

诊断学理论与实践 ›› 2025, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (04): 431-440.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2025.04.010
林莉亚, 吴希, 毛胤祺, 陈光明, 武文漫, 戴菁, 王学锋, 丁秋兰( )
)
收稿日期:2025-01-20
修回日期:2025-02-25
接受日期:2025-03-25
出版日期:2025-08-25
发布日期:2025-09-09
通讯作者:
丁秋兰 E-mail: qiulan_ding@126.com基金资助:
LIN Liya, WU Xi, MAO Yinqi, CHEN Guangming, WU Wenman, DAI Jing, WANG Xuefeng, DING Qiulan( )
)
Received:2025-01-20
Revised:2025-02-25
Accepted:2025-03-25
Published:2025-08-25
Online:2025-09-09
摘要:
目的:分析4例携带血管性血友病因子裂解酶13(a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin type 1 motifs 13,ADAMTS13)去整合素样结构域杂合突变的血栓患者其基因型和表型特征,探讨ADAMTS13功能缺陷与血栓形成之间的关联。方法:通过易栓症基因Panel检测筛查血栓患者的易栓症相关基因突变,纳入4个携带ADAMTS13去整合素样结构域突变的易栓症家系。采用凝固法检测患者的凝血功能,使用免疫比浊法测定血管性血友病因子(von Willebrand factor, vWF)抗原和活性,酶联免疫吸附法检测vWF的胶原结合能力。通过十二烷基硫酸钠-琼脂糖凝胶电泳分析vWF多聚体的分布情况并进行灰度值半定量分析。采用荧光共振能量转移法测定血浆中ADAMTS13活性,酶联免疫吸附法检测ADAMTS13抗原水平。使用PyMOL软件对野生型及突变型ADAMTS13蛋白的三维结构进行对比分析。结果:4个家系的先证者均经历不同程度的血栓事件,包括脑静脉窦血栓、肺栓塞及下肢深静脉血栓。ADAMTS13蛋白去整合素样结构域突变约占ADAMTS13单杂合突变的4/87。遗传分析显示,4例先证者均携带ADAMTS13基因去整合素样结构域单杂合突变(p.Pro301Ala、p.Pro301Arg、p.Arg349Cys),其中p.Pro301Ala和p.Pro301Arg为首次报道突变。凝血功能检测结果表明,4例患者ADAMTS13活性和抗原水平显著降低(Act为57.42%~72.88%,Ag为66.94%~78.34%),vWF活性和抗原水平升高(Act为158.2%~213.7%,Ag为167.2%~216.6%)。vWF多聚体电泳分析显示,患者血浆中高分子量多聚体(high-molecular-weight multimers, HMWMs)比例显著增加(灰度值166.6~218.9比117.4),提示HMWMs较正常人明显增多。结构分析进一步表明,突变位点位于ADAMTS13蛋白去整合素样结构域的关键区域,可能破坏蛋白稳定性及与vWF的结合能力。结论:本研究首次报道了位于ADAMTS13蛋白去整合素样结构域上的2个新突变(Pro301Ala 和 Pro301Arg),并再次验证了已知突变Arg349Cys的致病特性。结果证实这些突变可导致ADAMTS13蛋白表达水平下降,并进一步引起其酶活性的显著降低,表现为对vWF高分子量多聚体的裂解能力减弱,功能试验证实患者体内存在异常增多的vWF多聚体,破坏了ADAMTS13‐vWF轴的动态平衡,从而增加血栓形成的风险。
中图分类号:
林莉亚, 吴希, 毛胤祺, 陈光明, 武文漫, 戴菁, 王学锋, 丁秋兰. 三种ADAMTS13去整合素样结构域突变致蛋白功能缺陷及其与血栓关联的研究[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2025, 24(04): 431-440.
LIN Liya, WU Xi, MAO Yinqi, CHEN Guangming, WU Wenman, DAI Jing, WANG Xuefeng, DING Qiulan. Three disintegrin-like domain mutations of ADAMTS13: functional deficiency and association with thrombosis[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2025, 24(04): 431-440.
