1 Introduction
2 Experimental section
2.1 Materials
2.2 Evaluation of CO2 adsorption/desorption over absorbents
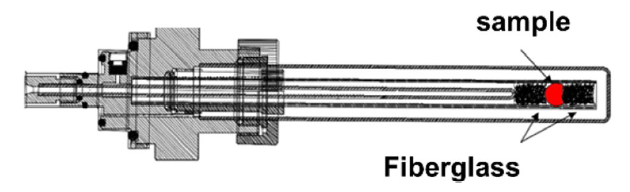
Fig. 1 Test equipment chart |
2.3 Effects of water vapor
3 Results and discussion
3.1 CO2 breakthrough experiments
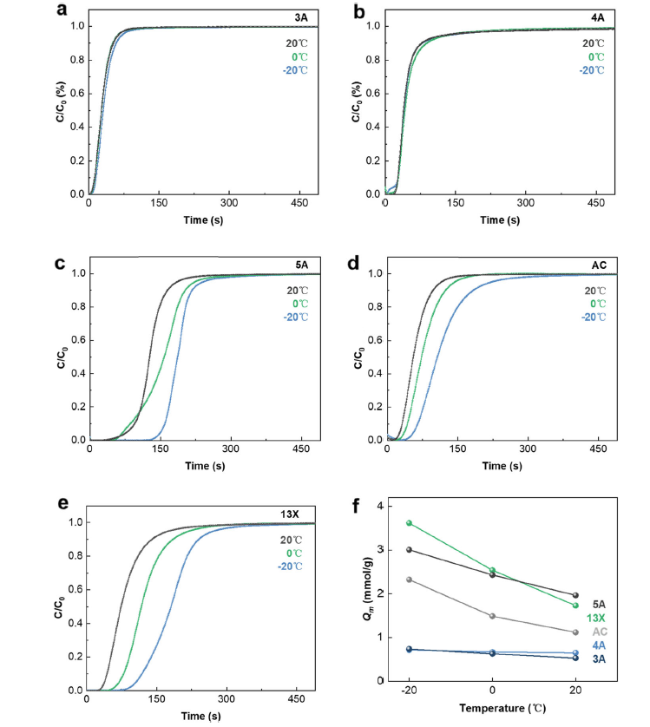
Fig. 2 The breakthrough curves of (a) 3A, (b) 4A, (c) 5A molecular sieve, (d) activated carbon and (e) 13X molecular sieve adsorbing CO2 in dry gas at different temperatures. (f) Maximum adsorption capacity of different adsorbents for CO2 at different temperatures |
3.2 The effect of temperature
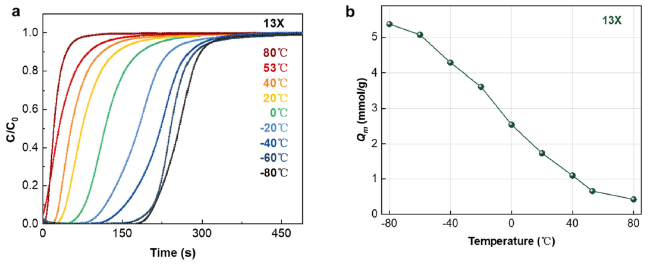
Fig. 3 a The breakthrough curves of 13X molecular sieve adsorbing CO2 in dry gas at different temperatures. bMaximum adsorption capacity of 13X molecular sieve for CO2 at different temperatures |
3.3 The effect of CO2 concentration
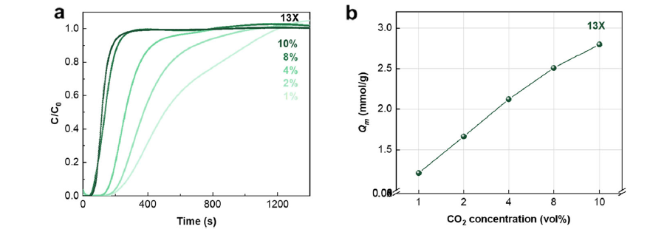
Fig. 4 a The penetration curve of 13X molecular sieve adsorbed CO2 in different concentrations of dry gas at 0 °C under ambient pressure. b The maximum adsorption capacity of 13X molecular sieve for different concentrations of CO2 at 0 °C under ambient pressure |
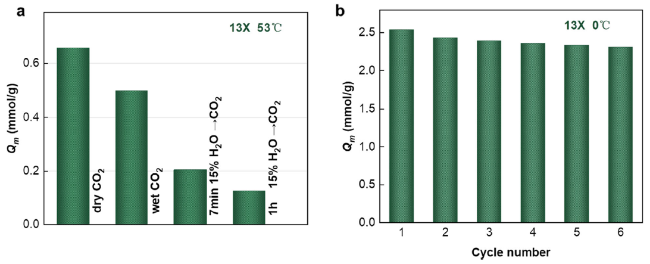
3.4 The effect of water vapor
Fig. 5 a Effect of water vapor on the adsorption of CO2. b Maximum adsorption capacity of 13X molecular sieve for CO2 in reusability experiments |
3.5 Reusability of the 13X molecular sieve
3.6 Energy penalty analysis
Table 1 Adsorption and desorption parameters |
| Parameters | Symbol | unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n (CO2)/tCO2 | / | kmol/ton | 22.72 |
| Desorption temperature [26] | Tre | °C | 120 |
| Solid specific heat of 13X | Cp13X | kJ/(kg·°C) | 0.95 |
| Specific heat of flu gas | Cp flu gas | kJ/(kg·°C) | 1.37 |
| Density of flu gas | ρ flu gas | kg/m3 | 1.34 |
| Heat of adsorption of CO2 [22] | ΔHCO2 | kJ/mol | 30.73 |
| Heat of adsorption of H2O [22] | ΔHH2O | kJ/mol | 53.29 |
