

Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice ›› 2023, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (03): 283-291.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2023.03.12
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
YIN Yongfang1, TANG Yonghua2( ), LIANG Yan1, CHEN Zhiren1, FEI Xiaochun3
), LIANG Yan1, CHEN Zhiren1, FEI Xiaochun3
Received:2023-01-18
Online:2023-06-25
Published:2023-11-17
CLC Number:
YIN Yongfang, TANG Yonghua, LIANG Yan, CHEN Zhiren, FEI Xiaochun. Clinical and imaging manifestations of Erdheim-Chester disease (six cases)[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(03): 283-291.
Table 1
Clinical data,clinical diagnosis and pathological diagnosis of ECD patients
| Serial number | Gender | age(years) | Clinical manifestation | Systems involved | Clinical diagnosis | Pathologic diagnosis | Genetic testing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Male | 11 | Ataxia, diabetes insipidus | Skin, central nervous system, skeletal system | LCH | LCH merges ECD | BRAF V600E gene(+) |
| Case 2 | Male | 33 | Diabetes insipidus, ametropia, Cough from drinking water | Skin, central nervous system, skeletal system, urinary system | LCH | ECD | BRAF V600E gene(+) |
| Case 3 | Male | 17 | Wrist pain, aggravated after exercise | Skeletal system, cardiovascular system, respiratory system | LCH | ECD | BRAF V600E gene(-) |