表1
基因检测及临床表型检测结果
| Proband | Gene Analysis | ADAMTS13: Act(%) | ADAMTS13: Ag(%) | VWF:Act (%) | VWF:Ag (%) | VWF:CB /VWF:Ag(Ratio) | ADAMTS13:Act /VWF:Ag(Ratio) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ADAMTS13 c.901C>G:p.Pro301Ala* | 62.03 | 70.35 | 211.6 | 214.9 | 1.47 | 0.289 |
| 2 | ADAMTS13 c.902C>G:p.Pro301Arg* | 67.35 | 75.46 | 213.7 | 216.6 | 1.28 | 0.311 |
| 3 | ADAMTS13 c.902C>G:p.Pro301Arg* | 72.88 | 78.34 | 158.2 | 167.2 | 1.39 | 0.436 |
| 4 | ADAMTS13 c.1045C>T:p.Arg349Cys | 57.42 | 66.94 | 179.5 | 188.9 | 1.33 | 0.304 |
| Normal range | 60.00-150.00 | 40.00-120.00 | 50.0-150.0 | 50.0-150.0 | 0.70-1.20 | 0.500-2.000 |
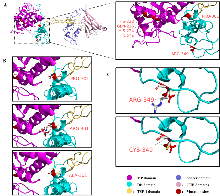
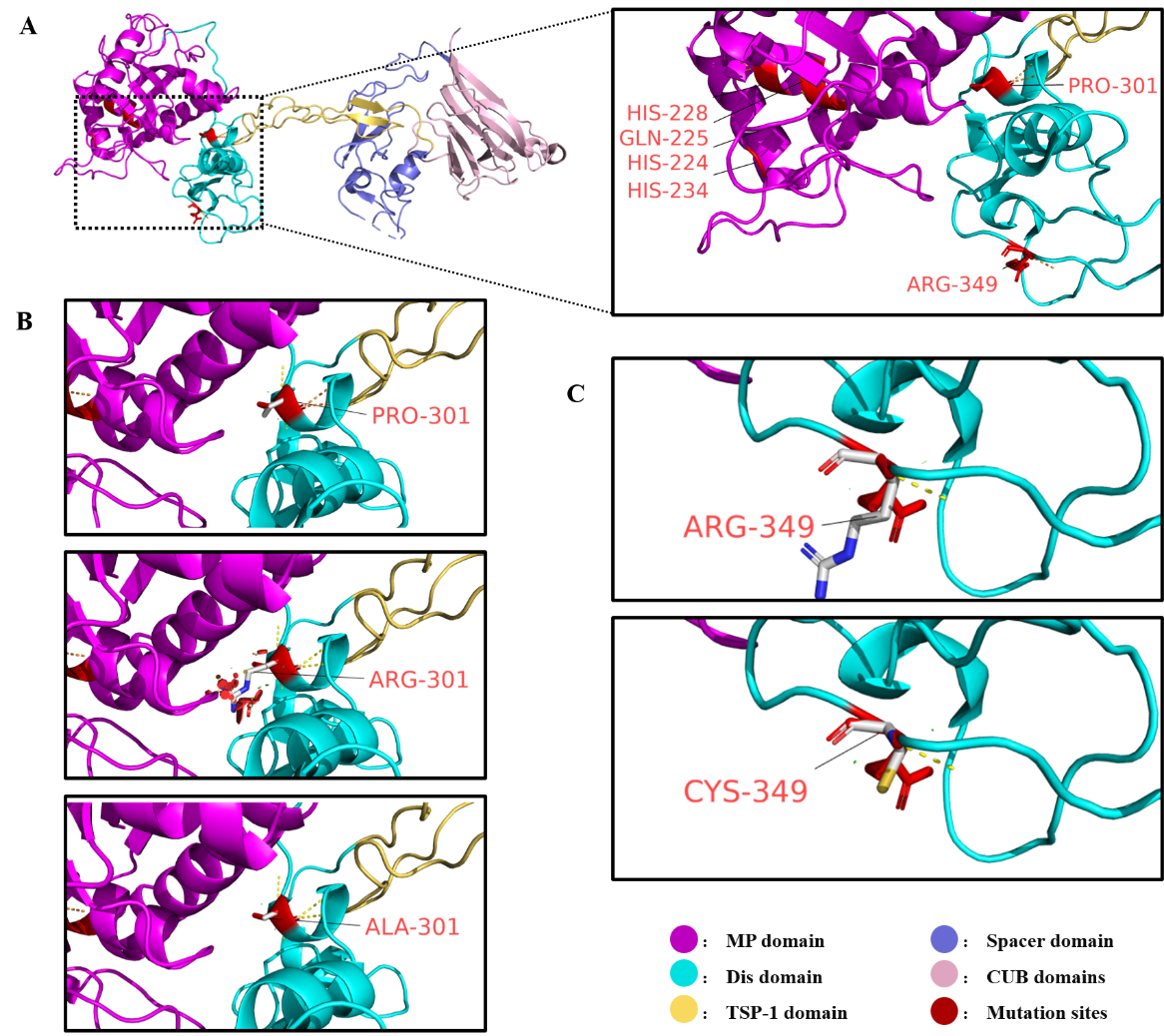
图4
ADAMTS13去整合素样结构域的2种氨基酸位点(Pro301、Arg349)及其突变对结构的影响 A:野生型ADAMTS13蛋白质结构,金属蛋白酶结构域上的催化活性中心(HIS-224、GLN-225、HIS-228、HIS-234)和本文研究的突变位点(PRO-301、ARG-349)以红色标出。B:野生型ADAMTS13氨基酸残基PRO-301与突变型ADAMTS13中氨基酸残基ALA-301、ARG-301的结构差异对比。突变后的ARG-301残基周围的红色圆盘表示发生的空间位阻效应。C:野生型ADAMTS13氨基酸残基ARG-349与突变型ADAMTS13中氨基酸残基CYS-349的结构差异对比。
| [1] | LEVY G G, NICHOLS W C, LIAN E C, et al. Mutations in a member of the ADAMTS gene family cause thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura[J]. Nature, 2001, 413(6855):488-494. |
| [2] | SADLER J E. Biochemistry and genetics of von Wille-brand factor[J]. Annu Rev Biochem, 1998, 67:395-424. |
| [3] |
DE GROOT R, BARDHAN A, RAMROOP N, et al. Essential role of the disintegrin-like domain in ADAMTS13 function[J]. Blood, 2009, 113(22):5609-5616.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-11-187914 pmid: 19234142 |
