Core
Gene and accession numbers
Introduction
Results
Generation of transgenic citrus overexpressing mSDE460
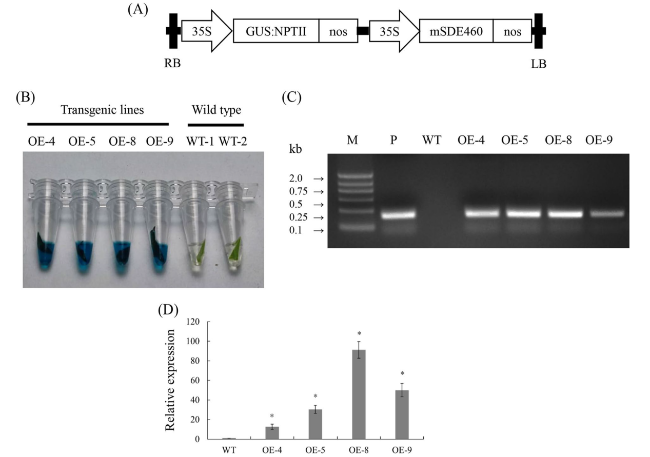
Fig. 1 Wanjincheng orange transgenic plants overexpressing mSDE460. A T-DNA structure of plant expression vector for the genetic transformation of citrus. A 35S, CaMV 35S promoter; GUS:NPTII, fusion of β-glucuronidase and neomycin phosphotransferase genes (for the screening of citrus transformants); mSDE460, the coding sequence of CaLasSDE460 mature protein; NOS, the nopaline synthase terminator; LB, left border; RB, right border. B Screening of transgenic plants by GUS histochemical staining. The blue stains indicated transformants. C Identification of transgenic plants by PCR. M, DNA marker, P, p35S:mSDE460 plasmid; WT, wildtype control; OE-#, transgenic plants. D Relative expression levels of mSDE460 in transgenic plants. Relative expression of CaLasSDE460 in transgenic plans was normalized against its expression in the WT using the citrus GAPDH gene (Mafra et al., 2012) as internal reference. Bars represent the average ± standard error of the means(n = 3). The primers used in (C) and (D) were listed in Supplementary Table 1. The asterisks indicate significant differences compared to WT control (p < 0.05, Student’s t-test) |
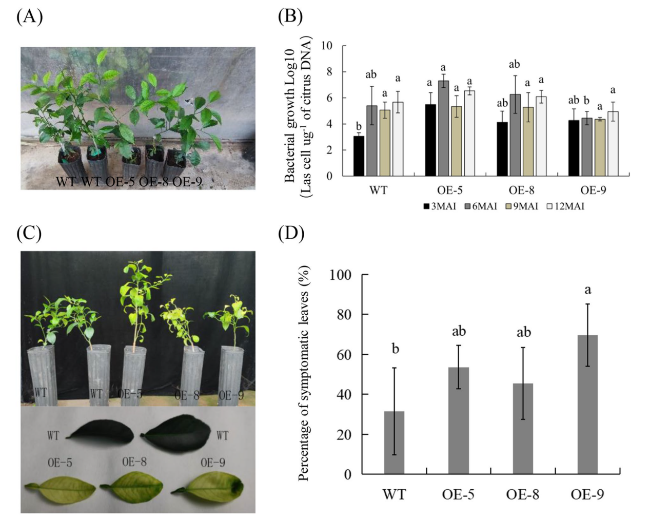
Fig. 2 Evaluation of Citrus HLB-resistance in transgenic plants. A Healthy wild-type (WT) and transgenic plants before CaLas-infected. B Quantitative analysis of CaLas growth in transgenic plants at 3, 6, 9 and 12 months after infection (MAI). The bacterial populations (CaLas cells µg.−1 of citrus DNA) were determined using qPCR. C HLB symptoms in the transgenic plants and WT controls at 9 MAI. D Statistic analysis of symptoms in the leaves at 16 MAI. Percentage (%) of symptomatic leaves per plant was calculated by the number of symptomatic leaves out of the total number of leaves. Bars represent the average ± standard error of the means from three plants per line (n = 3). WT, wild type; OE-#, transgenic plants. Different letters at the top of the bars indicate significant differences from the WT control (p < 0.05, Student’s t-test) |
Ectopic expression of mSDE460 enhanced symptom development in transgenic plants infected by CaLas
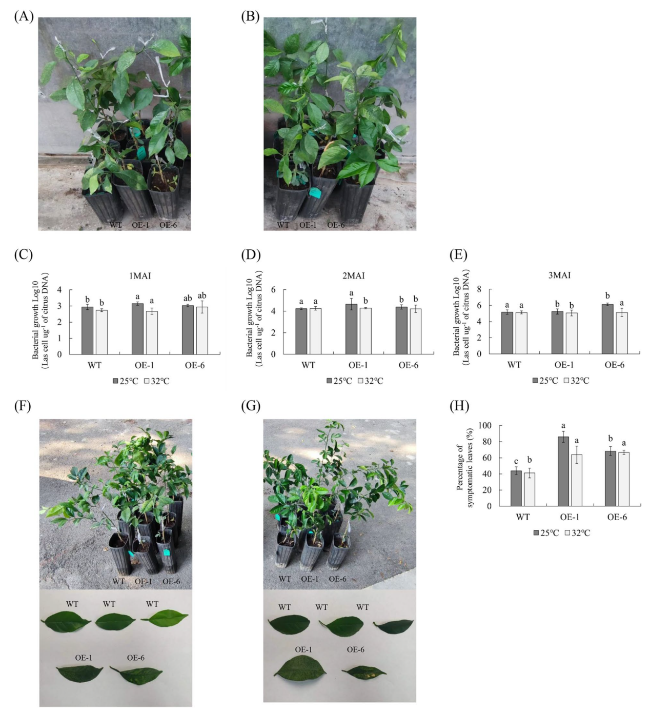
Effects of temperature on the function of CaLasSDE460 effector in citrus