| Case 4 | Male | 16 | Chest discomfort, right neck mass, fever, cough, dysphagia | Skin, skeletal system | LCH | ECD | BRAF V600E gene(+) |
| Case 5 | Female | 54 | Loss of appetite, edema of both lower limbs, general weakness, mass of left upper abdomen | Skin, retroperitoneal space | Retroperitoneal mesenchymal sarcoma | ECD | Not detected |
| Case 6 | Female | 64 | Periorbital yellow patch,chest space occupying | Skin, cardiovascular system, respiratory system | Xanthoma of orbit、 Lung cancer | ECD | Not detected |
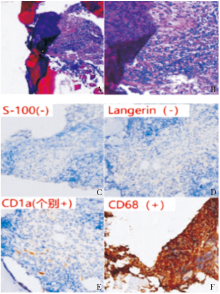
Figure 2
Pathological findings A,B: HE staining (×25, ×100) respectively, foamy or rich in lipid tissue cells, fibrosis with inflammatory cells infiltration.C-F Immunohistochemical staining CD34 (+), CD68 (+), according to (-), which CD1 alpha (individual +), S-100 (-), CD68 (+), AE1 / AE3 (-), which CD1 alpha (individual +), Langerin (-).
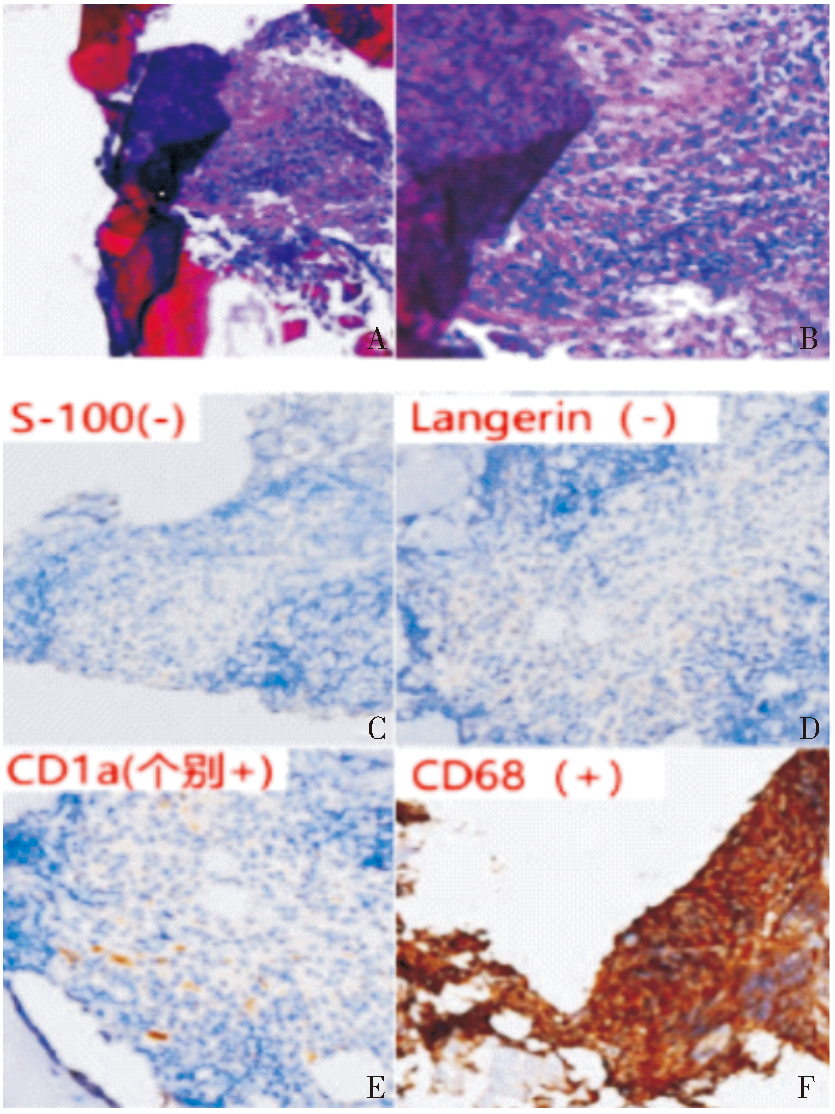
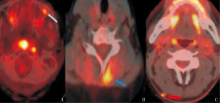
Figure 3
PET/CT findings of subcutaneous soft tissue lesions A:The subcutaneous hypermetabolism near the lateral canthus at the junction of the left anterior wall and lateral wall of the maxillary sinus in case 1 (thin arrow); B:A slightly thickened and hypermetabolic subcutaneous muscle in the left posterior neck in case 2 (thick blue arrow); C:A small nodular hypermetabolic subcutaneous muscle in the right posterior neck of in case 4 (thick red arrow).
