图/表 详细信息
Parkinson’s disease and gut microbiota: from clinical to mechanistic and therapeutic studies
Translational Neurodegeneration,
2023, 12(0):
59.
DOI: 10.1186/s40035-023-00392-8
| Ref. | Sample size | Sample | Control factors | Dietary instruments | Technique | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [ | PD: 34 Healthy: 34 | Fecal | Age-matched; no special dietary habits | Dietary habits were interviewed | Gas chromatography | PD is associated with certain gut microbiota and reduced fecal SCFAs |
| [ | PD: 75 Healthy: 50 | Serum | Aged 40-85 years, onset age 40-80 years, disease duration ≤ 12 years; age-matched; medications, diet, and demographics collected | FFQ | UPLC-MS; HILIC-MS | The microbiota of PD had decreased carbohydrate fermentation and butyrate synthesis and enhanced proteolytic fermentation and p-cresol and phenylacetylglutamine production. Patients with constipation and stool consistency had more proteolytic metabolites and taxonomic changes |
| [ | PD-MCI: 13 PD-NC: 14 Healthy: 13 | Fecal | Spouses as control; age-matched; BMI-matched; no serious chronic illnesses (e.g., hyperlipidemia, diabetes); no fat-rich diet | Questionnaire including caffeine and alcohol intake | GC-MS | SCFAs were similar in PD-MCI, PD-NC, and healthy, however, the isovaleric and isobutyric levels negatively correlated with the MMSE scores |
| [ | PD: 64 Healthy: 51 | Fecal | Spouses or family members as control; internal medicine, neurological, or unstable psychiatric illness excluded | N.A | GC-MS | Lipids, vitamins, amino acids, and other organic compounds changed. Most modified metabolites closely associated with Lachnospiraceae abundance |
| [ | PD: 8 Control: 10 | Serum | Early, L-DOPA-naïve PD; only male; 5 healthy controls, 5 diseased controls having cardiovascular risk factors | Omnivorous vegetarian probiotics | Targeted metabolomics | Disease severity is linked to mucin and host glycans breakdown by microbes. Gut-community metabolic modeling shows that PD bacteria cause folic acid deficiency and hyperhomocysteinemia |
