1 Introduction
2 Model development
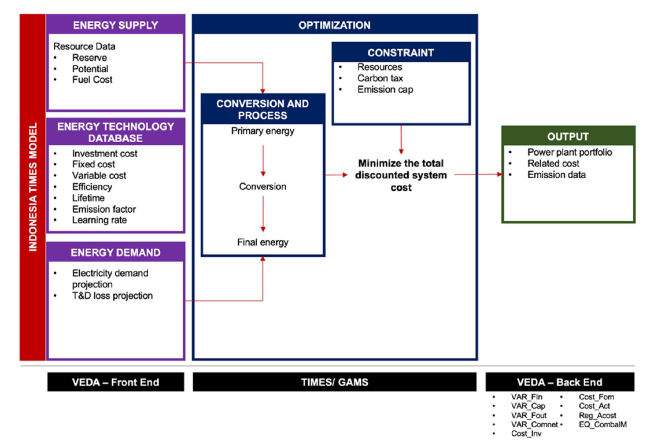
2.1 TIMES model generator
Fig. 1 Overview framework of the Indonesian electricity sector model structure |
2.2 Scenario
Table 1 Applied carbon price to see the effects of instituting carbon tax on the Indonesian power sector |
| Year | DGT | 10 USD | 25 USD | 35 USD | 50 USD | 75 USD | 150 USD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 2.02 | 2.02 | 2.02 | 2.02 | 2.02 | 2.02 | 2.02 |
| 2025 | 2.02 | 3.35 | 5.85 | 7.52 | 10.02 | 14.18 | 26.68 |
| 2030 | 2.02 | 4.68 | 9.68 | 13.01 | 18.01 | 26.35 | 51.35 |
| 2035 | 2.02 | 6.01 | 13.51 | 18.51 | 26.01 | 38.51 | 76.01 |
| 2040 | 2.02 | 7.34 | 17.34 | 24.01 | 34.01 | 50.67 | 100.7 |
| 2045 | 2.02 | 8.67 | 21.17 | 29.5 | 42 | 62.84 | 125.3 |
| 2050 | 2.02 | 10 | 25 | 35 | 50 | 75 | 150 |
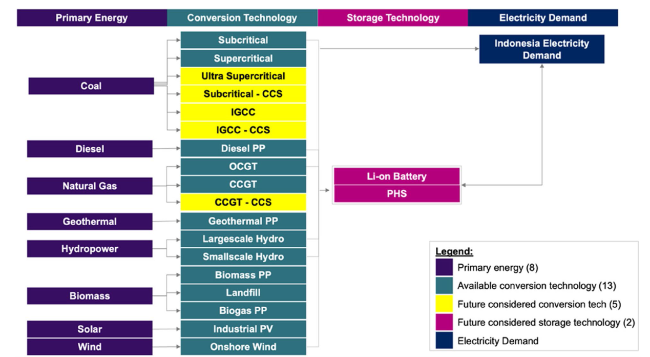
2.3 Reference energy system and model framework
Fig. 2 RES of Indonesia power sector |
