Core
Gene & accession numbers
Introduction
Results
Identification and distribution of gene family members in each plant taxon
Phylogenetic analysis and exploration of the evolutionary trajectory
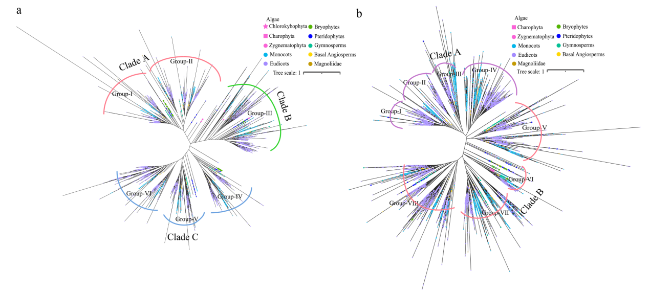
Fig. 1 Phylogenetic analysis of ARF and Aux/IAA family genes in 406 plants. a Construction of a phylogenetic tree using the protein sequences of all the ARF family genes from 406 species. b Construction of a phylogenetic tree using the protein sequences of all the Aux/IAA family genes from 406 species |
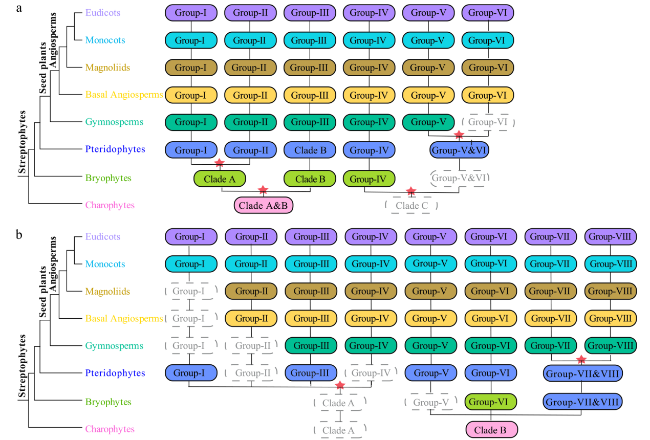
Fig. 2 The ancient evolutionary trajectory of ARF and Aux/IAA family genes in plants. a The evolutionary trajectory of ARF genes in plants. b The evolutionary trajectory of Aux/IAA genes in plants. The eight major plant lineages are represented by different colors’ solid round rectangles indicate the presence of ARF and Aux/IAA family genes in the corresponding plant lineages, and dashed rectangles suggest the absence of genes due to gene losses. Inferred ancient gene duplications are depicted as red pentacles |
Conserved motif identification and distribution
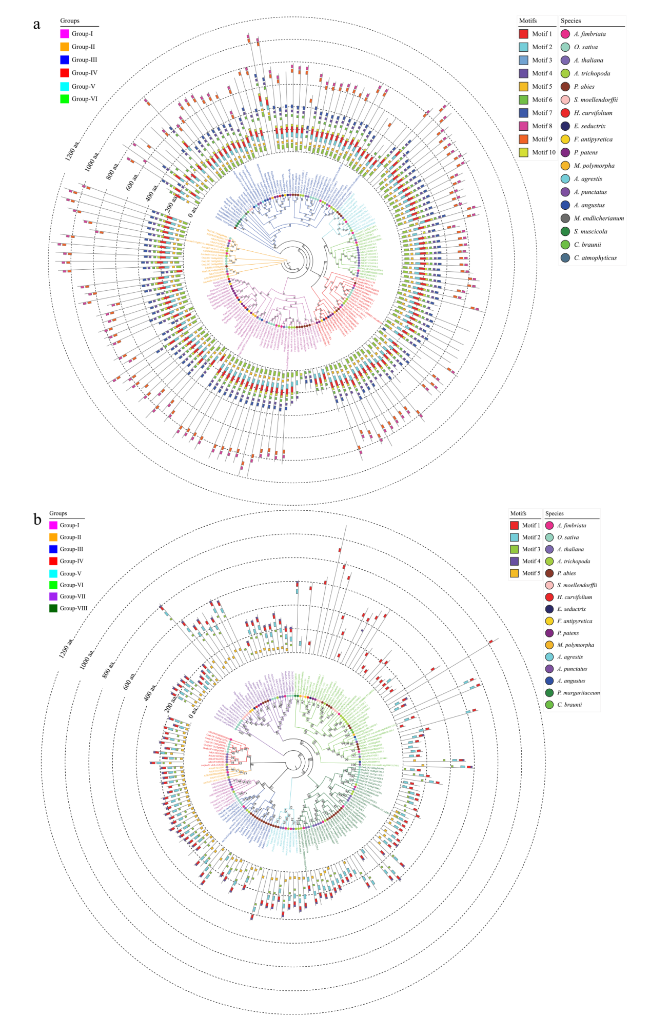
Fig. 3 Phylogenetic and conversed motif analyses of ARF and Aux/IAA family genes from representative species. a Phylogenetic and conversed motif analyses of ARF family genes from 18 representative species. b Phylogenetic and conversed motif analyses of Aux/IAA family genes from 16 representative species. A phylogenetic tree was constructed using FastTree software. The motifs were identified using the MEME program |
