025 | Electric heat pump sales share: 6% by 2025 Appliance Efficiency (non-HVAC): 100% by 2025 | |
| Industrial | Efficiency increaser elative to baseline projection: Share of natural gas and LPG use electrified: | 10% by 2030, 45% by 2045 | 10% by 2030; 20% by 2050 60% by 2045 | |
| Transportation | Smart Growth of LDV VMT reduction relative to Reference Aviation Efficiency: | 3% by 2030, 9% by 2050 10% by 2030, 40% by 2050 | ||
| Vehicle Electrification | ● DV: 60% by 2030, 100% by 2040; ● Bus: 60% by 2030, 100% by 2040; ● MDV/HDV: 35% by 2030; 95% by 2040 | ● LDV: 70% by 2030, 100% by 2035; ● Bus: 70% by 2030, 100% by 2035; ● MDV/HDV: 50% by 2030; 95% by 2040 | ● LDA: 25% by 2025; ● LDT: 8% by 2025; ● MDV/Bus: 2% by 2050 | |
| Zero Emissions Fuels | Biofuels Blend: Share of conventional fuel use replaced with biofuels | 100% renewable gas in CNG vehicles by 2030, 40% renewable diesel by 2030, ~ 100% renewable diesel by 2050, 8% renewable gas in pipeline by 2050 | 100% renewable gas in CNG vehicles by 2030, 40% renewable diesel by 2030, 100% renewable diesel by 2050, 100% renewable gasoline by 2050, 68% renewable jet kerosene by 2050, 18% renewable gas in pipeline by 2050 | 7% aggregate ethanol blend for gasoline, 8.4% biodiesel blend for heating oil in Downstate model segment by 2034 to account for areas with biodiesel mandates |
3.6 Scenario settings
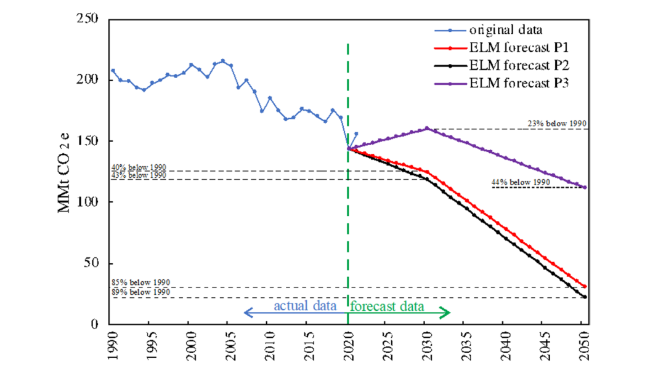
Table 3 Carbon emission percentage reduction for different pathways relative to 1990 |
| Economic sectors | 2030 | 2050 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | P3 | P1 | P2 | P3 | |
| Electric Power | 40% | 70% | 30% | 85% | 100% | 70% |
| Residential | 31% | 10% | 85% | 20% | ||
| Commercial | 31% | 10% | 85% | 17% | ||
| Industrial | 6% | 15% | 81% | 25% | ||
| Transportation | 31% | 30% | 86% | 55% | ||
| Total CO2 emission reduction | 40% | 43% | 23% | 85% | 89% | 44% |
4 Results and discussion
4.1 NY state CO2 emission data analysis and pre-processing
Table 4 NY state Fuel Combustion Emissions for different economic sectors, 1990-2020 (MMt CO2 e) |