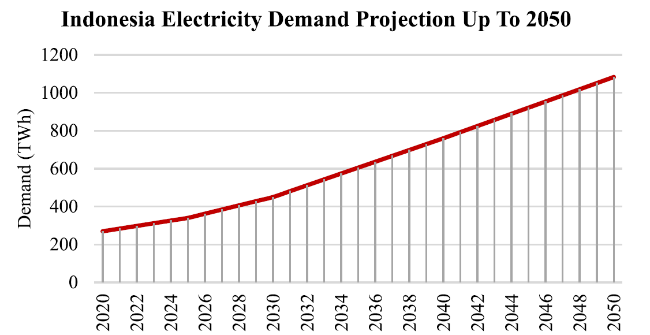
2.4 Electricity demand
2.5 Energy resource potential in Indonesia
| Resource | Reservea | Resourcea | Unit | 2020 R/P Ratiob | Import (TJ)a | Export (TJ)a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coal | 38,805.48 | 143,700.00 | million ton | 62 | 246,929 | 9,266,244 |
| Oil | 2.44 | 4.17 | billion barrels | 9 | 453,295 | 178,895 |
| Natural gas | 43.57 | 62.39 | Trillions of standard cubic feet of gas (TSCF) | 19.8 | - | 795,123 |
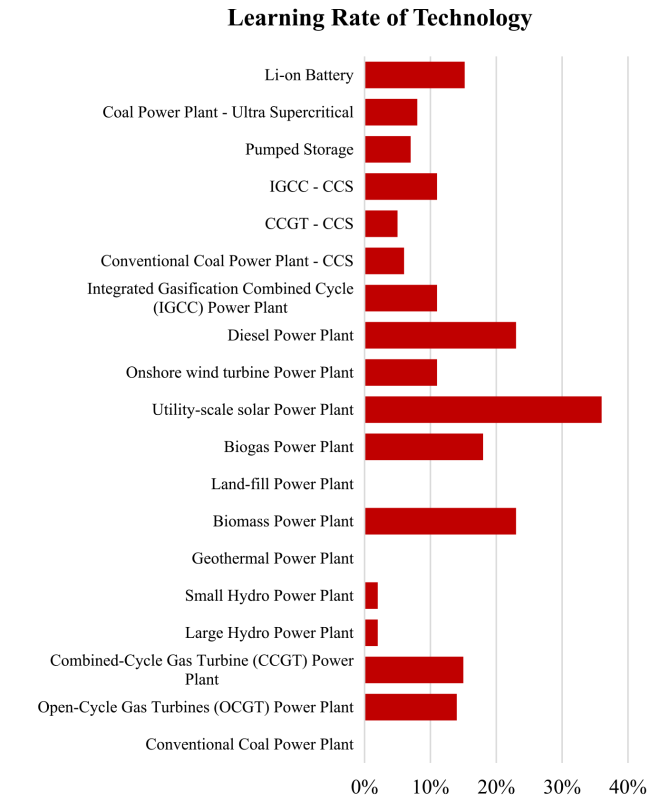
2.6 Techno-enviro-economic and flexibility parameters
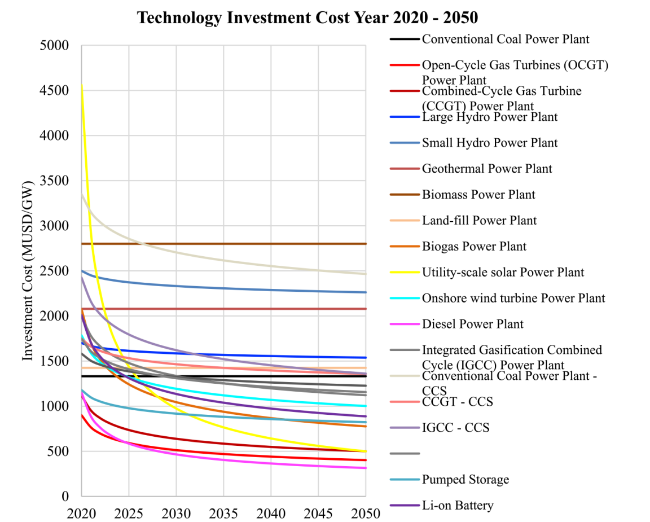
Fig. 5 Technology investment cost up until 2050 |
2.7 Fuel cost
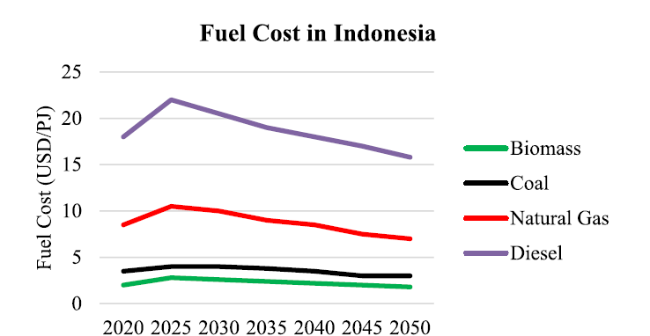
Fig. 6 Comparison of fuel prices in 2020-2050 (source: [23]) |
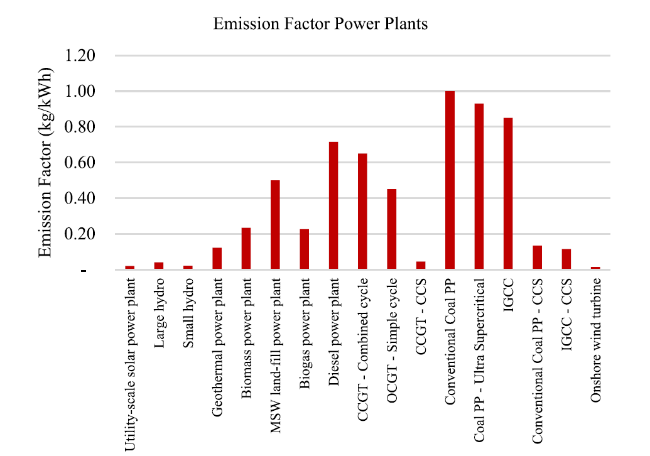
2.8 Emission factor
2.9 National electricity system performance
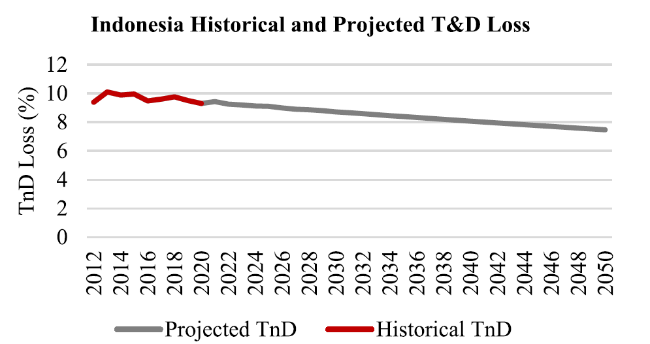