Identification of duplication types and statistical analysis
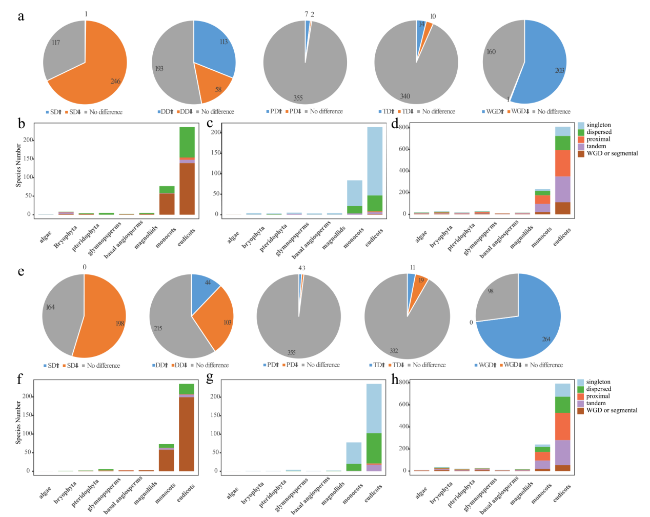
Fig. 4 Duplication type and significance analysis for 396 species. a The proportion of each significantly enriched or significantly reduced duplicate type of ARF family gene among the total duplicate type. b The number of duplicate types in which ARF family genes were significantly enriched in each taxon. c The number of duplicate types in which ARF family genes were significantly reduced in each taxon. d The number of duplicate species did not change significantly for each taxon of ARF family genes. e The proportion of each significantly enriched or significantly reduced duplicate type of Aux/IAA family gene in the total duplicate type. f The number of duplicate species in which Aux/IAA family genes were significantly enriched in each taxon. g The number of duplicate species in which Aux/IAA family genes were significantly reduced in each taxon. h The number of duplicate species did not change significantly for each taxon of the Aux/IAA family genes |
Comparative analysis of the duplication types in different plant taxa
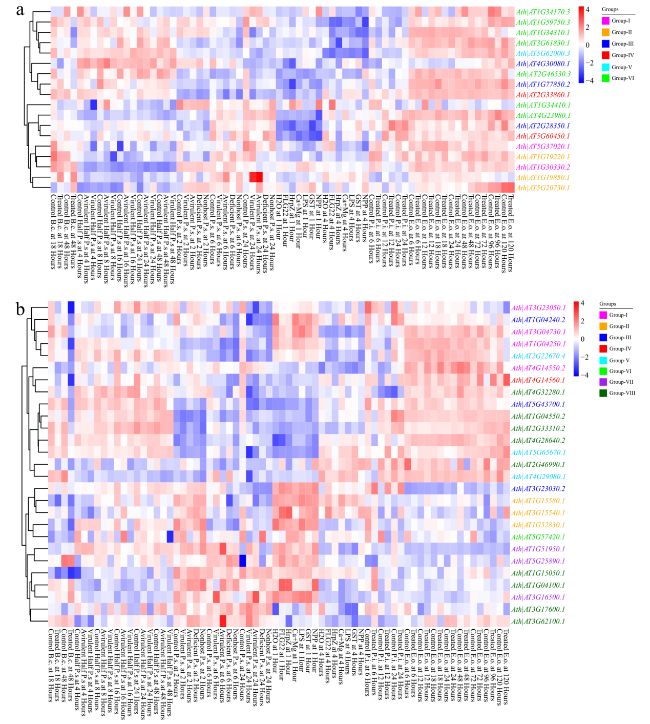
Gene expression analysis under different conditions