Fig. 3 Evaluation of Citrus Huanglongbing (HLB) resistance in CaLasSDE460 transgenic plants under 25 °C and 32 °C treatment for three months. A and B Healthy wild-type (WT) and transgenic plants before CaLas-infected. C Quantitative analysis of CaLas contents in WT and transgenic plants under 25 °C and 32 °C treatment for one month. D Quantitative analysis of CaLas contents in WT and transgenic plants under 25 °C and 32 °C treatment for two months. E Quantitative analysis of CaLas contents in WT and transgenic plants under 25 °C and 32 °C treatment for three months. F HLB symptoms in the transgenic plants and WT controls under 25 °C treatment for three months. G HLB symptoms in the transgenic plants and WT controls under 32 °C treatment for three months. The bacterial populations (CaLas cells µg.−1 of citrus DNA) were determined using qPCR. (H) Statistic analysis of symptoms in the leaves under 25 °C and 32 °C treatment for three months. Percentage (%) of symptomatic leaves per plant was calculated by the number of symptomatic leaves out of the total number of leaves. Bars represent the average ± standard error of the means from three plants per lines(n = 3). WT, wild type; OE-#, transgenic plants. Different letters at the top of the bars indicates significant differences from the WT control (p < 0.05, Student’s t-test) |
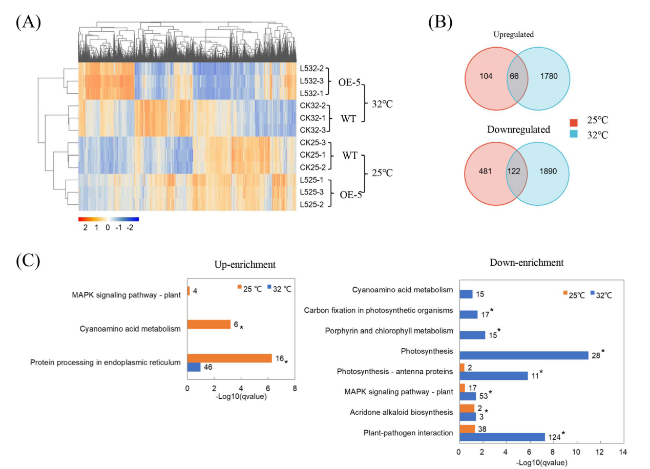
An overview of transcriptomic changes in transgenic plants
Fig. 4 The overall gene expression profile of transgenic citrus overexpressing CaLasSDE460 compared to wild-type (WT) control. A Heatmap analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between transgenic lines and WT lines at 25 °C and 32 °C. Transgenic lines showed a similar hierarchical clustering pattern. B Venn diagrams showed the overlaps of DEGs between 25 °C and 32 °C treatment. 66 upregulated and 122 downregulated DEGs were identified at both 25 °C and 32 °C treatment. C Enrichment comparison of the KEGG pathways between 25 °C and 32 °C treatment in the transgenic plant. All the DEGs were used to the analysis. The representative KEGG pathway having up-regulated (Up-enrichment) and down-regulated (Down-enrichment) were presented here. *indicates differentially represented KEGG pathways (q-value < 0.05, Fisher’s exact test) |
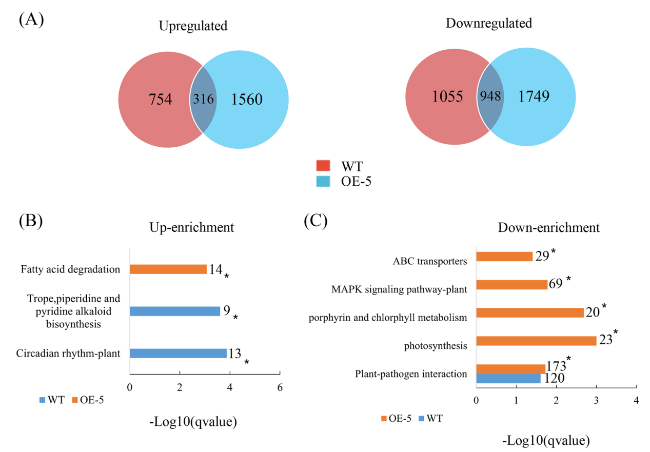