| [4] |
FENG Y, LI X Y, XIAO J, et al. ADAMTS13: more than a regulator of thrombosis[J]. Int J Hematol, 2016, 104(5):534-539.
pmid: 27696191 |
| [5] |
ZHENG X, CHUNG D, TAKAYAMA T K, et al. Structure of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS13), a metalloprotease involved in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura[J]. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276(44):41059-41063.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.C100515200 pmid: 11557746 |
| [6] | HOMMAIS A, RAYES J, HOULLIER A, et al. Molecular characterization of four ADAMTS13 mutations responsible for congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (Upshaw-Schulman syndrome)[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2007, 98(3):593-599. |
| [7] | DE WAELE L, VERMEERSCH L, NGUYEN T T, et al. In vitro characterization of a novel Arg102 mutation in the ADAMTS13 metalloprotease domain[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2023, 21(3):682-690. |
| [8] |
JIANG Y, HUANG D, KONDO Y, et al. Novel mutations in ADAMTS13 CUB domains cause abnormal pre-mRNA splicing and defective secretion of ADAMTS13[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2020, 24(7):4356-4361.
doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15025 pmid: 32073234 |
| [9] |
丁秋兰, 王学锋. 遗传性易栓症的表型和基因诊断流程[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2019, 18(2):127-132.
doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2019.02.002 |
| DING Q L, WANG X L. The phenotype and flowchart of gene diagnosis in inherited thrombophilia[J]. J Diagn Concepts Pract, 2019, 18(2):127-132. | |
| [10] | 李蕾, 吴希, 戴菁, 等. 中国118例颅内静脉窦血栓患者的临床特点及危险因素分析[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2023, 22(3):261-269. |
| LI L, WU X, DAI J, et al. Clinical characteristics and risk factor analysis of 118 patients with cerebral venous sinus thrombosis[J]. J Diagn Concepts Pract, 2023, 22(3):261-269. | |
| [11] | 李蕾, 吴希, 许冠群, 等. 基于新一代测序技术的易栓症基因检测Panel的建立及其在中国静脉血栓患者遗传背景研究中的临床应用[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2019, 18(4):394-401. |
| LI L, WU X, XU G Q, et al. Establishment and applica tion of thrombophilia gene detection Panel based on next generation sequencing in identification of genetic back ground of Chinese patients with venous thromboembolism[J]. J Diagn Concepts Pract, 2019, 18(4):394-401. | |
| [12] | LIANG Q, ZHANG Z, DING B, et al. A noncanonical spli-cing variant c.875-5 T > G in von Willebrand factor causes in-frame exon skipping and type 2A von Willebrand disease[J]. Thromb Res, 2024, 236:51-60. |
| [13] | 金佩佩, 梁茜, 戴菁, 等. 一例2N型遗传性血管性血友病家系的表型诊断和基因型分析[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2018, 17(2):151-154. |
| JIN P P, LIANG Q, DAI J, et al. Phenotype and genotype analysis of a Chinese pedigree with 2N type von Wille-brand disease[J]. J Diagn Concepts Pract, 2018, 17(2):151-154. | |
| [14] | LIANG Q, QIN H, DING Q L, et al. Molecular and clinical profile of VWD in a large cohort of Chinese population: application of next generation sequencing and CNVplex® technique[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2017, 117(8):1534-1548. |
| [15] |
BUDDE U, SCHNEPPENHEIM R, EIKENBOOM J, et al. Detailed von Willebrand factor multimer analysis in patients with von Willebrand disease in the European study, molecular and clinical markers for the diagnosis and management of type 1 von Willebrand disease (MCMDM-1VWD)[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2008, 6(5):762-771.
doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2008.02945.x pmid: 18315556 |
| [16] | EDVARDSEN M S, HANSEN E-S, UELAND T, et al. Impact of the von Willebrand factor-ADAMTS-13 axis on the risk of future venous thromboembolism[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2023, 21(5):1227-1237. |
| [17] | TAYLOR A, VENDRAMIN C, SINGH D, et al. von Wille-brand factor/ADAMTS13 ratio at presentation of acute ischemic brain injury is predictive of outcome[J]. Blood Adv, 2020, 4(2):398-407. |
| [18] | LANCELLOTTI S, SACCO M, TARDUGNO M, et al. The von Willebrand factor-ADAMTS-13 axis:a two-faced Janus in bleeding and thrombosis[J/OL]. 2022[2025-01-20]. https://www.btvb.org/btvb/article/view/11. |
| [19] | PHILIPPE A, GENDRON N, BORY O, et al. Von Wille-brand factor collagen-binding capacity predicts in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients: insight from vWF/ADAMTS13 ratio imbalance[J]. Angiogenesis, 2021, 24(3):407-411. |
| [20] |