Fig. 5 The absolute expression values of ARF and Aux/IAA family genes under various biotic stresses in A. thaliana. a The expression levels of ARF family genes under various biotic stresses. b The expression levels of Aux/IAA family genes under various biotic stresses. The expression data of ARF and Aux/IAA family genes were obtained from the Arabidopsis eFP Browser |
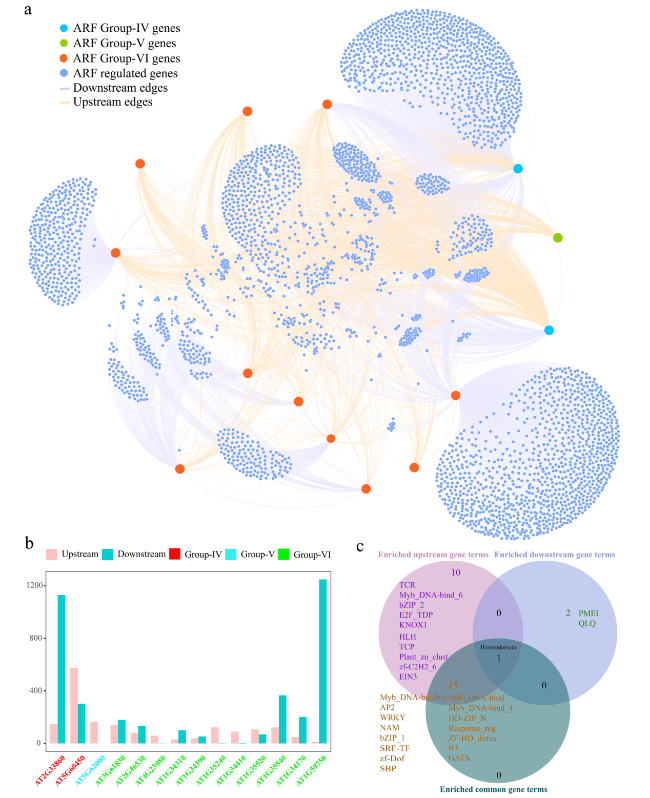
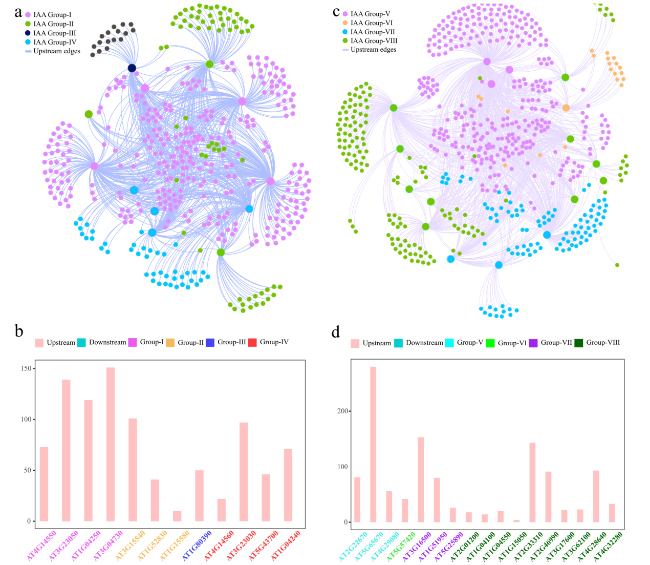
Upstream and downstream gene retrieval and interaction network construction
Fig. 6 Interaction network of clade C genes of the ARF gene family and their upstream and downstream genes in A. thaliana. a Construction of the network of clade C genes of the ARF gene family using Gephi software. b The number of upstream and downstream genes for each clade C gene of the ARF gene family in the network. c The specific and shared terms among the upstream, downstream, and common gene-enriched terms |
Fig. 7 Interaction network of the clade A and B genes of the Aux/IAA gene family and their upstream and downstream genes in A. thaliana. a Construction of the network among clade A genes of the Aux/IAA gene family using Gephi software. b The number of upstream and downstream genes for each clade A gene of the Aux/IAA gene family in the network. c Construction of the network among clade B genes of the Aux/IAA gene family using Gephi software. d The number of upstream and downstream genes for each clade B gene of the Aux/IAA gene family in the network |