Core
Gene and accession numbers
Introduction
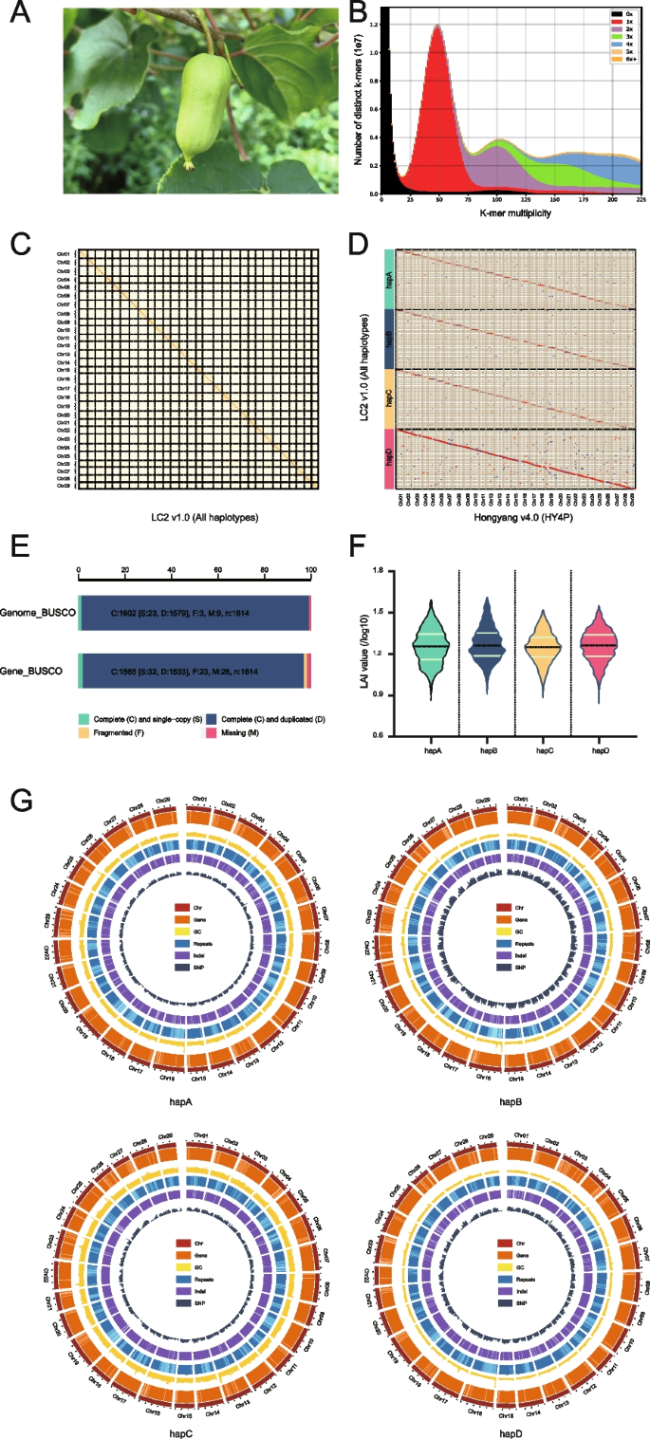
Fig. 1 Quality assessment of the LC2 v1.0 genome assembly. A The plant with fruit of A. arguta cv. ‘Longcheng No.2’. B Comparison of the amount of distinct K-mers absent and copy number variation between LC2 v1.0 assembly and raw HiFi reads. The plots are colored to illustrate the times of specific K-mers referred from the reads appeared in the assembly. The blackness represents K-mers missing from the assembly, while color of red, purple, green, blue, yellow or orange represents K-mers that appear 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or ≥ 6 times in the assembly, respectively. C Heatmap displaying Hi-C interacting signals of LC2 v1.0 chromosomes. Each homologous group contains four chromosomes. D Collinearity between the four haplotypes of LC2 v1.0 and HY4P. HY4P was used for adjusting the orientation of LC2 v1.0 chromosomes. E Genome BUSCO and gene BUSCO assessments exhibiting proportions classified as categories of complete and single-copy (S, green), complete and duplicated (D, blue), fragmented (F, yellow), and missing (M, pink). F Distribution of LAI scores among the assemblies of four haplotypes of LC2 v1.0. G Genomic features of the four haplotypes of LC2 v1.0. Tracks from outside to inside are chromosome identifiers (Chr), gene density (Gene), guanine-cytosine (GC) content, repeat density (Repeats), InDel density (InDel) and SNP density (SNP). All statistics were computed for windows of 500 Kb |
Results
Haplotype resolved assembly of a tetraploid A. arguta genome
Table 1 Summary statistics of A. arguta genome assemblies |