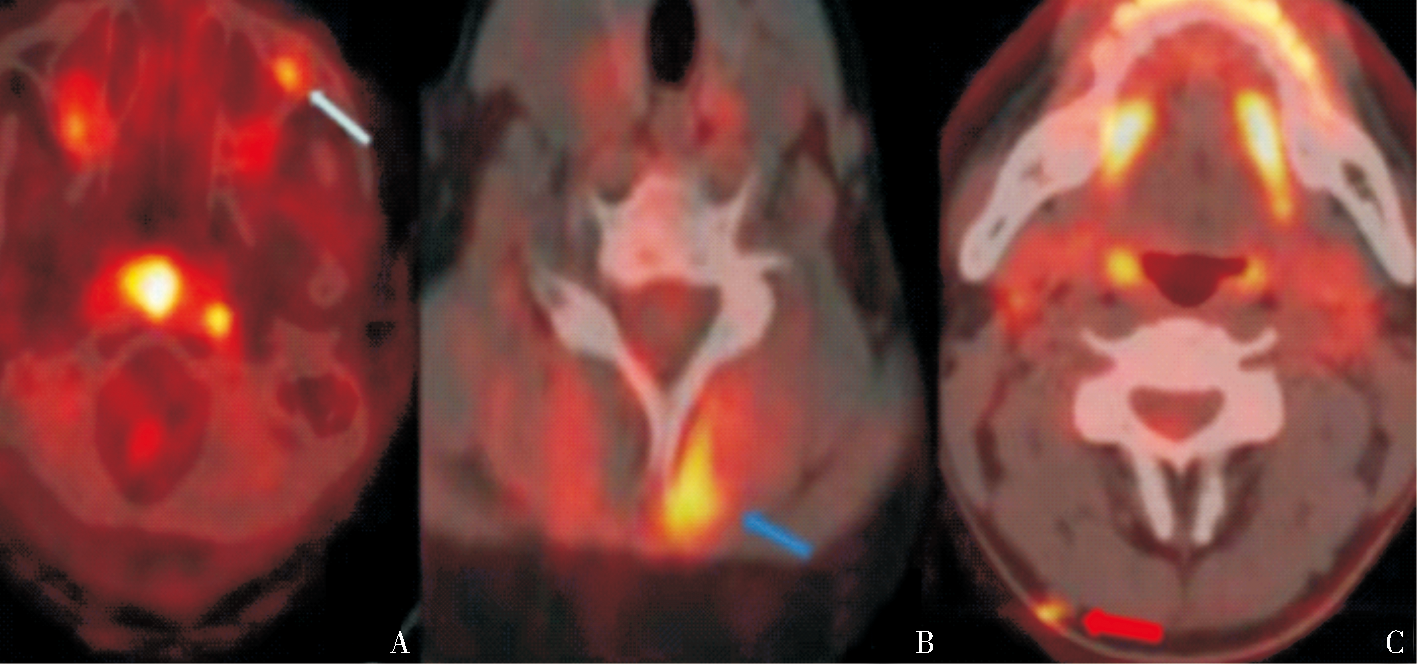

Figure 4
MRI and PET/CT findings of Pituitary lesions A:T1WI enhancement sequence shows pituitary stalk enlargement and obvious enhancement in case 1(blue arrow); B:T1WI sequence shows loss of normal neuropituitary hyperintensity in case 1 (red arrow); C:Shows decreased PET /CT pituitary metabolism in case 2(green arrow)
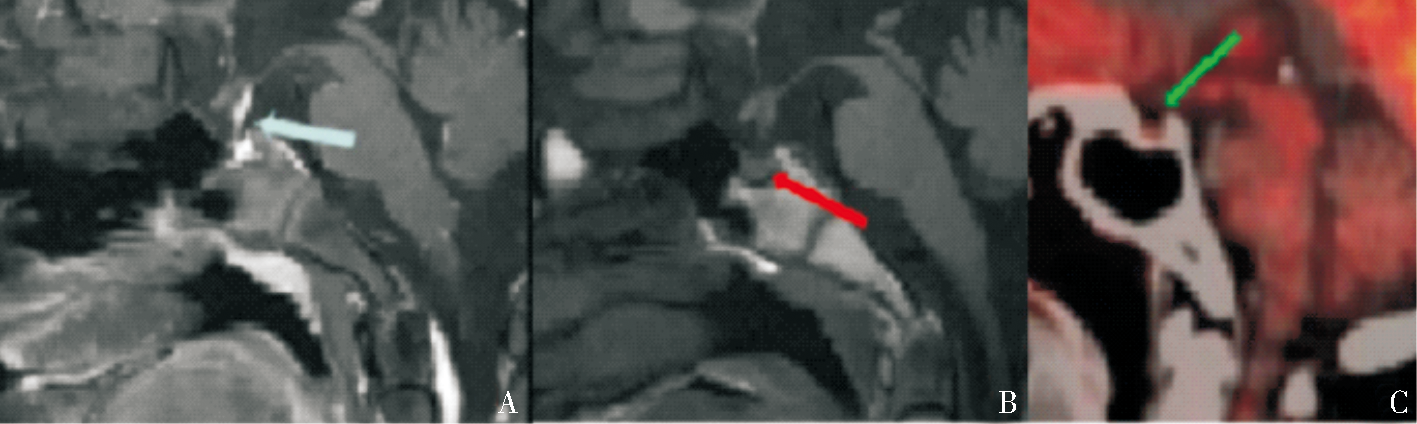
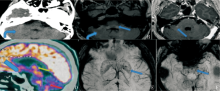
Figure 5
CT, MRI and PET/CT findings of cerebellar lesions A:CT shows cerebellar atrophy in case 1 (curved arrow); D:18F-FDG-PET/CT shows uneven decreased metabolism in the pituitary gland (thick blue arrow), bilateral cerebellar hemispheres (red arrow), dorsal thalamus, and increased metabolism in the pontine dorsal tegmental region in case 1(green arrow); B, C, E, F:MRI T2-FLAIR sequence shows multiple patchy high signals in the brain stem (blue arrow) and bilateral cerebellar hemispheres in case 2(curved arrow); C:T1WI enhanced sequence shows obvious enhancement in small patches of some lesions in the right pontine brachium in case 2(blue arrow); E, F :2 SWI sequence shows multiple small speckles of low signal intensity in bilateral basal ganglia and brainstem (blue arrow) in case 2.