Fig. 8 Transmission and distribution losses in Indonesia % (source: [26]) |
3 Model validation
Table 4 Validation result of Indonesian TIMES model up until 2050 |
| Plant Type | Power Generation (TWh) | Power Generation Share % | Power Generation Error Rate | Power Generation Share Difference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual RUPTL 2020 | Model Result | Actual RUPTL 2020 | Model Result | |||
| Coal | 180.2 | 180.19 | 66.30% | 66.92% | 0.01% | 0.62% |
| Diesel | 6.9 | 6.90 | 2.54% | 2.56% | 0.01% | 0.02% |
| Natural gas | 45.67 | 45.67 | 16.80% | 16.96% | 0.01% | 0.16% |
| Hydro | 17.9 | 17.90 | 6.59% | 6.65% | 0.01% | 0.06% |
| Geothermal | 15.56 | 15.56 | 5.73% | 5.78% | 0.01% | 0.05% |
| Wind | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.17% | 0.17% | 0.01% | 0.00% |
| Solar | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.05% | 0.05% | 0.01% | 0.00% |
| Biomass | 2.41 | 2.43 | 0.89% | 0.90% | 0.96% | 0.01% |
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Impact of carbon price
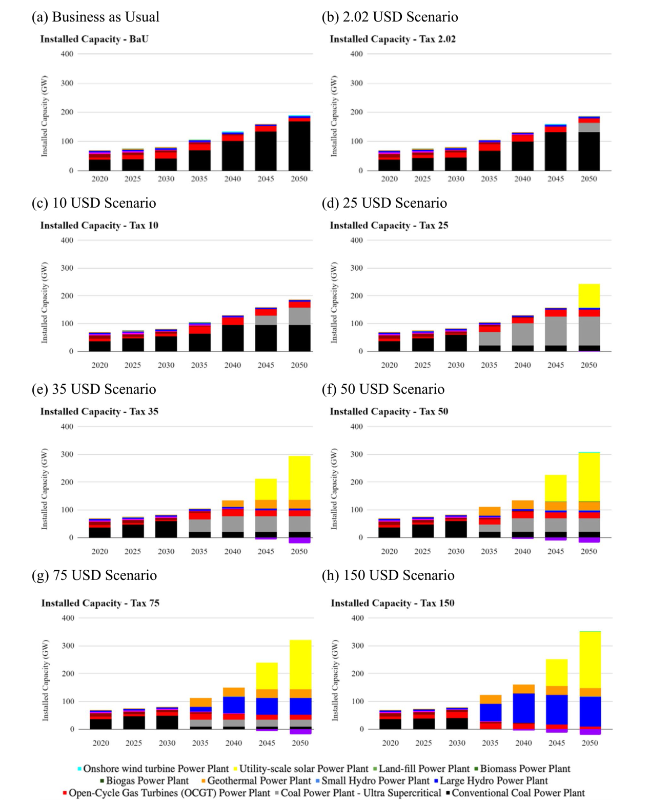
Fig. 9 Installed capacity until 2050 for a business as usual b 2.02 USD scenario c 10 USD scenario d 25 USD scenario e 35 USD scenario f 50 USD scenario g 75 USD scenario h 150 USD scenario |
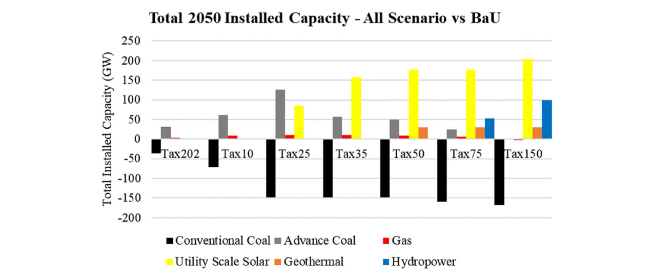
Fig. 10 2050 installed capacity - all scenario vs BaU |
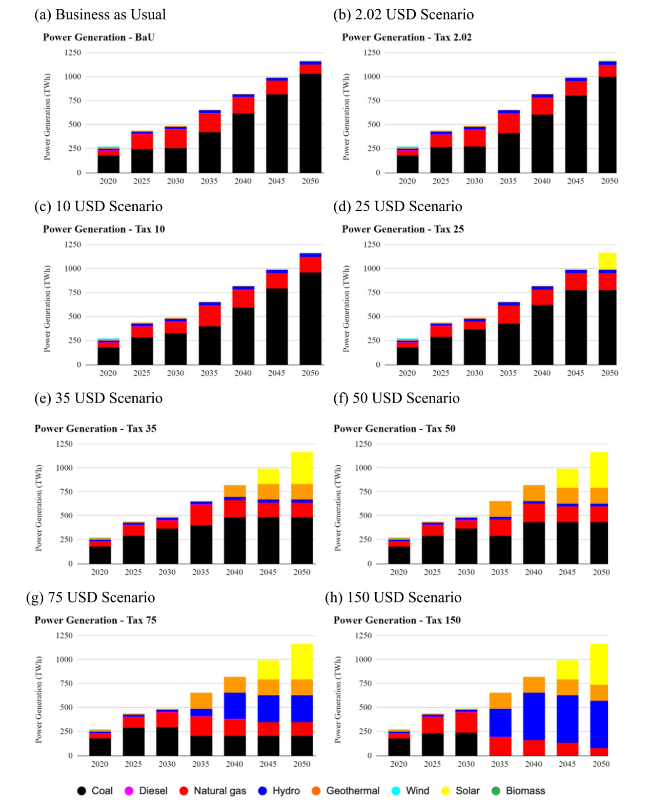
Fig. 11 Power Generation Until 2050 for a business as usual b 2.02 USD scenario c 10 USD scenario d 25 USD scenario e 35 USD scenario f 50 USD scenario g 75 USD scenario h 150 USD scenario |
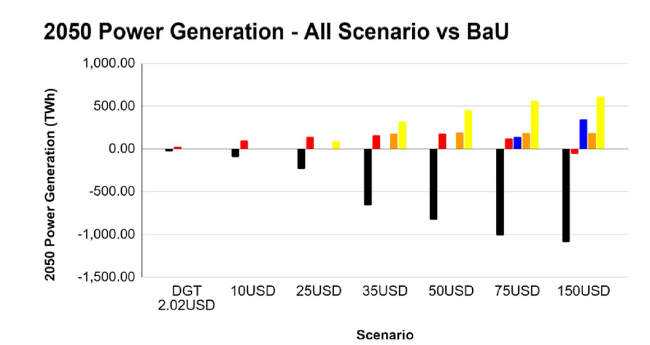
Fig. 12 2050 power generation - all carbon price scenario vs BaU |
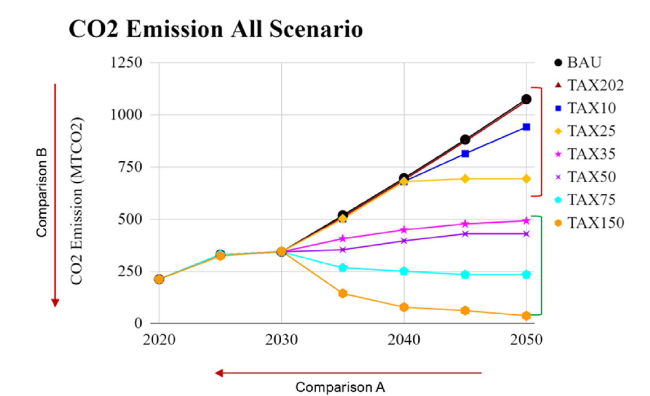
Fig. 13 CO2 emission 2020-2050 in different carbon price scenario |
Table 5 Emission comparison table in different carbon price scenario |
