1 Introduction
Table 1 Overview of datasets used in previous main wind and solar energy assessments in China |
| Reference | Study period | Data sources | Spatial resolution | Time resolution | Wind speed height | Validation against wind masts | Validation against solar irradiation station | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wind energy assessments | [12] | 2001-2010 | 200 sites from 3TIER (https://www.3tier.com/) | Site scale | Hourly | 100 m (onshore) | No | - |
| [13] | 1979-2015 | MEERA reanalysis/ (https://gmao.gsfc.nasa.gov/reanalysis/) | ~ 56 × 61 km | Hourly | 80 m (onshore), 120 m (offshore) | No | - | |
| [14] | 1980-2018 | MEERA-2 reanalysis (https://gmao.gsfc.nasa.gov/reanalysis/) | ~ 56 × 61 km | Hourly | 100 m (offshore) | No | - | |
| [15] | 1995-2016 | CMA WRF simulation | 3 × 3 km | Hourly | 100 m (onshore and offshore) | Yes | - | |
| This study | 1995-2016 | CMA WRF simulation | 3 × 3 km | Hourly | 100 m (onshore and offshore) | Yes | - | |
| Solar energy assessments | [16] | 2001-2010 | 200 sites from 3TIER (https://www.3tier.com/) | Site scale | Hourly | - | - | No |
| [17] | 2015-2016 | GEOS-5 FP (https://gmao.gsfc.nasa.gov/) | ~ 25 × 30 km | Hourly | - | - | No | |
| [18] | 2015 | ERA5-Land (https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/) | ~ 10 × 10 km | Hourly | - | - | No | |
| This study | 2007-2014 | CAS Satellite-based model | 5 × 5 km | Hourly | - | - | Yes |
Note: ‘-’ indicates data not provided or not relevant |
2 Data and methodology
2.1 Wind power assessment
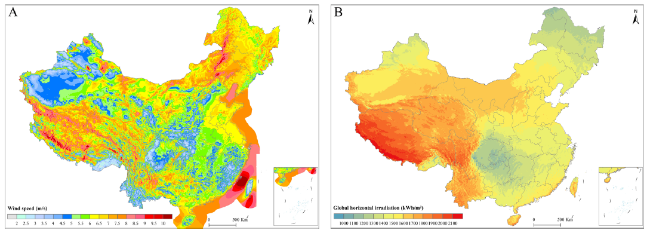
Fig. 1 A Spatial distribution of annual mean wind speed in 1995-2016 on land and offshore China at 100 m; B Spatial distribution of global horizontal irradiation in 2007-2014 on land China |
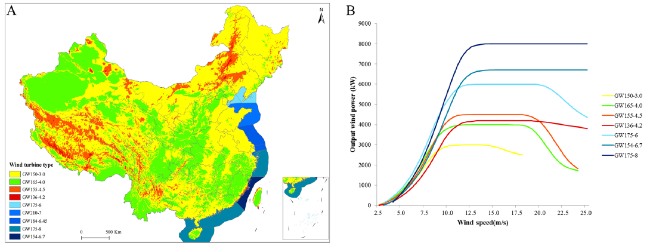
Table 2 Wind turbine types, parameters, and corresponding suitable area criteria |
| Turbine type | Rotor diameter (m) | Capacity (MW) | Suitable area criteria | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Onshore | GW150-3.0 | 150 | 3.0 | wind speed < 5.5 m/s |
| GW165-4.0 | 165 | 4.0 | 5.5 m/s ≤ wind speed < 7.5 m/s | |
| GW155-4.5 | 155 | 4.5 | 7.5 m/s ≤ wind speed < 9.2 m/s | |
| GW136-4.2 | 136 | 4.2 | wind speed ≥9.2 m/s | |
| Offshore | GW175-6 | 175 | 6 | Liaoning, Hebei, Tianjin, Shandong, Jiangsu, Shanghai |
| GW154-6.7 | 154 | 6.7 | Fujian | |
| GW175-8 | 175 | 8 | Zhejiang, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan | |
Note: 1 MW = 103 kW |
Fig. 2 A Spatial distribution of onshore and offshore wind turbine types; B Example generating power curves of wind turbines with a standard air density of 1.225 kg/m3 |
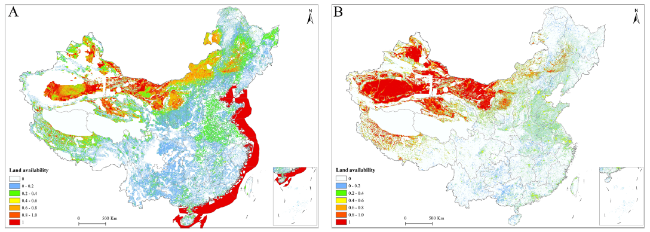