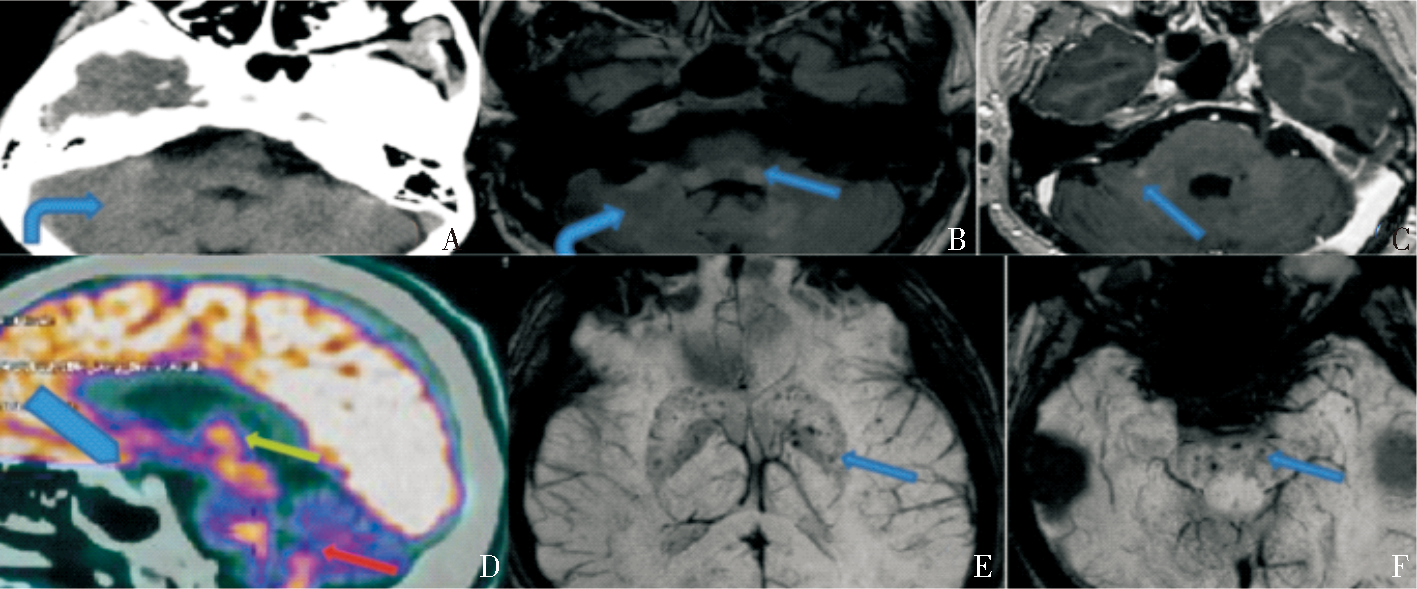
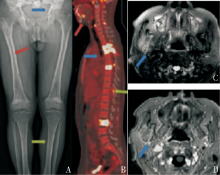
Figure 6
X-ray、MRI and PET/CT findings of bone lesion A:X-ray showed typical signs of symmetrical bone sclerosis in the pelvis, femur and tibia of both lower limbs, blurred edge of cancellous sclerosis area, smooth bone cortex, without periosteal reaction and bone destruction like perforation or erosion. There was no surrounding soft tissue mass in case 2 (blue-red-green arrows). B: FDG-PET/CT showed vertebral body, upper and lower jaw bones, spinous process or interspinous ligament, SUVmax15.2-17.1 in case1 (blue arrow). C-D: MRI shows hyperintensity in the right infratemporal fossa soft tissue on T2WI, heterogeneous enhancement on T1WI, and hyperintensity with limited diffusion on DWI in case 1 (blue arrow).