| Scenario (USD/ tCO2e) | 2050 to 2020 Comparison (A) | 2050 Comparison to BaU (million tCO2e) (B) | 2050 Emission Intensity (gCO2e/ kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BaU | 408.95% | N/A | 923.16 |
| 2.02 USD | 404.50% | -9.38 | 915.10 |
| 10 USD | 345.56% | -133.81 | 808.18 |
| 25 USD | 228.23% | -381.47 | 595.37 |
| 35 USD | 118.92% | -612.22 | 397.09 |
| 50 USD | 103.39% | -645.00 | 368.92 |
| 75 USD | 10.56% | -840.96 | 200.54 |
| 150 USD | -83.26% | -1039.00 | 30.36 |
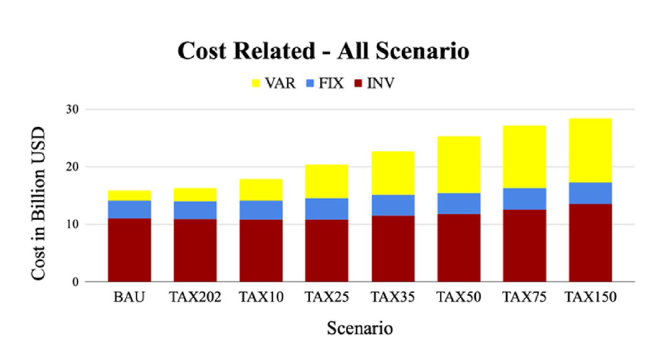
Fig. 14 Cumulative cost 2020-2050 in different carbon price scenario |
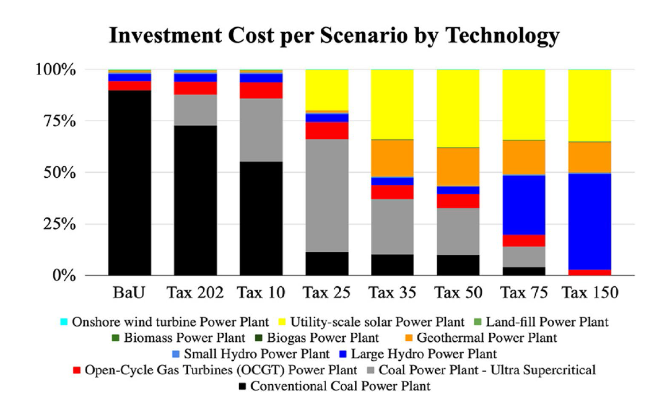
Fig. 15 Share of cumulative cost 2020-2050 per technology in different carbon price scenario |
Table 6 Indonesia average cost of electricity generation for from 2020-2050 in different carbon price scenario |
| Scenario | Average Cost of Electricity Generation from 2020-2050 (USD/ kWh) |
|---|---|
| BAU | 0.029 |
| TAX 2.02 | 0.024 |