| [ | PD: 104 Non-PD: 96 | Fecal | 91 spouses, 5 siblings as control; diet, lifestyle and housing condition considered | FFQ | NMR; LC-MS | Neuroprotective chemicals such as SCFAs, ubiquinones, and salicylate, as well as ceramides, sphingosine, and TMAO, are linked to PD metabolite features and functional changes. Clinical signs include cognitive impairment, BMI, frailty, constipation, and physical activity are also linked to it |
Table 3 Altered gut microbial metabolites in patients with PD
本文的其它图/表
-
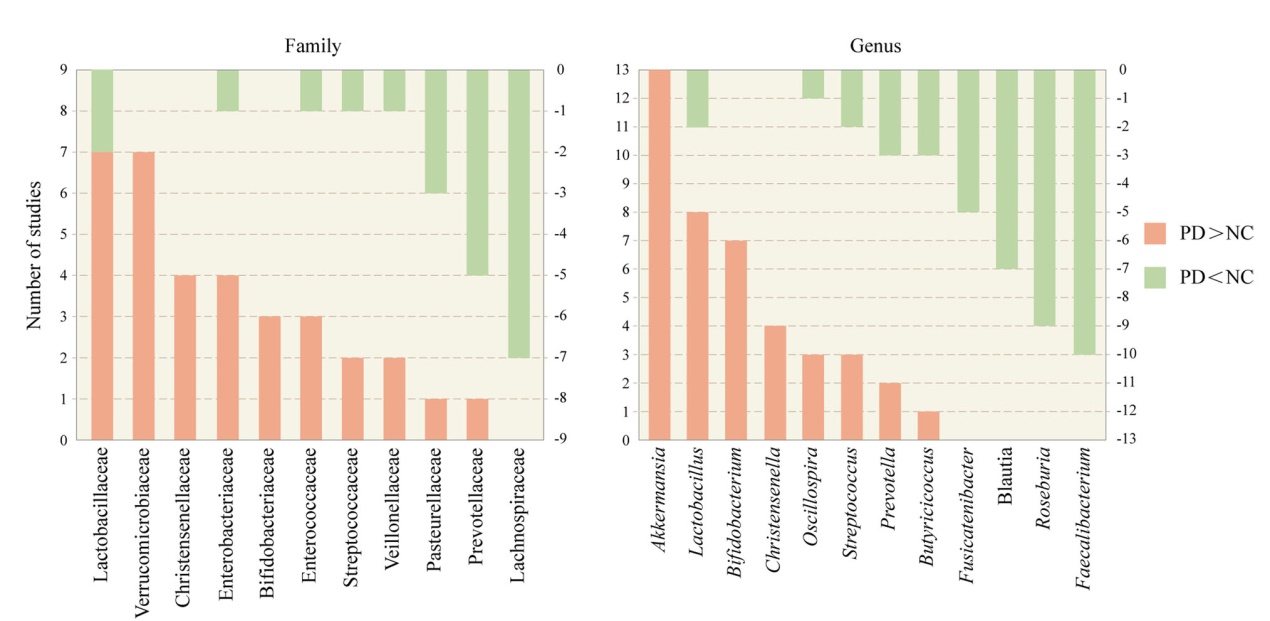 Fig. 1 The most commonly reported 11 families and 12 genera of gut microbiota that are different between the PD and the NC groups. Orange bars represent the number of studies in which PD had a higher abundance than NC. Cyan bars represent the number of studies in which PD had a lower abundance than NC. PD, Parkinson’s disease, NC, normal control
Fig. 1 The most commonly reported 11 families and 12 genera of gut microbiota that are different between the PD and the NC groups. Orange bars represent the number of studies in which PD had a higher abundance than NC. Cyan bars represent the number of studies in which PD had a lower abundance than NC. PD, Parkinson’s disease, NC, normal control
-
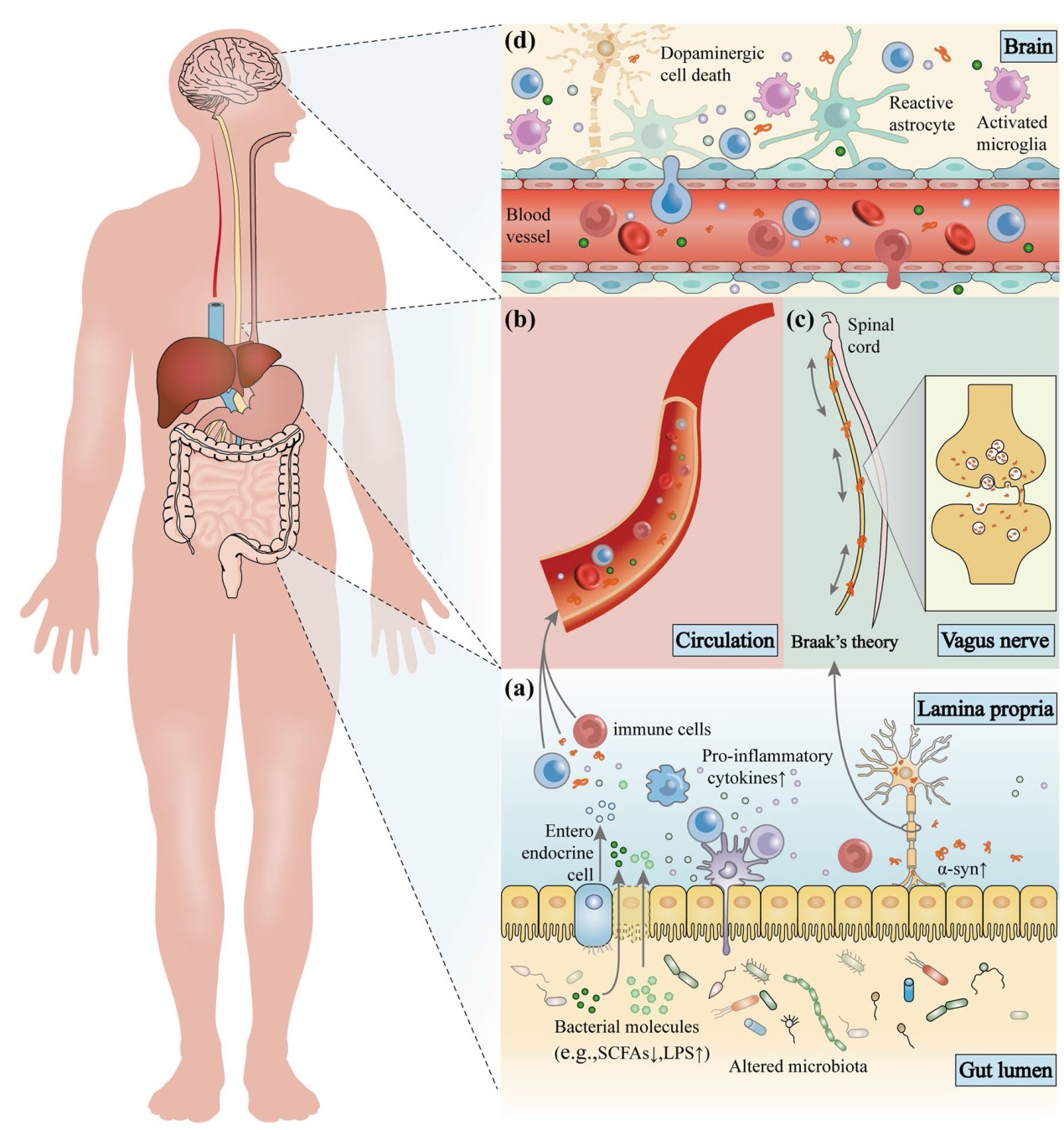 Fig. 3 The microbiota-gut-brain axis in Parkinson’s disease (PD). Disordered gut microbes, through the microbiota-gut-brain axis, play a role in the pathogenesis of PD via the immune, endocrine, and nervous systems. a Alterations in intestinal microbes and their metabolites can leave the gut in an inflammatory state. These substances can cross the damaged intestinal barrier, activate mucosal immune cells, induce the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and promote misfolding and