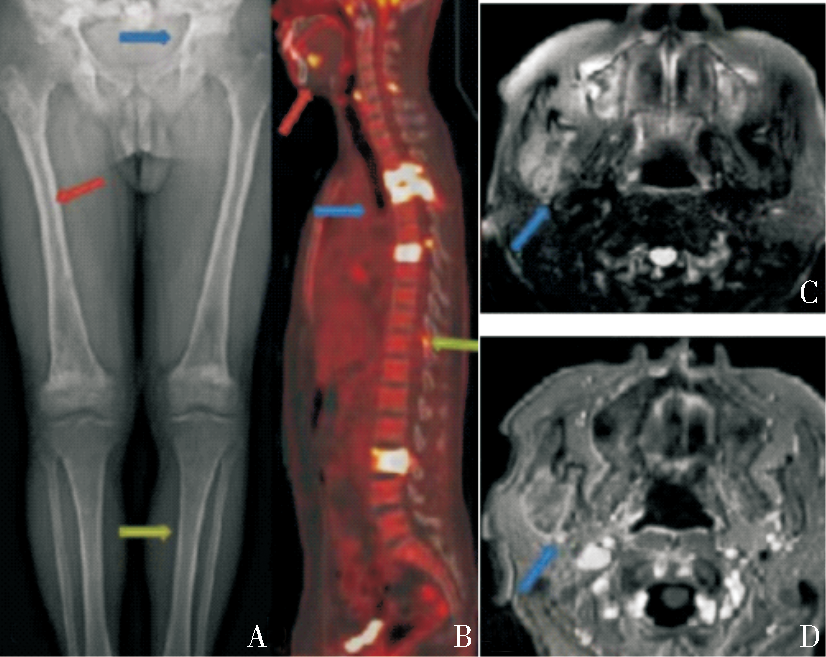
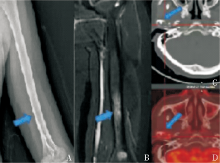
Figure 7
X-ray、MRI and PET/CT findings of bone lesion A,B :Initial X-ray of the humerus was false negative, and positive MRI showed high FS-T2WI signal in the medullary cavity of the middle and lower humerus in case 1(blue arrow); C,D: Osteolytic lesion, PET/CT showed osteolytic bone destruction in the right temporomandibular joint, and part of the bone cortex was blurred and discontinuous with increased metabolism. SUV max about 15.18, no surrounding soft tissue mass in case 5(blue arrow).
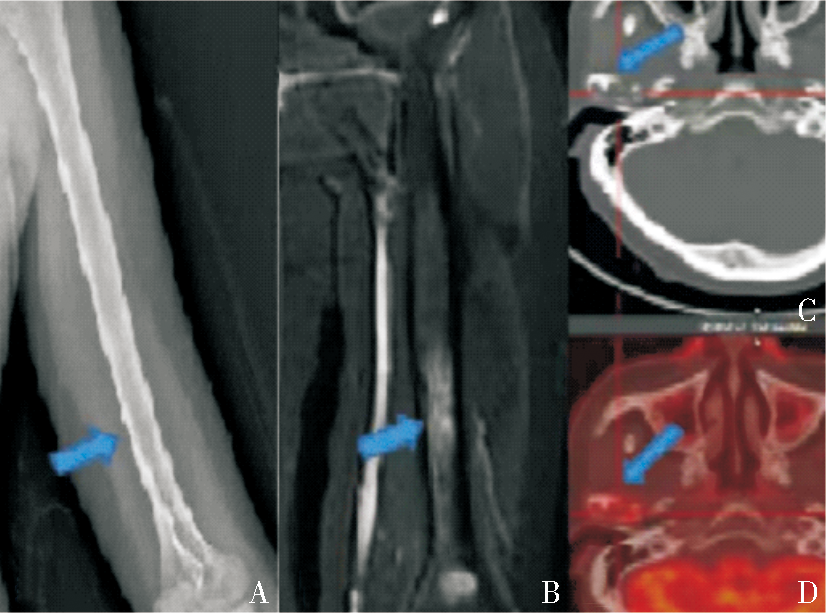
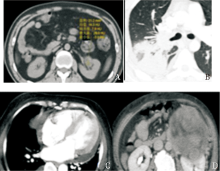
Figure 8
CT findings of other lesion A: The density of renal sinus soft tissue,with irregular shape and rough edge, and the CT value was about 13HU in case 2; B-C:With pericardial effusion and consolidation of the right lower lobe of the lung in case 3; D :Left retroperitoneal mass with compression of the left renal vein in case 15.