| Economic sectors | 1990 | 2005 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Power | 63.2 | 55.4 | 29.1 | 27.7 | 22.0 | 24.4 | 21.4 | 23.4 |
| Residential | 33.8 | 39.4 | 35.3 | 30.7 | 31.4 | 36.4 | 35.7 | 31.5 |
| Commercial | 26.8 | 28.6 | 22.8 | 21.7 | 22.1 | 23.2 | 22.9 | 20.3 |
| Industrial | 19.6 | 14.7 | 9.5 | 9.2 | 8.9 | 9.1 | 9.0 | 8.0 |
| Transportation | 63.9 | 73.4 | 77.6 | 80.8 | 81.5 | 82.0 | 79.8 | 60.1 |
Source State Energy Data System (SEDS), U.S. Energy Information Administration \* MERGEFORMAT [36] |
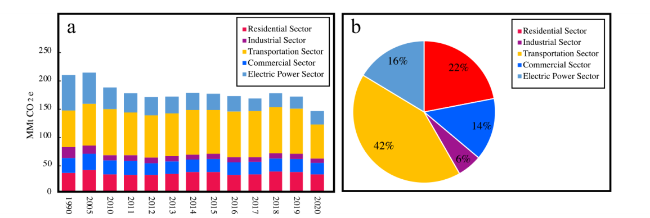
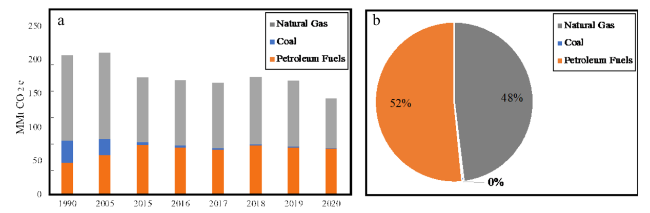
Fig. 8 (a) New York carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuel consumption (1990-2020) (b) Energy-related CO2 in New York State: relative to 2020 for different economic sectors |
Table 5 NY state fuel combustion emissions by fuel category, 1990-2020 (MMt CO2 e) |
| Fuel Category | 1990 | 2005 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Gas | 47.23 | 58.54 | 73.70 | 70.52 | 67.37 | 73.53 | 70.57 | 68.86 |
| Coal | 33.15 | 24.49 | 3.92 | 2.82 | 1.86 | 1.59 | 1.30 | 0.54 |
| Petroleum fuels | 126.95 | 128.47 | 96.73 | 96.80 | 96.61 | 99.98 | 97.10 | 73.97 |
Fig. 9 (a) NY state Fuel Combustion Emissions by Fuel Category, 1990-2020 (MMt CO2 e) (b) Energy-related CO2 in New York State: and relative to 2020 for different Types of Fuel |
4.2 New York State carbon emission forecasting results and projections for fuel categories
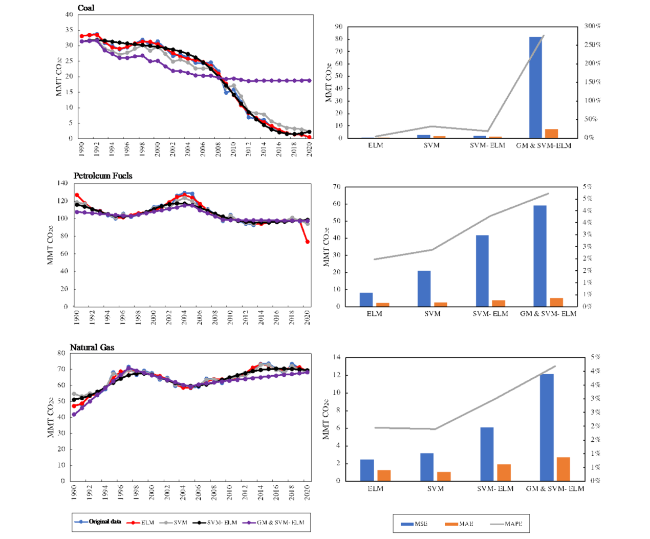
Fig. 10 Validation of the comparison between the original amount of carbon emissions and the forecasting output of four models for Coal, Petroleum fuels and natural gas. Evaluation of models the comparison of prediction errors |
Table 6 The evaluation of four models |
| Model | Type of Fuel | MSE | MAE | MAPE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELM: | Coal | 0.753 | 0.600 | 5% |
| Petroleum fuels | 8.217 | 2.111 | 2% | |
| Natural Gas | 2.470 | 1.276 | 2% | |
| SVM: | Coal | 2.979 | 1.724 | 32% |
| Petroleum fuels | 20.936 | 2.369 | 2% | |
| Natural Gas | 3.179 | 1.090 | 2% | |
| SVM-ELM: | Coal | 1.962 | 1.199 | 19% |
| Petroleum fuels | 41.662 | 3.883 | 4% | |