aggregation of α-syn. b Increased intestinal permeability allows release of signaling molecules by intestinal microbes and activated immune cells as well as through metabolic secretion to enter the circulation and cause systemic inflammation. c Misfolded α-syn in the gut can be transferred to the brain through intercellular transmission via the vagus nerve, and this transmission may be bidirectional. d The damaged blood-brain barrier and vagal pathways allow pathological products and α-syn to enter the brain, promoting the activation of immune cells in the brain, including microglia and astrocytes, causing neuroinflammation, and ultimately leading to the loss of dopaminergic neurons and the development of PD
Fig. 3 The microbiota-gut-brain axis in Parkinson’s disease (PD). Disordered gut microbes, through the microbiota-gut-brain axis, play a role in the pathogenesis of PD via the immune, endocrine, and nervous systems. a Alterations in intestinal microbes and their metabolites can leave the gut in an inflammatory state. These substances can cross the damaged intestinal barrier, activate mucosal immune cells, induce the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and promote misfolding and aggregation of α-syn. b Increased intestinal permeability allows release of signaling molecules by intestinal microbes and activated immune cells as well as through metabolic secretion to enter the circulation and cause systemic inflammation. c Misfolded α-syn in the gut can be transferred to the brain through intercellular transmission via the vagus nerve, and this transmission may be bidirectional. d The damaged blood-brain barrier and vagal pathways allow pathological products and α-syn to enter the brain, promoting the activation of immune cells in the brain, including microglia and astrocytes, causing neuroinflammation, and ultimately leading to the loss of dopaminergic neurons and the development of PD