| TAX 10 | 0.032 |
| TAX 25 | 0.037 |
| TAX 35 | 0.041 |
| TAX 50 | 0.046 |
| TAX 75 | 0.049 |
| TAX 150 | 0.051 |
4.2 Approximate price needed for 2030 NDC
Table 7 Emission reduction NDC target (source: [11]) |
| Sector | GHG Emission Reduction Target (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| 29% Reduction | 41% Reduction | |
| Energy | 11.00% | 14.00% |
| Waste | 0.38% | 1.00% |
| IPPU/ Industry | 0.10% | 0.11% |
| Agriculture | 0.32% | 0.12% |
| Forestry | 17.20% | 23.00% |
Table 8 Emission reduction scenarios to estimate the required carbon price for Indonesia’s 2030 NDC |
| CO2 Emission | Unit | |
|---|---|---|
| Projection of Indonesia’s CO2 Emissions in 2030 | 316.67 | million tCO2e |
| Scenario 29% decrease (Energy: 11% decrease) | 281.83 | million tCO2e |
| Scenario 41% decrease (Energy: 14% decrease) | 272.33 | million tCO2e |
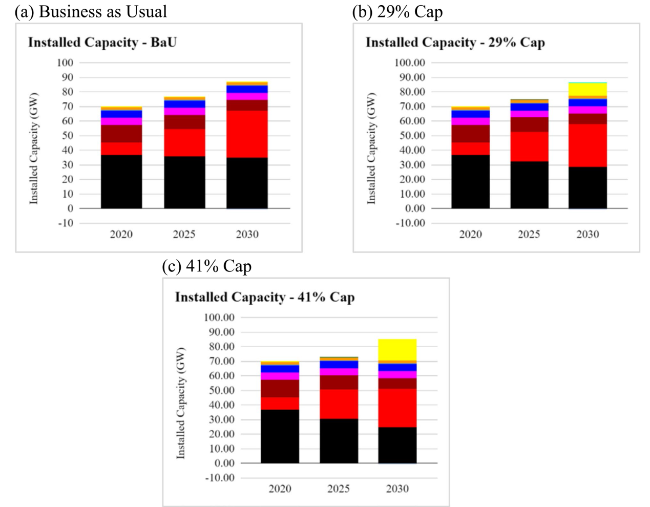
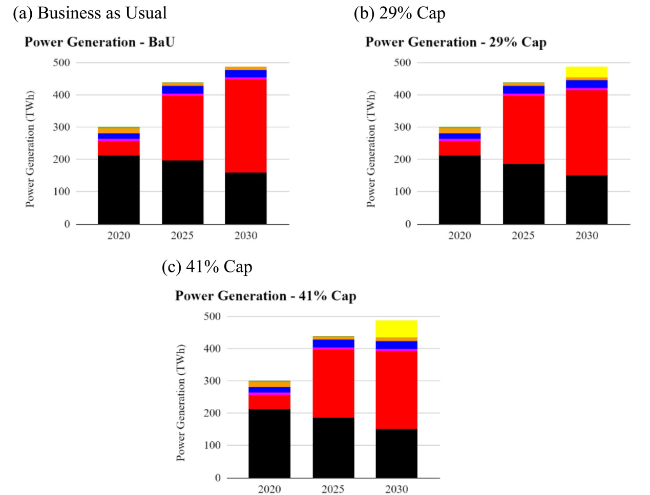