AI J H, SMITH P, WANG S W, et al. The proximal carboxyl-terminal domains of ADAMTS13 determine substrate specificity and are all required for cleavage of von Willebrand factor[J]. J Biol Chem, 2005, 280(33):29428-29434.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M505513200 pmid: 15975930 |
| [21] | FUJIMURA Y, MATSUMOTO M, KOKAME K, et al. Pregnancy-induced thrombocytopenia and TTP, and the risk of fetal death, in Upshaw-Schulman syndrome: a series of 15 pregnancies in 9 genotyped patients[J]. Br J Haematol, 2009, 144(5):742-754. |
| [22] | AKIYAMA M, TAKEDA S, KOKAME K, et al. Crystal structures of the noncatalytic domains of ADAMTS13 reveal multiple discontinuous exosites for von Willebrand factor[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2009, 106(46):19274-19279. |
| [23] | HASSENPFLUG W A, OBSER T, BODE J, et al. Genetic and functional characterization of ADAMTS13 variants in a patient cohort with upshaw-schulman syndrome investigated in Germany[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2018, 118(4): 709-722. |
| [1] | 杨铭康, 刘禹, 许冠群, 王剑飚, 王学锋, 梁茜. vWF相关指标在诊断乙肝患者肝硬化进展中的价值[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2024, 23(06): 574-579. |
| [2] | 周丽华, 沈茹, 屈柯暄, 王爱华, 陈有会, 袁志敏. ABO血型基因第7外显子695 T>C突变导致Bw11亚型的研究[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2024, 23(04): 392-397. |
| [3] | 朱维维, 李倩, 吴凡, 翟志敏. 100例骨髓增生异常性肿瘤患者基因突变及其与临床特征间的关系[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2024, 23(03): 305-312. |
| [4] | 沈连军, 吴蔚, 吉薇, 王红, 孙幸, 施青青, 孙梅, 顾健, 倪军. 急性粒-单核细胞白血病患者造血干细胞移植后微血栓形成凝血指标监测及治疗1例报告[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2024, 23(02): 180-183. |
| [5] | 郝旭, 王伟铭. 依靠肾活检确诊的以肾脏病变为主要表现的法布里病1例报告[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2022, 21(04): 527-529. |
| [6] | 周璐, 雷航, 洪叶, 金爽, 董永勤, 王学锋, 蔡晓红. 一个新的ABO*A等位基因导致的AwB亚型及其分子机制研究[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2021, 20(06): 547-551. |
| [7] | 雷航, 范亮峰, 蔡晓红, 王钰箐, 刘曦, 金沙, 沈伟, 陆琼, 向东, 王学锋, 邹纬. 中国人群血型ABO亚型的分子基础研究[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2020, 19(04): 364-369. |
| [8] | 彭真萍, 项喜喜, 张苏江, 李佳明. 以类白血病反应为首发表现的慢性中性粒细胞白血病二例并文献复习[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2020, 19(02): 122-128. |
| [9] | 冯薇, 朱好辉. 彩超在评估自体动静脉内瘘狭窄、血栓生成情况中的应用价值分析[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2019, 18(03): 360-364. |
| [10] | 蔡蓉, 闵学文, 陈美蓉, 沈娅婷, 石群立, 周晓蝶. BRAF V600E(VE1)在甲状腺乳头状癌中的表达及其临床意义[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2018, 17(05): 552-556. |
| [11] | 王登峰, 崔文燕, 邹纬, 李芳, 王学锋, 蔡晓红. α-1,3- N-乙酰半乳糖胺基转移酶p.M142I突变导致Ax亚型的分子机制研究[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2018, 17(03): 260-265. |
| [12] | 陆静, 胥雨菲, 卿艳荣, 韩聪, 李牛, 郁婷婷, 姚如恩, 王剑. 一个Rett综合征合并努南综合征家系的基因诊断[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2018, 17(02): 147-150. |
| [13] | 金佩佩, 梁茜, 戴菁, 丁秋兰, 孙顺昌, 王学锋. 一例2N型遗传性血管性血友病家系的表型诊断和基因型分析[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2018, 17(02): 151-154. |
| [14] | 常春康,. 骨髓增生异常综合征WHO(2016)分型的修正[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2016, 15(03): 222-225. |
| [15] | 陈乐, 黄婷, 谢梦琦, 陆文丽, 马晓宇, 王歆琼, 许春娣, 李卫,. 幼年型粒单核细胞白血病2例报道及文献复习[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2015, 14(03): 235-238. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||