

Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice ›› 2025, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (01): 35-42.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2025.01.006
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Hongwei1,2, ZHU Ting1, LIU Yan1, HOU Yanqiang2, FAN Guangjian1( )
)
Received:2024-10-15
Accepted:2024-12-31
Online:2025-02-25
Published:2025-02-05
Contact:
FAN Guangjian
E-mail:gjfan@shsmu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
CHEN Hongwei, ZHU Ting, LIU Yan, HOU Yanqiang, FAN Guangjian. Study on exploring Scimp in peripheral blood as a biodiagnostic marker for MAFLD-related cirrhosis based on animal experiments[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2025, 24(01): 35-42.
Table 1
Primer sequences for real-time PCR of genes
| Primer | 5'-F | 5'-R |
|---|---|---|
| Hbq1b | AGCAATGTTGGAATCTACACGA | TTTAACCTGGCTGGAACCT |
| Scrn1 | TGGTGGACCGGAGAGGAT | AGAATCTATGCAAACGCCACT |
| Ranbp10 | CTCTGTACGAGCCACCCAC | CAGAAGGAATGCCCATCATCG |
| Sez6 | ATTGCTATGAGCCCTTTGTCAA | GCTGGTTCTGTCTCATTCCAC |
| Scimp | CGGTCTCCACTGATCCAGA | CTGTGTAAGCCCGTTTCAGC |
| Wipf3 | CTGCCACCCATACCACCT | GTGGCTCTCTCACGTCCT |
| Cpne8 | TGTACGGGCCAACCAACTTT | TCCGTCACAATGAGGAGCAC |
| Bglap | CTCAACAATGGACTTGGAGCCC | CACATGCCCTAAACGGTGGT |
| Nup210l | TTGCCATACAGCCTTTATACGAA | ATTCAGCAACAAGAACTGCC |
| Rab3ip | GTGAGAGAGGCGAACGTCAA | AGGCGATGTTGGAGAACTGG |
| Gp1bb | CCTGAGCGCGAGTTCTACC | CTCATCCTCCGCCACGTA |
| Bhlhb9 | ATCCCCTTATTCATAAAATAGCACAG | GGAAGAGTTCAGAGTAATAACAGCC |
| Emid1 | CTCAGTCCCAGCTACCCC | GAAGCTCCCAAGAATCAACTCT |
| Ubd | AAATGATCGAGAATGTGACTGC | GATCTTTCCATCTTCCAGCCTC |
| Gprasp2 | GCTAAACATCAGGCTAACACCA | CCAGCCCAAAAGCAAAACG |
| Plekhb1 | GTTTGCCCTAAGGTCAGGTG | TACCCAGATCCGCCTCTCAA |
| Oscar | GTTATCACTGCCGCTACCG | TACCAGCAGTTCCAGAGCA |
| GAPDH | TCAACGACCCCTTCATTGAC | GTTTCCCGTTGATGACCAG |
Figure 1
Pathological staining of liver tissues in SD ratsNote: Liver tissues from SD rats were stained with HE, Oil Red O, and Sirius Red, and observed under 200× magnification (scale bar: 200 μm). In the NC group, all three staining methods showed normal liver tissue architecture. In the HFD group, where rats spontaneously developed mild hepatic fibrosis, HE staining revealed cytoplasmic vacuoles of varying sizes; Oil Red O staining showed numerous red lipid droplets; and Sirius Red staining indicated minimal collagen fiber proliferation. In the LF group, which had progressed to liver cirrhosis, HE staining showed fibrous tissue proliferation, pseudolobule formation, and abundant cytoplasmic fat vacuoles of diverse shapes; Oil Red O staining revealed lipid droplets of uneven sizes; and Sirius Red staining demonstrated extensive collagen fiber proliferation accompanied by pseudolobule formation. In the images, green arrows indicate fat vacuoles, red arrows indicate pseudolobules, yellow arrows indicate lipid droplets, and blue arrows indicate collagen fibers.