Table 2 Overall energy penalty analysis of removing 1 ton CO2 from flue gas |
| Temperature | °C | −80 | −60 | −40 | −20 | 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O Content | v% | 5 × 10−5 | 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 2.3 | 7.3 | 19.7 | 46.8 |
| CO2 Content | v% | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Adsorption data | ||||||||||
| Adsorption capacity for CO2 | Qm mmol/g | 5.38 | 5.07 | 4.29 | 3.62 | 2.51 | 1.67 | 0.97 | 0.50 | 0.11 |
| Adsorbed CO2 | mCO2 kg | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| Adsorbed H2O | mH2O kg | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.4 | 4 | 25 | 94 | 299 | 806 | 1915 |
| Adsorbent mass | m13X ton | 4.23 | 4.48 | 5.30 | 6.28 | 9.04 | 13.6 | 23.4 | 45.5 | 212 |
| Desorption heat per mass of CO2 | ||||||||||
| CO2 adsorption heat | ΔECO2 GJ/ton | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 |
| Heating molecular sieve | ΔE13X GJ/ton | 0.80 | 0.77 | 0.81 | 0.84 | 1.03 | 1.29 | 1.78 | 2.89 | 8.07 |
| H2O adsorption heat | ΔEH2O GJ/ton | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.28 | 0.90 | 2.39 | 5.67 |
| Heat penalty | ΔE1 GJ/ton | 1.50 | 1.46 | 1.51 | 1.54 | 1.80 | 2.27 | 3.38 | 5.98. | 14.4 |
| Refrigeration energy per mass of CO2 | ||||||||||
| CO2 adsorption heat in the lower stage | ΔQCO2 GJ/ton | 0.48 | 0.47 | 0.43 | 0.38 | 0.23 | / | / | / | / |
| Molecular sieve cooling | ΔQ13X GJ/ton | 0.40 | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.24 | 0.17 | / | / | / | / |
| Flue gas cooling | ΔQgas GJ/ton | 0.73 | 0.59 | 0.44 | 0.29 | 0.15 | / | / | / | / |
| Total cooling load | ΔQ GJ/ton | 1.61 | 1.39 | 1.17 | 0.91 | 0.55 | / | / | / | / |
| Equivalent heat penalty | ΔE2 GJ/ton | 11.94 | 4.89 | 1.96 | 0.71 | 0.21 | / | / | / | / |
| Total energy penalty of CO2 capture | ||||||||||
| In total | ΔE GJ/ton | 13.4 | 6.35 | 3.47 | 2.25 | 2.01 | 2.27 | 3.38 | 5.98 | 14.4 |