Table 3 Utilization coefficients of land use type for onshore turbine siting |
| Land use type | Utilization coefficient |
|---|---|
| Water bodies, permanent wetlands, snow, ice, urban and built-up lands, closed forest | 0 |
| Shrublands | 0.2 |
| Croplands | 0.25 |
| Open forest and other forest | 0.65 |
| Grasslands | 0.8 |
| Barren or sparsely vegetated | 1 |
Fig. 3 Spatial distribution of the utilization coefficient for (A) turbine siting and (B) PV siting |
2.2 PV power assessment
Table 4 Utilization coefficients of land use type for PV siting |
| Land use type | Utilization coefficient |
|---|---|
| Water bodies, permanent wetlands, snow, ice, forests, closed grasslands, croplands | 0 |
| Shrublands | 0.2 |
| urban and built-up lands | 0.5 |
| Sparse grasslands | 0.8 |
| Barren or sparsely vegetated | 1 |
3 Results
3.1 The technical potential of onshore wind power in China
Table 5 The wind and PV power potential and electricity demand in 2020 |
| Regional grid | Province | Installed capacity (million kW) | Power (109 kWh) | Electricity consumption (109 kWh) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wind | Onshore wind | Offshore wind (Near/Far) | PV | Central PV | Distributed PV | Wind | PV | |||
| Northeast | East Inner Mongolia | 619 | 619 | 0 | 923 | 835 | 88 | 1744 | 1296 | 62.8 |
| Heilongjiang | 706 | 706 | 0 | 301 | 149 | 152 | 1937 | 394 | 101.4 | |
| Jilin | 304 | 304 | 0 | 356 | 243 | 113 | 861 | 466 | 80.5 | |
| Liaoning | 289 | 176 | 113 (80/33) | 191 | 17 | 174 | 777 | 238 | 242.3 | |
| Northwest | Gansu | 321 | 321 | 0 | 2758 | 2682 | 76 | 718 | 4128 | 137.6 |
| Ningxia | 82 | 82 | 0 | 282 | 253 | 29 | 241 | 391 | 103.8 | |
| Qinghai | 186 | 186 | 0 | 3914 | 3886 | 28 | 379 | 6491 | 74.2 | |
| Shaanxi | 165 | 165 | 0 | 372 | 298 | 75 | 448 | 458 | 174.1 | |
| Xinjiang | 618 | 618 | 0 | 21198 | 21054 | 144 | 1293 | 29265 | 299.8 | |
| North | Beijing | 0 | 0 | 0 | 61 | 2 | 59 | 0 | 72 | 114 |
| Hebei | 334 | 281 | 53 (53/0) | 338 | 59 | 279 | 988 | 587 | 393.4 | |
| Shandong | 596 | 296 | 300 (178/122) | 417 | 21 | 395 | 1636 | 552 | 694 | |
| Shanxi | 127 | 127 | 0 | 311 | 194 | 117 | 364 | 439 | 234.2 | |
| Tianjin | 15 | 11 | 4 (4/0) | 42 | 0 | 42 | 42 | 50 | 87.5 | |
| West Inner Mongolia | 2078 | 2078 | 0 | 8537 | 8395 | 142 | 5399 | 12871 | 327.1 | |
| Southeast | Chongqing | 43 | 43 | 0 | 22 | 1 | 21 | 108 | 3 | 118.7 |
| Guizhou | 109 | 109 | 0 | 104 | 76 | 28 | 296 | 105 | 158.6 | |
| Sichuan | 223 | 223 | 0 | 157 | 75 | 82 | 621 | 182 | 286.5 | |
| Tibet | 524 | 524 | 0 | 3332 | 3327 | 4 | 1375 | 6177 | 8.2 | |
| South | Guangdong | 677 | 141 | 536 (220/316) | 202 | 19 | 182 | 1977 | 257 | 692.6 |
| Guangxi | 250 | 181 | 69 (69/0) | 187 | 101 | 86 | 708 | 222 | 202.5 | |