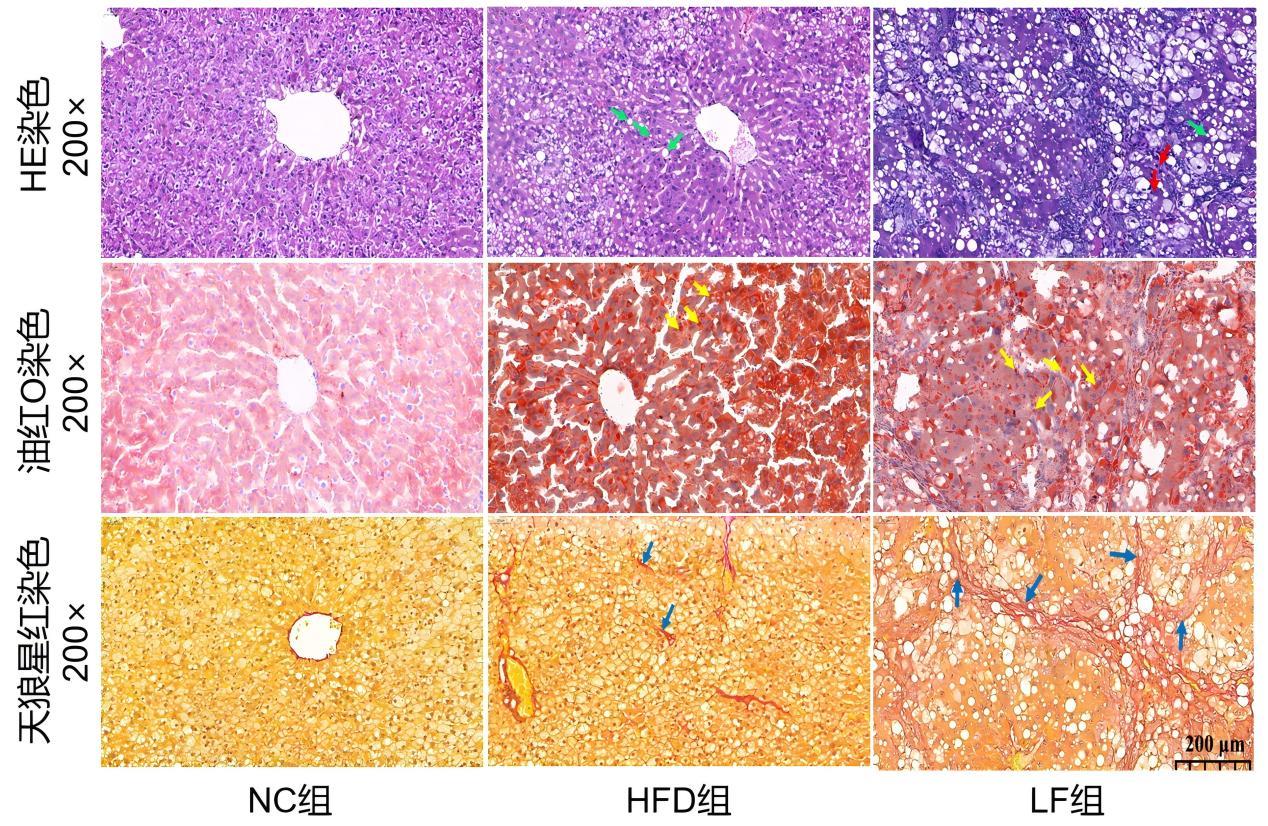
Figure 2
Expression levels of the 17 genes screened by blood mRNA sequencing in the NC, HFD, and LF groupsNote: The x-axis represents the genes, and the y-axis represents the normalized counts after logarithmic transformation of the sequencing data. * Indicates a statistically significant difference between the HFD group and the NC group (P<0.05); ψ indicates a statistically significant difference between the LF group and the NC group (P<0.05); Λ indicates a statistically significant difference between the LF group and the HFD group (P<0.05).It is of research significance to illustrate the expression trends of Rab3ip, Emid1, Scimp, Scrn1, Sez6, Nup210l, Gp1bb, Cpne8, and Oscar genes in the NC, HFD, and LF groups.