| Genomic feature | hapA | hapB | hapC | hapD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total size of assembled unitigs (Mb) | 2,919.0 | |||
| Number of unitigs | 1,104,265 | |||
| N50 value of unitig length (Mb) | 0.94 | |||
| Total size of assembled genomes (Mb) | 615.2 | 595.0 | 570.2 | 552.7 |
| Number of base chromosomes | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 |
| Number of telomeres (pairs) | 38 (12) | 38 (13) | 33 (11) | 33 (9) |
| Number of definite centromeres | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 |
| Genome BUSCOs (%) | 99.2 | |||
| TE size (%) | 41.02 | 39.51 | 38.85 | 38.89 |
| GC content (%) | 35.45 | 35.43 | 35.41 | 35.49 |
| LTR assembly index score | 16.86 | 17.62 | 16.93 | 17.15 |
| Gene BUSCOs (%) | 97.0 | |||
| Number of genes/transcripts | 42,263/52,105 | 41,377/51,041 | 39,833/49,271 | 39,222/48,363 |
| Number of shared genes | 40,859 | 40,063 | 38,638 | 38,098 |
| Number of specific genes | 1,404 | 1,314 | 1,195 | 1,124 |
Relatively conserved potential candidates of telomeres and centromeres
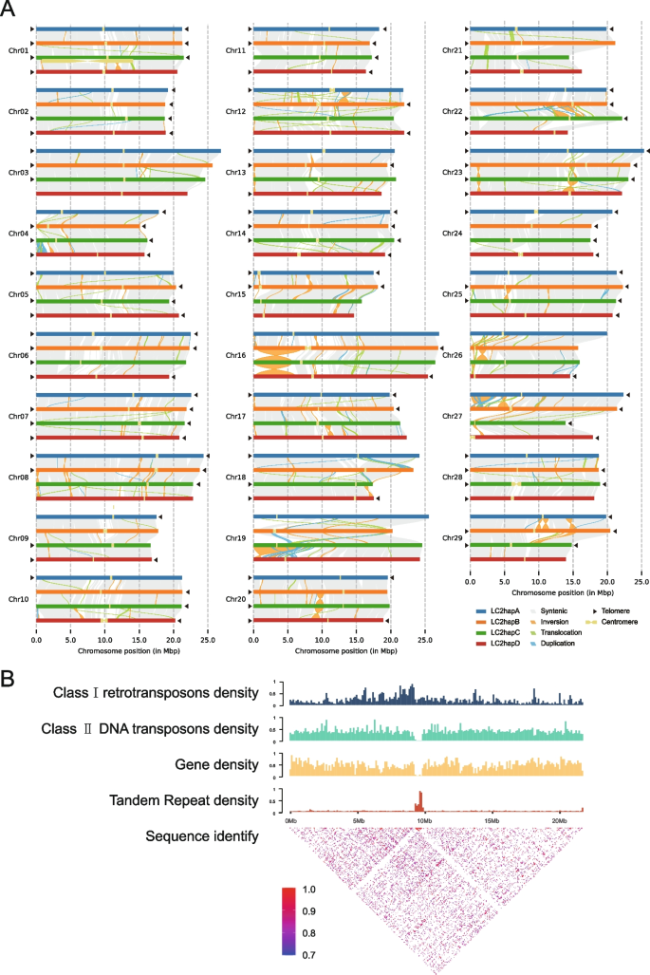
Fig. 2 Structure validation of LC2 v1.0 genome. A Structure of the haplotype-resolved chromosomes in LC2 v1.0. All 116 chromosomes of four haplotypes are drawn to scale and the ruler indicates chromosome length. Collinearity between haplotypes with syntenic regions is shown as gray lines, inversions as orange lines, translocations as green lines, and duplications as blue lines. Black triangles indicate the presence of telomere. Yellow dumbbell shapes represent the locations and sizes of centromeric regions. B