| Natural Gas | 6.094 | 1.899 | 3% | |
| GM & SVM-ELM: | Coal | 81.966 | 7.264 | 276% |
| Petroleum fuels | 59.079 | 4.994 | 5% | |
| Natural Gas | 12.152 | 2.711 | 4% |
4.3 NY state CO2 emission scenario-based prediction
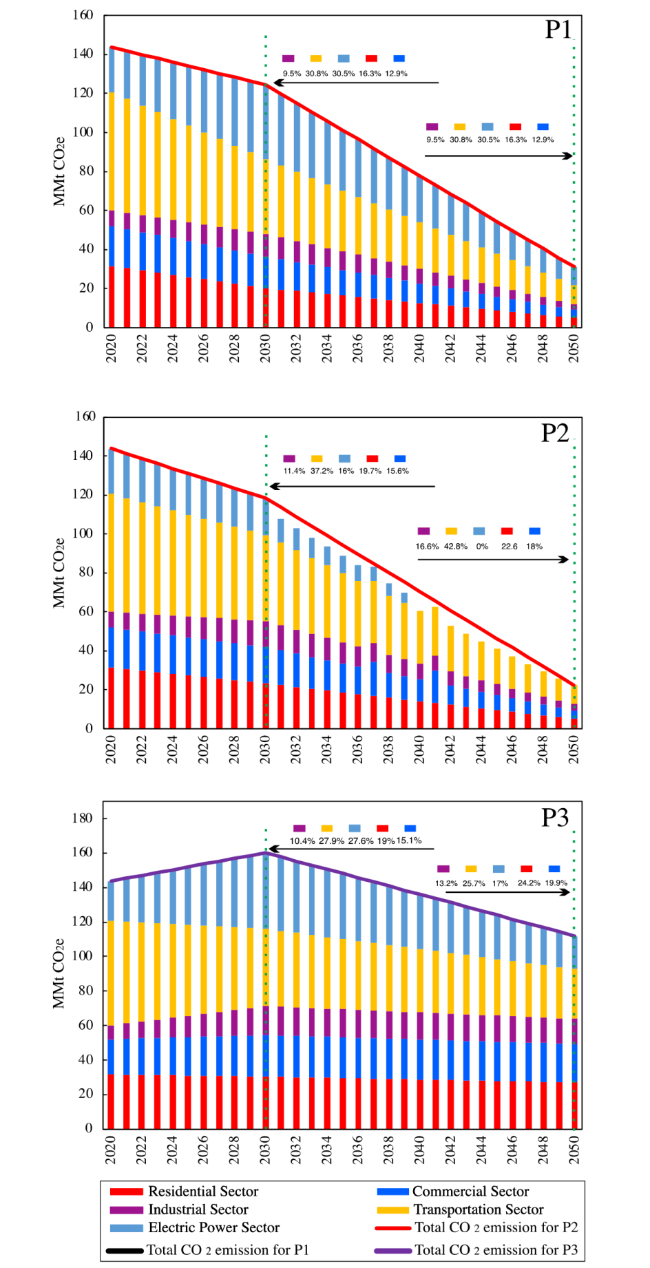
Fig. 11 Scenario-based prediction of NY state, total CO2 emission from 2020-2050 |
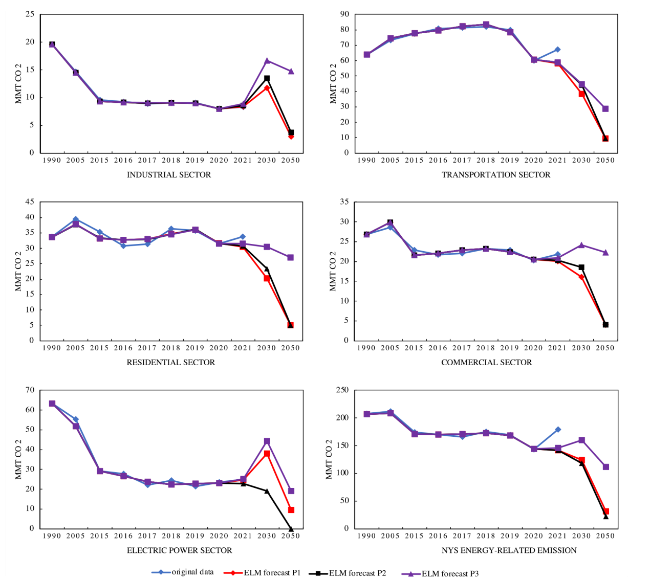
Fig. 12 Pathway1 (P1), Pathway 2 (P2), Pathway 3 (P3) prediction of NY state CO2 emissions for residential (a), commercial (b), industrial (c), transportation (d), electric power (e), and total state energy-related CO2 e by sector (f). for the period 1990-2050 based on the E LM model |
Table 7 Predicted values of CO2 emissions for New York State, MMtCO2 e. in different economic sectors |
| Residential Sector | Commercial Sector | Industrial Sector | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| original data | ELM forecast | original data | ELM forecast | original data | ELM forecast | |||||||
| P1 | P2 | P3 | P1 | P2 | P3 | P1 | P2 | P3 | ||||
| 1990 | 33.79 | 33.629 | 33.624 | 33.63 | 26.835 | 26.833 | 26.835 | 26.84 | 19.605 | 19.557 | 19.561 | 19.56 |
| 2005 | 39.406 | 37.794 | 37.737 | 37.78 | 28.636 | 29.874 | 29.871 | 29.87 | 14.704 | 14.52 | 14.52 | 14.52 |
| 2015 | 35.342 | 33.166 | 33.254 | 33.2 | 22.844 | 21.601 | 21.603 | 21.6 | 9.534 | 9.324 | 9.324 | 9.32 |
| 2016 | 30.719 | 32.714 | 32.695 | 32.7 | 21.739 | 22.093 | 22.096 | 22.1 | 9.218 | 9.123 | 9.126 | 9.13 |
| 2017 | 31.368 | 33.003 | 32.877 | 32.95 | 22.07 | 22.866 | 22.867 | 22.87 | 8.872 | 9.018 | 9.021 | 9.03 |
| 2018 | 36.393 | 34.595 | 34.533 | 34.57 | 23.204 | 23.208 | 23.206 | 23.2 | 9.07 | 9.058 | 9.058 | 9.06 |
| 2019 | 35.72 | 35.992 | 36.158 | 36.06 | 22.92 | 22.406 | 22.405 | 22.41 | 9.037 | 8.985 | 8.981 | 8.97 |
| 2020 | 31.501 | 31.589 | 31.528 | 31.56 | 20.321 | 20.507 | 20.508 | 20.51 | 7.99 | 8.011 | 8.012 | 8.02 |
| 2021 | 33.702 | 30.458 | 30.707 | 31.45 | 21.763 | 20.067 | 20.309 | 20.87 | 8.284 | 8.386 | 8.564 | 8.88 |
| 2030 | 20.274 | 23.314 | 30.41 | 16.101 | 18.516 | 24.15 | 11.763 | 13.528 | 16.67 | |||