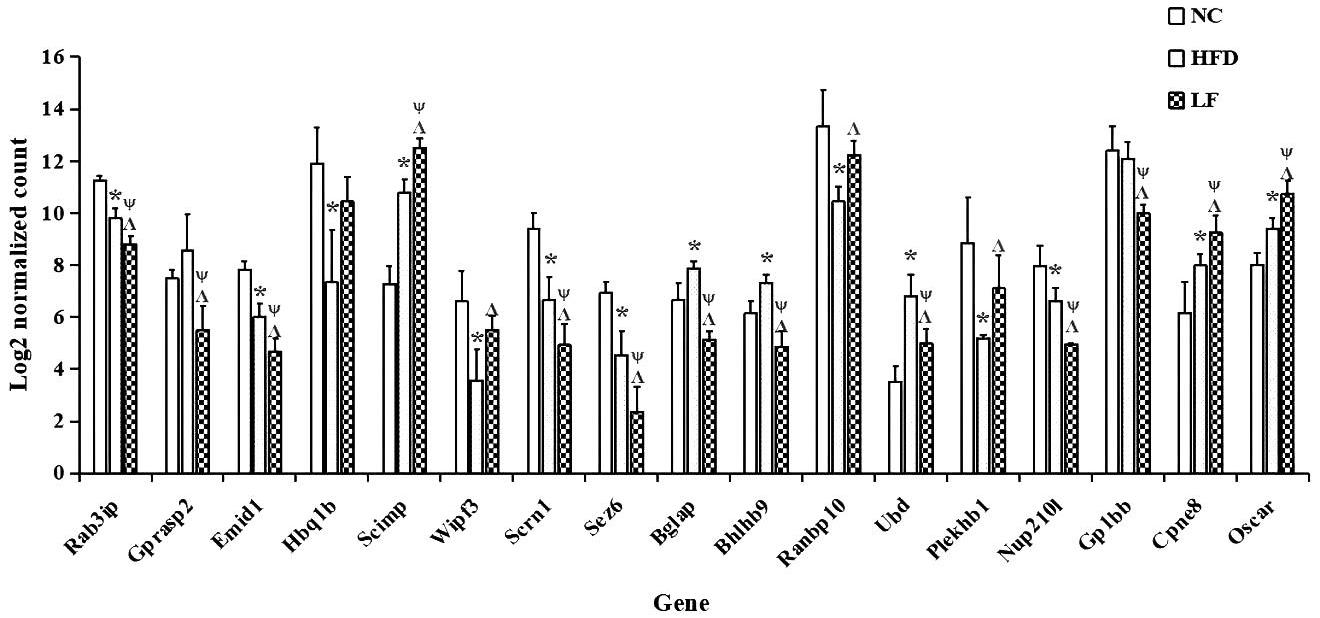
Figure 3
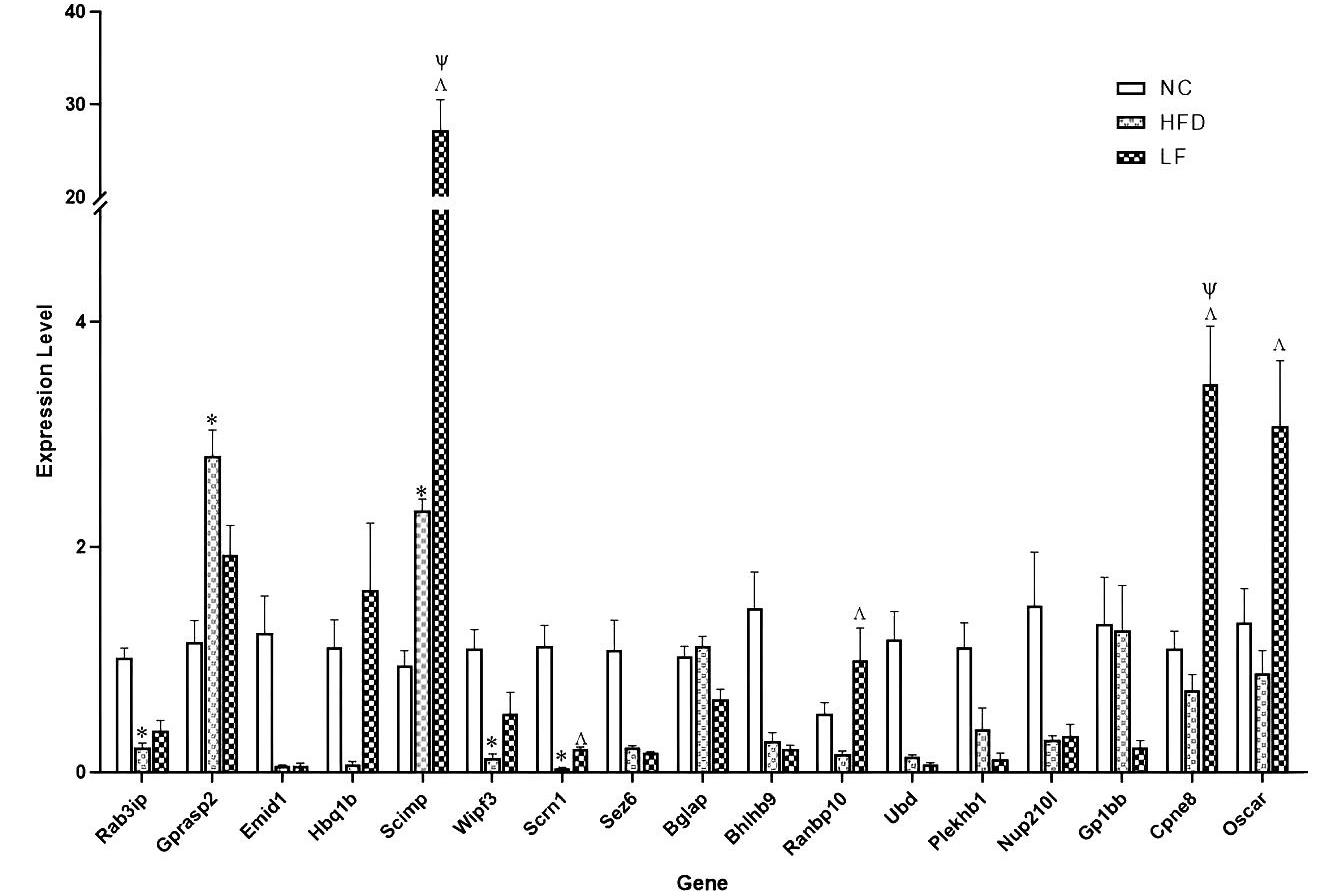
The expression profiles of 17 genes in the NC, HFD, and LF groups as determined by RT-qPCRNote: Expression levels of the 17 genes analyzed by RT-qPCR in blood samples from the NC, HFD, and LF groups in SD rats. The x-axis represents the genes, and the y-axis represents the standardized expression levels obtained from the quantitative analysis. * Indicates a statistically significant difference between the HFD group and the NC group (P<0.05); ψ indicates a statistically significant difference between the LF group and the NC group (P<0.05); Λ indicates a statistically significant difference between the LF group and the HFD group (P<0.05).This figure demonstrates that the expression levels and trends of the 17 genes differ between mRNA sequencing and RT-qPCR.
| [1] |
LI X Y, WANG J, GONG X,et al. Upregulation of BCL-2 by acridone derivative through gene promoter i-motif for alleviating liver damage of NAFLD/NASH[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(15):8255-8268.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa615 pmid: 32710621 |
| [2] | YUAN M, HE J, HU X,et al. Hypertension and NAFLD risk: Insights from the NHANES 2017-2018 and Mendelian randomization analyses[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2024, 137(4):457-464. |
| [3] | SONG C W, LV W, LI Y H,et al. Alleviating the effect of quinoa and the underlying mechanism on hepatic steatosis in high-fat diet-fed rats[J]. Nutrition & Metabolism, 2021, 18(1):106. |
| [4] | DINIZ T A, JUNIOR E A D L, TEIXEIRA A A,et al. Aerobic training improves NAFLD markers and insulin resistance through AMPK-PPAR-α signaling in obese mice[J]. Life Sciences, 2021, 266:118868. |
| [5] |
ZHANG L J, LIU C H, YIN L F,et al. Mangiferin relieves CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1):4172.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30582-3 pmid: 36914687 |
| [6] |
LIAO S L, HE H, ZENG Y P,et al. A nomogram for predicting metabolic steatohepatitis: The combination of NAMPT, RALGDS, GADD45B, FOSL2, RTP3, and RASD1[J]. Open Medicine, 2021, 16(1):773-785.