Characterization of the centromere on Chr12 of the hapB. The histogram shows Class I retrotransposons, Class II DNA transposons, gene and tandem repeat density of Chr12. The heatmap shows pairwise similarity of the 50 Kb sequence along the whole chromosome of Chr12 |
Allele-specific expression caused by structural variations between haplotypes
Phylogenetic analysis reveals evolutionary history of the tetraploidization
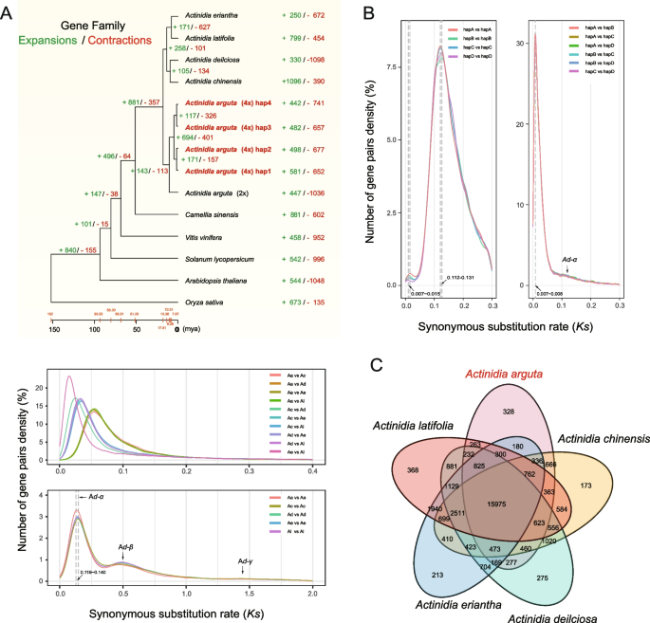
Fig. 3 Phylogenetic relationships, comparative genomics, and evolutionary analyses of Actinidia arguta. A The phylogenetic tree showing gene family expansions/contractions and divergence time (top panel), Ks values of orthologous genes pairs (middle panel) or estimating for whole genome duplication (WGD) of Actinidia species including A. arguta (Aa), A. chinensis (Ac), A. deliciosa (Ad), A. eriantha (Ae) and A. latifolia (Al) using paralogous genes pairs (bottom panel). 2x or 4x represents diploid or tetraploid, respectively. The phylogenetic tree was constructed for eleven species based on the orthologous genes. Species divergence time was calculated by r8s, and the expansions or contractions of gene families were analyzed using CAFÉ 5. B Ks values calculated from paralogous pairs (left panel) and allelic pairs (right panel) throughout the four individual haplotypes. C Venn diagram of gene families from five Actinidia species |
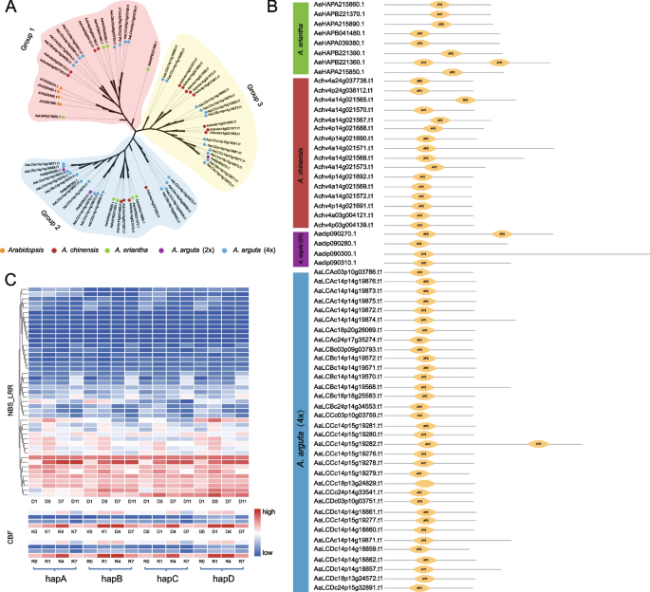
Expansion of NBS-LRR and CBF gene families by tetraploidization enhances environmental adaptation
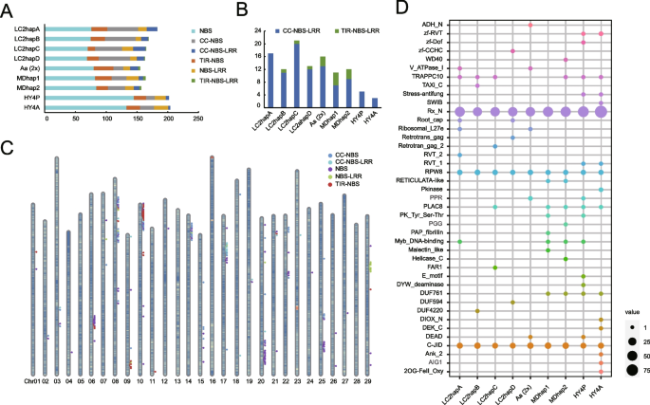