Fig. 5 Transcriptomic characteristics of transgenic citrus overexpressing CaLasSDE460 in response to temperature compared to wild-type (WT) control. A Venn diagrams showing the overlaps of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between WT and OE-5 transgenic plants at 32 °C compared to 25 °C. 316 upregulated and 948 downregulated DEGs were identified at WT and OE-5 transgenic plants, respectively. B and C enrichment comparison of the KEGG pathways between WT and OE-5 transgenic plants. All the DEGs were used to the analysis. The representative KEGG pathways having up-regulated (Up-enrichment) and down-regulated (Down-enrichment) were presented here. * indicates differentially represented KEGG pathways (q-value < 0.05, Fisher’s exact test) |
Transcriptional characteristics of defense response in transgenic plants
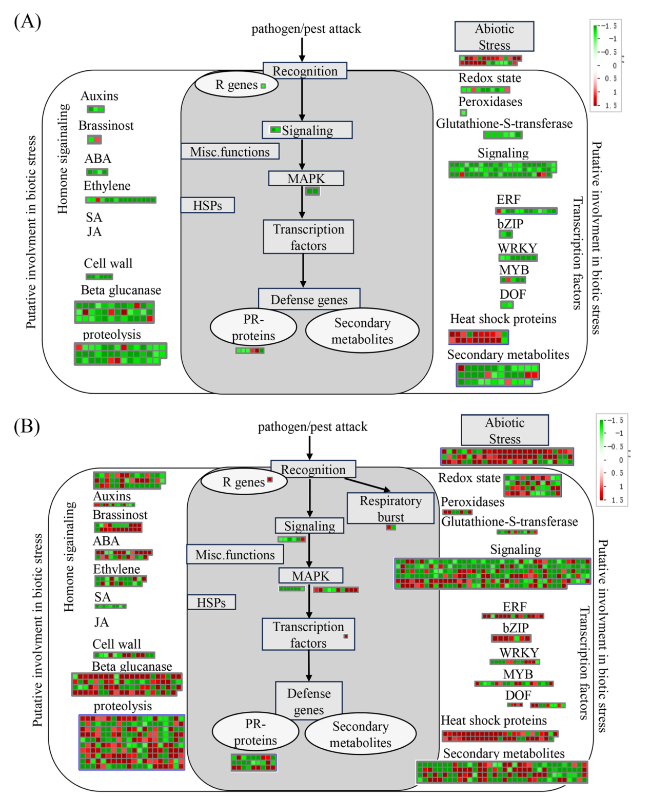
Fig. 6 MapMan visualizes the functional categories of differentially expressed genes in transgenic citrus with expression of CaLasSDE460 at 25 °C (A) and 32 °C (B), compared to wild-type plants. Every square block indicates a DEG. Significantly up-regulated and down-regulated genes are displayed in red and green, respectively |
Table 1 The representative DEGs involved in citrus defense response in OE-5 transgenic plant compared to WT control |
| Gene Id | Description | log2 (Fold change) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 °C | 32 °C | ||
| Hormone metabolism | |||
| Cs_ont_5g033020 | NCED3, a key enzyme for abscisic acid biosynthesis | -2.00 | 6.73 |
| Cs_ont_2g025170 | GRAM domain family protein | -1.92 | 1.63 |
| Cs_ont_1g027050 | CsSAMT1 methylating salicylic acid | -2.35 | -6.98 |
| Cs_ont_2g022650 | UDP-Glycosyltransferase affecting auxin homeostasis | 1.07 | 4.83 |
| Cs_ont_2g033670 | LOX2 for jasmonic acid accumulation | -1.86 | -5.95 |
| Cs_ont_7g001050 | HXXXD-type acyl-transferase family protein | 1.33 | -2.03 |
| Cell wall | |||
| Cs_ont_7g027340 | UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase family protein | -1.47 | 2.38 |
| Cs_ont_5g012770 | Xyloglucan galactosyltransferase | -2.67 | 1.21 |
| Cs_ont_5g007250 | A protein similar to a beta-xylosidase | 2.00 | -1.20 |
| Cs_ont_4g026360 | Xyloglucan endotransglycosylase-related protein | -1.90 | 1.34 |
| Cs_ont_3g025070 | Beta-d-xylosidase | 1.18 | -2.67 |
| Redox glutaredoxin | |||