doi: 10.1515/med-2021-0286 pmid: 34041361 |
| [7] |
WU X Z, YUAN C B, PAN J X,et al. CXCL9, IL2RB, and SPP1, potential diagnostic biomarkers in the co-morbidity pattern of atherosclerosis and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1):16364.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66287-4 pmid: 39013959 |
| [8] | YAN J Y, FENG Y Y, FANG X W,et al. Anti-liver fibrosis effects of the total flavonoids of litchi semen on CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats associated with the upregulation of retinol metabolism[J]. Pharmaceutical Biology, 2022, 60(1):1264-1277. |
| [9] | 沈颖筱, 施惠海, 罗家乐,等.非酒精性脂肪性肝病肝纤维化风险预测模型的应用与进展[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2023, 27(9):131-136, 142. |
| SHEN Y X, SHI H H, LUO J L,et al. Application and progress of liver fibrosis risk prediction model for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Med Pract, 2023, 27(9):131-136, 142. | |
| [10] | 赵梓硕, 朱玉光, 马燕山,等.不同高脂饲料配方对建立非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠模型的影响[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2024, 29(5):543-553. |
| ZHAO Z S, ZHU Y G, MA Y S,et al. Effects of different formulations of high-fat diet on establishment of a non-alcoholic fatty liver model in rats[J]. Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2024, 29(5):543-553. | |
| [11] | 张垚, 叶嘉豪, 范星宇,等.基于数据挖掘的肝硬化动物模型分析[J]. 湖北民族大学学报(医学版), 2024, 41(2):28-32. |
| ZHANG Y, YE J H, FAN X Y,et al.Analysis of Animal Models of Cirrhosis Based on Data Mining[J]. J Hubei Minzu Univ Med Ed, 2024, 41(2):28-32. | |
| [12] |
PEI X L, LIU L, WANG J R,et al. Exosomal secreted SCIMP regulates communication between macrophages and neutrophils in pneumonia[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1):691.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44714-4 pmid: 38263143 |
| [13] |
LI Q S, FRANCKE S, SNOEYS J,et al. Genome-wide association study of abnormal elevation of ALT in patients exposed to atabecestat[J]. BMC Genomics, 2023, 24(1):513.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09625-6 pmid: 37658353 |
| [14] | SUN X L, TIAN A X, LI P,et al. SCIMP:A Novel Targeted Gene for Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Progression[J]. Orthopaedic Surgery, 2023, 15(5):1375-1383. |
| [15] | 朱海伟, 梁琳琅. 2型糖尿病合并非酒精性脂肪性肝病患者维生素D水平与肝纤维化的关系[J]. 中国临床研究, 2023, 36(5):670-674. |
| ZHU H W, LIANG L L. Correlation between 25 Hydroxyvitamin D level and liver fibrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chin J Clin Res, 2023, 36(5):670-674. |
| [1] | YANG Mingkang, LIU Yu, XU Guanqun, WANG Jianbiao, WANG Xuefeng, LIANG Qian. Value of vWF-related indicators in the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis progression in patients with hepatitis B [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(06): 574-579. |
| [2] | LIU Yue, WU Hanlin, TONG Wuqing, XU Jing. The value of autoantibody and D-dimer detection in evaluating the prognosis of patients with chronic hepatitis B and hepatitis B cirrhosis [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(02): 173-179. |
| [3] | YANG Wenkang, ZHANG Jun, WANG Shuqiu, XIANG BA Yangzong, YANG Cuiping. Pathogenic factors and clinical characteristics of 104 cirrhosis cases in Shangri-La area, Yunnan [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2022, 21(06): 730-734. |
| [4] | ZHAO Yingmei, NIE Hongming, ZHANG Jue, HUANG Yan. Detection of five coagulation indices in patients with cirrhosis and its clinical significance [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2021, 20(05): 480-483. |
| [5] | WANG Lijuan, PAN Zilai, SU Wenting, XU Jingci, RAO Min, LIU Xiao. Feasibility study on the portal vein imaging using non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography with flow inversion recovery sequence in the cirrhotic portal hypertension [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2020, 19(05): 494-498. |
| [6] | WANG Xiaoyu, XU Yan, WANG Libing, WU Yunlin, CHEN Ping, ZHANG Guohua. The effect of endoscopic variceal ligation on portal hypertensive gastropathy in liver cirrhosis patients [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2016, 15(05): 468-471. |
| [7] | GU Leilei, ZHU Shiyan, XIN Xiaorong, XIE Ling, ZHOU Yufen, YU Xiaojun, WU Yunlin. The clinical diagnosis of hemorrhagic portal hypertensive gastropathy (PHG) [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2016, 15(05): 459-463. |
| [8] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2013, 12(05): 556-558. |
| [9] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2013, 12(05): 516-521. |
| [10] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2013, 12(02): 224-227. |
| [11] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2012, 11(04): 411-414. |
| [12] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2009, 8(04): 405-409. |
| [13] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2007, 6(04): 299-303. |
| [14] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2007, 6(02): 127-130. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||