Fig. 4 Genome-wide identification of NBS-LRR gene family in Actinidia arguta, A. chinensis and A. eriantha. A Classification of the NBS-LRR genes in the different genomes. Six colors represent different types of NBS-LRR genes. B The number of TNL or CNL type in different genomes. C Chromosomal distribution of NBS-LRR genes in hapA of A. arguta (4x). D The integrated domains of NBS-LRR genes in the different genomes |
Fig. 5 Genome-wide identification of CBF gene family in A. arguta and four-allele genes expression pattern in different gene families. A Phylogenetic tree of CBF genes in A. arguta, A. chinensis, A. eriantha and Arabidopsis thaliana. 2x or 4x represents diploid or tetraploid, respectively. B Protein domain analysis of CBF genes. C The expression patterns of four-allele genes in NBS-LRR at different storage stages (1, 3, 7, 11 days post-harvest), and CBF gene families in different cultivars ‘Kuilv male’ (K) and ‘Ruby-3’ (R) under different durations (0, 1, 4, 7 h of -25°C) of frozen-treated. D represent day(s) after postharvest |
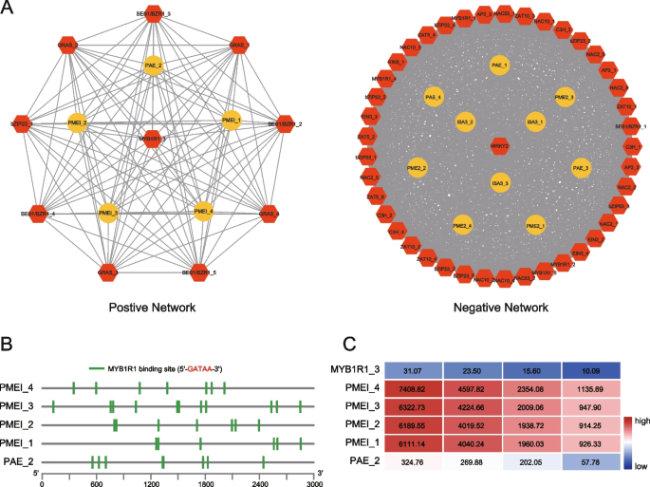
Construction of texture-related regulatory network by WGCNA
Fig. 6 The regulatory network involved in mediating fruit texture of Actinidia arguta. A Diagram visualizing the positive or negative network regulating fruit texture. Yellow circles or red hexagons represent structural genes or transcription factors, respectively. B Analysis of the promoters of the structural genes (Pectin methylesterase inhibitors: PMEI, Pectin acetylesterase: PAE) in positive network. C The expression pattern of candidate genes and transcription factors screened by WGCNA. Red or blue represents high or low expression, respectively |