| 2050 | 5.069 | 5.068 | 27.03 | 4.026 | 4.026 | 22.27 | 2.941 | 3.725 | 14.71 | |||
| Transportation Sector | Electric Power Sector | NYS energy-related Emission | ||||||||||
| original data | ELM forecast | original data | ELM forecast | original data | ELM forecast | |||||||
| P1 | P2 | P3 | P1 | P2 | P3 | P1 | P2 | P3 | ||||
| 1990 | 63.903 | 63.938 | 63.938 | 63.94 | 63.192 | 63.223 | 63.228 | 63.21 | 207.324 | 207.179 | 207.178 | 207.18 |
| 2005 | 73.363 | 74.499 | 74.505 | 74.49 | 55.394 | 51.881 | 51.862 | 51.9 | 211.504 | 208.586 | 208.589 | 208.59 |
| 2015 | 77.553 | 77.685 | 77.676 | 77.69 | 29.086 | 29.109 | 29.122 | 29.1 | 174.36 | 170.878 | 170.873 | 170.87 |
| 2016 | 80.801 | 79.617 | 79.628 | 79.62 | 27.673 | 26.519 | 26.547 | 26.49 | 170.151 | 170.076 | 170.078 | 170.08 |
| 2017 | 81.478 | 82.299 | 82.321 | 82.29 | 22.041 | 23.834 | 23.842 | 23.82 | 165.83 | 171.036 | 171.045 | 171.05 |
| 2018 | 82.012 | 83.406 | 83.41 | 83.4 | 24.417 | 22.374 | 22.354 | 22.39 | 175.097 | 172.642 | 172.647 | 172.65 |
| 2019 | 79.849 | 78.342 | 78.315 | 78.35 | 21.446 | 22.742 | 22.731 | 22.76 | 168.971 | 168.453 | 168.442 | 168.44 |
| 2020 | 60.119 | 60.521 | 60.533 | 60.52 | 23.445 | 23.128 | 23.136 | 23.12 | 143.377 | 143.764 | 143.769 | 143.77 |
| 2021 | 67.295 | 58.303 | 58.89 | 58.94 | 25.004 | 24.606 | 22.718 | 25.23 | 179.486 | 141.827 | 141.233 | 145.41 |
| 2030 | 38.34 | 44.093 | 44.73 | 37.914 | 18.956 | 44.23 | 124.395 | 118.41 | 160.19 | |||
| 2050 | 9.584 | 9.585 | 28.76 | 9.478 | 0 | 18.96 | 31.099 | 22.405 | 111.96 | |||
Table 8 Share of carbon emission in NYS under different scenarios in 2030 and 2050 (%) |
| 2030 | 2050 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | P3 | P1 | P2 | P3 | |
| Residential Sector | 16.3 | 19.7 | 19 | 16.3 | 22.6 | 24.2 |
| Commercial Sector | 12.9 | 15.6 | 15.1 | 12.9 | 18 | 19.9 |
| Industrial Sector | 9.5 | 11.4 | 10.4 | 9.5 | 16.6 | 13.2 |
| Transportation Sector | 30.8 | 37.2 | 27.9 | 30.8 | 42.8 | 25.7 |
| Electric Power Sector | 30.5 | 16 | 27.6 | 30.5 | 0 | 17 |
Fig. 13 Share of carbon emission in NYS for different Pathways from 2020 to 2050 |