-
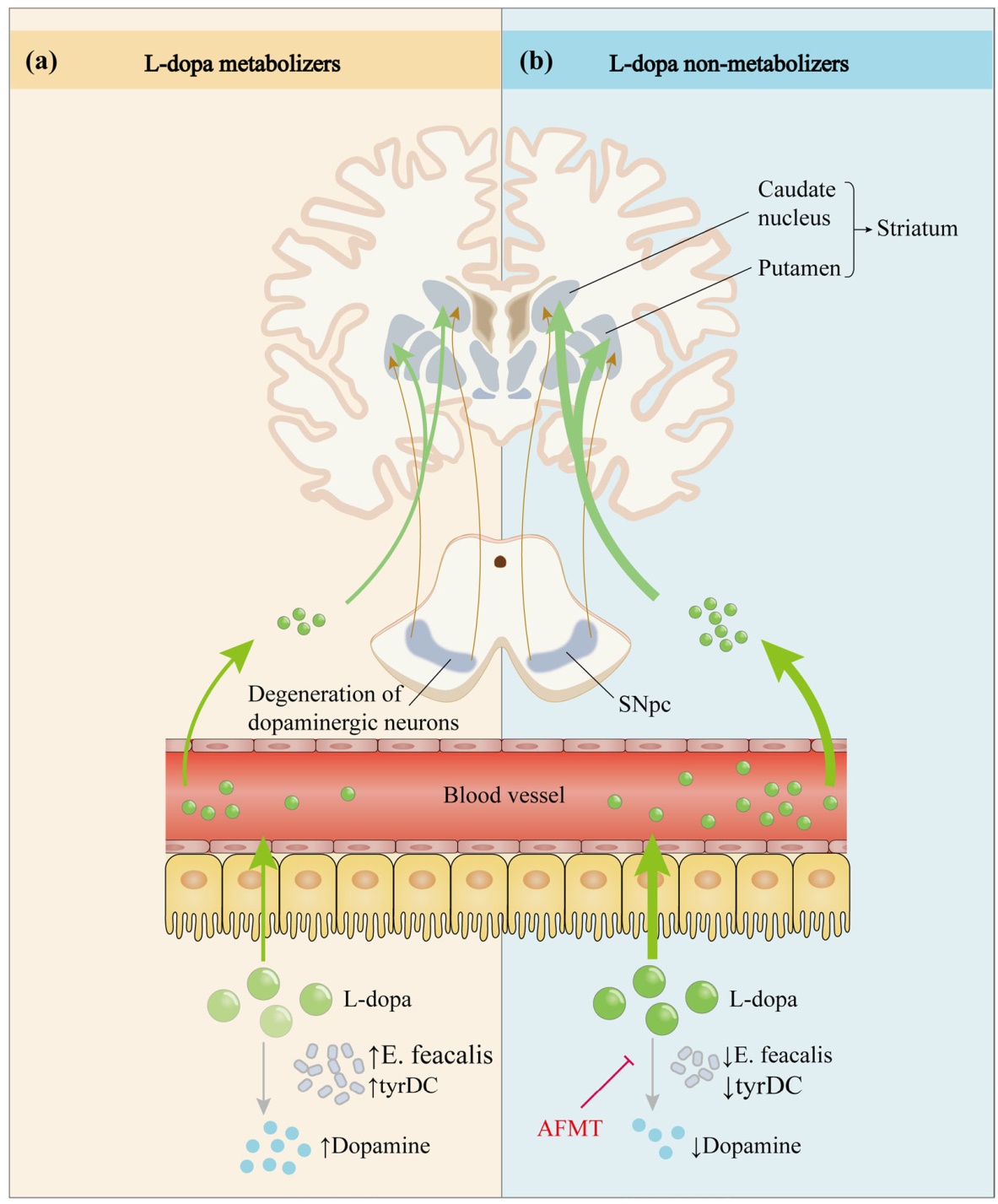 Fig. 4 Effect of intestinal microbes on the metabolic pathway of levodopa. After oral administration, L-dopa enters the circulation through active transport in the intestine and crosses the blood-brain barrier into the brain, where it exerts anti-Parkinson’s disease effects by restoring striatal dopaminergic neurotransmission. However, only a small fraction of the drug eventually reaches the brain due to interference by various factors. Studies have revealed that tyrDC from Enterococcus faecalis can convert L-dopa to dopamine in the intestine and affect its absorption. a Elevated E. feacalis and tyrDC levels enable more L-dopa to be metabolized to dopamine in the intestine, resulting in impaired L-dopa absorption. b Conversely, a decrease in tyrDC allows more L-dopa to be absorbed and utilized. In addition, the small molecule inhibitor (S)-α-fluoromethyltyrosine (AFMT) can suppress tyrDC, thereby increasing the bioavailability of L-dopa
Fig. 4 Effect of intestinal microbes on the metabolic pathway of levodopa. After oral administration, L-dopa enters the circulation through active transport in the intestine and crosses the blood-brain barrier into the brain, where it exerts anti-Parkinson’s disease effects by restoring striatal dopaminergic neurotransmission. However, only a small fraction of the drug eventually reaches the brain due to interference by various factors. Studies have revealed that tyrDC from Enterococcus faecalis can convert L-dopa to dopamine in the intestine and affect its absorption. a Elevated E. feacalis and tyrDC levels enable more L-dopa to be metabolized to dopamine in the intestine, resulting in impaired L-dopa absorption. b Conversely, a decrease in tyrDC allows more L-dopa to be absorbed and utilized. In addition, the small molecule inhibitor (S)-α-fluoromethyltyrosine (AFMT) can suppress tyrDC, thereby increasing the bioavailability of L-dopa