| Hainan | 246 | 45 | 201 (41/160) | 29 | 10 | 19 | 563 | 33 | 36.2 | |
| Taiwan | 10 | 10 | 0 | 28 | 0 | 28 | / | / | / | |
| Xianggang | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | / | / | / | |
| Yunnan | 132 | 132 | 0 | 115 | 60 | 55 | 374 | 159 | 202.6 | |
| Central | Henan | 291 | 291 | 0 | 303 | 14 | 289 | 869 | 377 | 339.2 |
| Hubei | 206 | 206 | 0 | 157 | 33 | 124 | 558 | 188 | 214.4 | |
| Hunan | 174 | 174 | 0 | 91 | 9 | 83 | 462 | 96 | 192.9 | |
| Jiangxi | 152 | 152 | 0 | 97 | 27 | 70 | 423 | 109 | 162.7 | |
| East | Anhui | 225 | 225 | 0 | 233 | 11 | 222 | 679 | 280 | 242.8 |
| Fujian | 321 | 32 | 289 (159/130) | 91 | 18 | 73 | 957 | 102 | 248.3 | |
| Jiangsu | 441 | 177 | 264 (242/22) | 302 | 5 | 297 | 1200 | 372 | 637.4 | |
| Shanghai | 55 | 10 | 45 (36/9) | 38 | 0 | 37 | 150 | 51 | 157.6 | |
| Zhejiang | 429 | 50 | 379 (113/266) | 112 | 4 | 108 | 1163 | 121 | 483 | |
| National | 10948 | 8694 | 2254 | 45604 | 41878 | 3726 | 29308 | 66529 | 7511 | |
3.2 The technical potential of offshore wind power in China
3.3 The technical potential of centralized PV power in China
3.4 Technical potential of distributed PV power in China
3.5 Comparison with other studies
Table 6 Summary of relevant results of wind power generation in this study and comparison with other studies |
| Reference | Capacity potential (TW) | Power potential (PWh) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wind | Onshore wind | Offshore wind | Wind | Onshore wind | Offshore wind | |
| [12] | 1.3-2.27 | 0.83-1.8 | 0.47 | - | 1.24-2.64 | 0.81 |
| [13] | - | - | - | 13.1-39.5 | - | 1.5-5.6 |
| [14] | - | - | 3.4 | - | - | 11.85 |
| [15] | 4.3 | 3.9 | 0.4 | - | - | - |
| This study | 10.95 | 8.69 | 2.25 | 29.3 | 21.4 | 7.91 |
Note: ‘-’ indicates data not provided or not relevant. 1 TW = 109 kW. 1 PWh = 1012 kWh |
Table 7 Summary of relevant results of PV power generation in this study and comparison with other studies |
| Reference | Capacity potential (TW) | Power potential (PWh) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PV | Central PV | Distributed PV | PV | Central PV | Distributed PV | |
| [16] | 39.51 | 39.3 | 0.21 | 70.17 | 69.9 | 0.27 |
| [17] | 58.9 | - | - | 100.8 | - | - |
| [18] | 79.464 | - | - | 131.942 | - | - |
| This study | 45.6 | 41.9 | 3.7 | 66.5 | 62 | 4.5 |
Note: ‘-’ indicates data not provided or not relevant. 1 TW = 109 kW. 1 PWh = 1012 kWh |
4 Conclusions
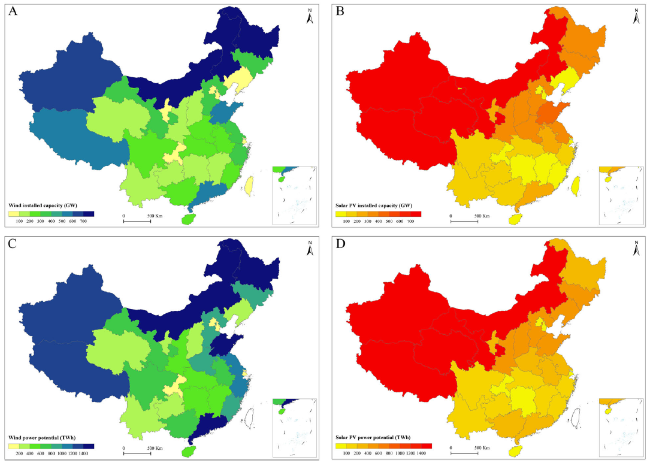
Fig. 4 The wind and PV capacity potential and power potential across mainland China. A The wind capacity potential across mainland China. B The PV capacity potential across mainland China. C The wind power across mainland China. D The PV power across mainland China |