| Cs_ont_2g027370 | Regulation of protein redox state | -1.94 | 2.38 |
| Cs_ont_4g017280 | Glutathione transferases | -1.33 | 3.00 |
| Cs_ont_7g025640 | Early-responsive to dehydration 9 (erd9) | -1.34 | 1.75 |
| Signaling | |||
| Cs_ont_6g012480 | Calcium-binding allergen Bet v 3 (Bet v III) | -1.58 | -2.22 |
| Cs_ont_3g000240 | Calmodulin like 37 (CML37) | -2.15 | 2.27 |
| Cs_ont_4g012420 | Calcium-binding EF-hand family protein | -2.56 | 1.34 |
| Cs_ont_3g011780 | A Rho GTPase-activating protein | -2.41 | 1.55 |
| MAPK | |||
| Cs_ont_8g000450 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 14 (MAPKKK14) | -1.69 | 4.70 |
| Defense gene | |||
| Cs_ont_5g034570 | Kunitz family trypsin and protease inhibitor protein | 1.86 | -2.40 |
| Heat shock protein | |||
| Cs_ont_7g003880 | Heat shock cognate protein 70-1 (HSC70-1) | -2.82 | 1.26 |
| Cs_ont_1g010380 | Heat shock protein 70 (HSP70b) | 1.51 | 4.50 |
Table 2 The representative DEGs involved in citrus defense response in WT and OE-5 transgenic plant at 32 °C |
| Gene Id | Description | log2 (Fold change) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| WT | OE-5 | ||
| Hormone metabolism | |||
| Cs_ont_5g033020 | NCED3, a key enzyme for abscisic acidbiosynthesis | -4.11 | 6.73 |
| Cs_ont_2g025170 | GRAM domain family protein | -2.15 | 1.49 |
| Cs_ont_1g027050 | CsSAMT1 methylatingsalicylic acid | 1.33 | -2.49 |
| Cs_ont_2g022650 | UDP-Glycosyltransferase affecting auxin homeostasis | 1.93 | 5.49 |
| Cell wall | |||
| Cs_ont_7g027340 | UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase family protein | -1.79 | 2.11 |
| Cs_ont_3g025070 | Beta-d-xylosidase | 1.74 | -3.49 |
| Cs_ont_4g026430 | Hydrolase activity | 7.04 | -1.86 |
| Redox glutaredoxin | |||
| Cs_ont_2g027370 | Regulation of protein redox state | -1.06 | 3.57 |
| Cs_ont_4g017280 | Glutathione transferases | -1.25 | 3.09 |
| Signaling | |||
| Cs_ont_6g012480 | Calcium-binding allergen Bet v 3 (Bet v III) | -2.54 | -3.21 |
| Cs_ont_3g000240 | Calmodulin like 37 (CML37) | -2.61 | 2.00 |
| Cs_ont_4g012420 | Calcium-binding EF-hand family protein | -2.18 | 1.72 |
| Protein degradation | |||
| Cs_ont_7g024750 | Ubiquitin-protein ligase activity | -4.54 | 3.89 |
| Misc.functions | |||
| Cs_ont_6g018900 | Glutathione transferase L3 (GSTL3) | -1.35 | -8.75 |
| Abiotic stress | |||
| Cs_ont_5g008470 | Encodes a membrane-bound protein | -1.43 | 6.27 |