Fig. 16 Indonesia 2030 NDC emission reduction installed capacity for a business as usual b 29% cap c 41% cap scenarios |
Fig. 17 Indonesia 2030 NDC emission reduction power generation for a business as usual b 29% cap c 41% cap scenarios |
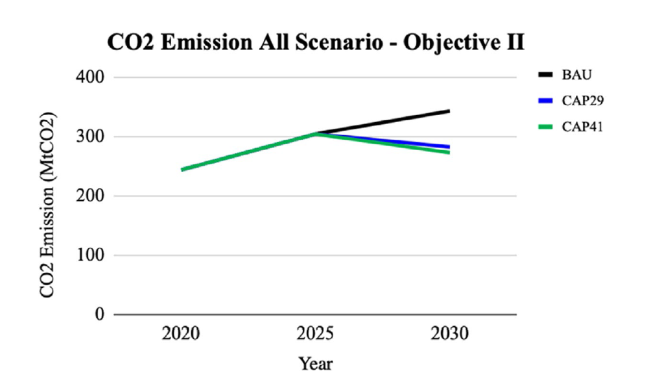
Fig. 18 CO2 emission until 2030 for Indonesia 2030 NDC emission reduction scenarios |
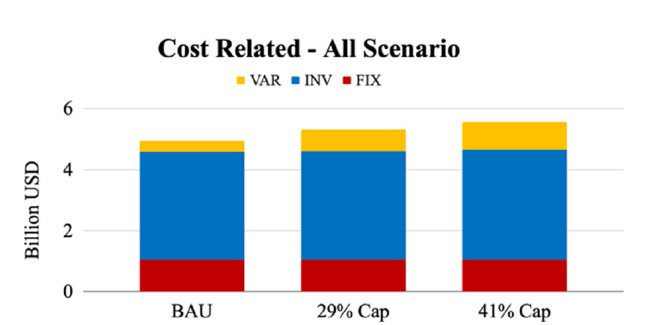
Fig. 19 Total cost of emission reduction scenarios for Indonesia 2030 NDC |
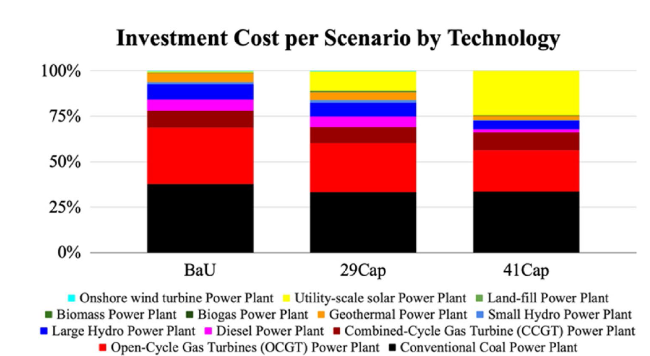
Fig. 20 Total cost per technology for Indonesia’s 2030 NDC emission reduction scenarios |
Table 9 Generated carbon price by the 2030 model |
| Scenario | Carbon Price (USD/ tCO2e) |
|---|---|
| 29% Reduction | 39.65 |
| 41% Reduction | 43.78 |
Table 10 ICPF carbon price floor types based on country income |
| Type of Country | IMF Floor Price (USD per tCO2e) |
|---|---|
| Low Income | 25 |
| Middle Income | 50 |
| High Income | 75 |