-
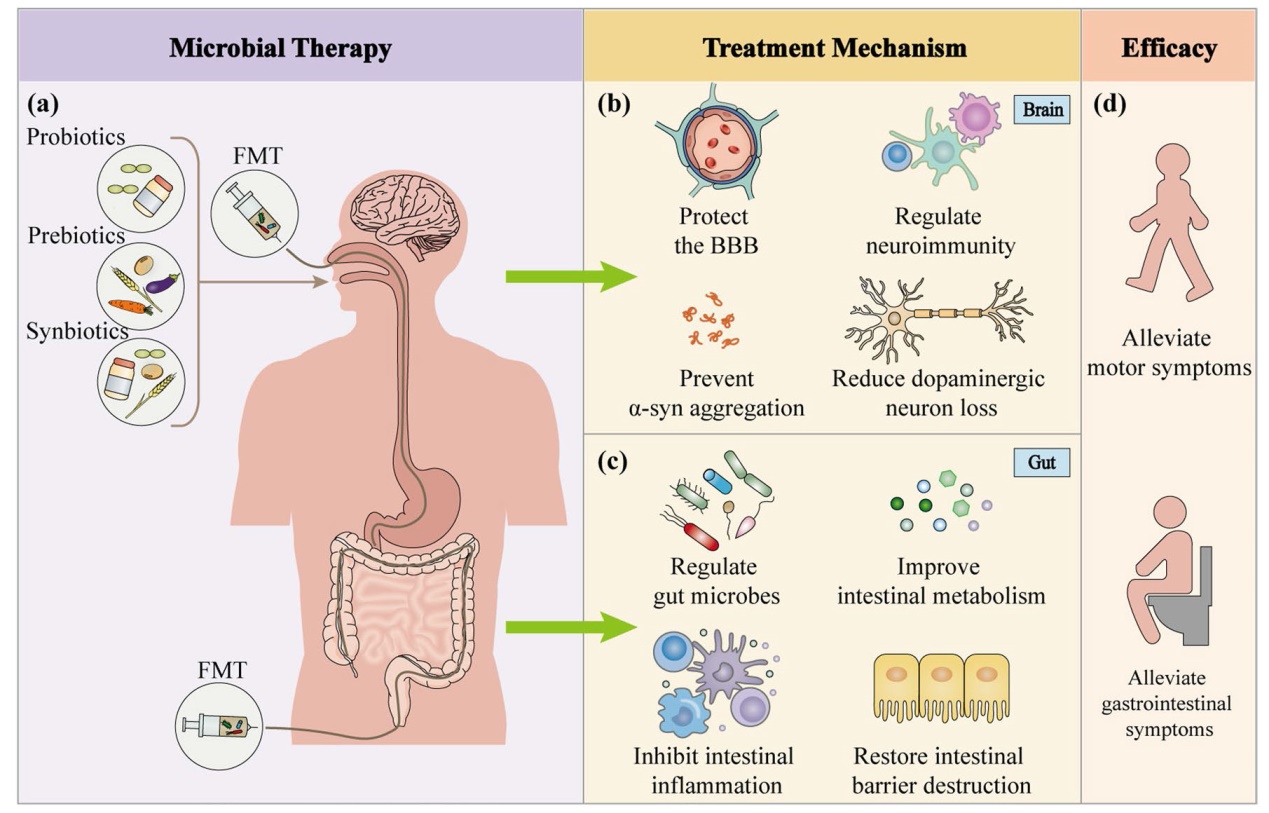 Fig. 5 Microbial therapies for Parkinson’s disease. a Probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation are the most commonly used microbial therapies for PD. These therapies can be administered through oral, nasogastric, rectal, or colonoscopic route. b Microbial therapies have neuroprotective effects on the brain by reducing the blood-brain barrier damage, decreasing microglial and astrocytic activation, suppressing neuroinflammation, and inhibiting α-syn aggregation, thereby preventing the death of dopaminergic neurons. c In the gut, microbial therapies can regulate gut microbes, improve intestinal metabolism, modulate the intestinal mucosal immune system, inhibit gut inflammation, and restore gut barrier damage, resulting in improved intestinal symptoms. d In conclusion, microbial therapies relieve nonmotor symptoms of PD, particularly constipation, as well as the motor symptoms through multiple pathways
Fig. 5 Microbial therapies for Parkinson’s disease. a Probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation are the most commonly used microbial therapies for PD. These therapies can be administered through oral, nasogastric, rectal, or colonoscopic route. b Microbial therapies have neuroprotective effects on the brain by reducing the blood-brain barrier damage, decreasing microglial and astrocytic activation, suppressing neuroinflammation, and inhibiting α-syn aggregation, thereby preventing the death of dopaminergic neurons. c In the gut, microbial therapies can regulate gut microbes, improve intestinal metabolism, modulate the intestinal mucosal immune system, inhibit gut inflammation, and restore gut barrier damage, resulting in improved intestinal symptoms. d In conclusion, microbial therapies relieve nonmotor symptoms of PD, particularly constipation, as well as the motor symptoms through multiple pathways