| [1] |
CIVES M, SIMONE V, RIZZO F M, et al. Erdheim-Chester disease: a systematic review[J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2015, 95(1):1-11.
doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2015.02.004 pmid: 25744785 |
| [2] |
CHESTER W. Über Lipoidgranulomatose[J]. Virchows Arch. path Anat, 1930, 279:561-602.
doi: 10.1007/BF01942684 URL |
| [3] | WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)[M].revised 4th edition. Lyon, 2017. |
| [4] | 付欣, 张丽英, 马静, 等. Erdheim-Chester病的临床病理分析[J]. 诊断病理学杂志, 2019, 26(12):822-826, 830. |
| FU X, ZHANG L Y, MA J, et al. Clinicopathological features of Erdheim-Chester disease[J]. J DIag Pathol, 2019, 26(12):822-826, 830. | |
| [5] | 刘玲春, 朴月善, 卢德宏. 几种常见的累及中枢神经系统的非朗格汉斯细胞组织细胞增生症[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2015, 54(12):1057-1059. |
| LIU L C, PIAO Y S, LU D H, et al. Several common Non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis involving the central nervous system[J]. Chin J Intern Med, 2015, 54(12):1057-1059. | |
| [6] |
HERVIER B, HAROCHE J, ARNAUD L, et al. Association of both Langerhans cell histiocytosis and Erdheim-Chester disease linked to the BRAFV600E mutation[J]. Blood, 2014, 124(7):1119-1126.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-12-543793 pmid: 24894769 |
| [7] |
MILNE P, BIGLEY V, BACON C M, et al. Hematopoie-tic origin of Langerhans cell histiocytosis and Erdheim-Chester disease in adults[J]. Blood, 2017, 130(2):167-175.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-12-757823 URL |
| [8] |
DURHAM B H, ROOS-WEIL D, BAILLOU C, et al. Functional evidence for derivation of systemic histiocytic neoplasms from hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells[J]. Blood, 2017, 130(2):176-180.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-12-757377 pmid: 28566492 |
| [9] |
CAVALLI G, GUGLIELMI B, BERTI A, et al. The multifaceted clinical presentations and manifestations of Erdheim-Chester disease: comprehensive review of the literature and of 10 new cases[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2013, 72(10):1691-1695.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202542 pmid: 23396641 |
| [10] |
ARNAUD L, GOROCHOV G, CHARLOTTE F, et al. Systemic perturbation of cytokine and chemokine networks in Erdheim-Chester disease: a single-center series of 37 patients[J]. Blood, 2011, 117(10):2783-2790.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-10-313510 pmid: 21205927 |
| [11] |
HAROCHE J, COHEN-AUBART F, AMOURA Z. Erdheim-Chester disease[J]. Blood, 2020, 135(16):1311-1318.
doi: 10.1182/blood.2019002766 pmid: 32107533 |
| [12] |
DION E, GRAEF C, MIQUEL A, et al. Bone involvement in Erdheim-Chester disease: imaging findings including periostitis and partial epiphyseal involvement[J]. Radiology, 2006, 238(2):632-639.
pmid: 16371583 |
| [13] | 王志芳, 常春康, 章振林. 以双下肢疼痛为主要表现的Erdheim-Chester病一例[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2021, 14(2):169-174. |
| WANG Z F, CHANG C K, ZHANG Z L, et al. Erdhein-Chester disease with bilateral lower limb pain as the main manifestation: a case report[J]. Chin J Osteoporos Bone Miner Res, 2021, 14(2):169-174. | |
| [14] |
ARNAUD L, GOROCHOV G, CHARLOTTE F, et al. Systemic perturbation of cytokine and chemokine networks in Erdheim-Chester disease: a single-center series of 37 patients[J]. Blood, 2011, 117(10):2783-2790.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-10-313510 pmid: 21205927 |
| [15] |
HAROCHE J, COHEN-AUBART F, AMOURA Z. Erdheim-Chester disease[J]. Blood, 2020, 135(16):1311-1318.
doi: 10.1182/blood.2019002766 pmid: 32107533 |
| [16] | JULIEN H, FLEUR COHEN A, ZAHIRAMOU A, et al. Erdheim-Chester disease[J]. Blood Review Series, 2020, 135 (16):1311-1318. |
| [17] |
GOTTLIEB R, CHEN A. MR findings of Erdheim-Chester disease[J]. J Comput Assist Tomogr, 2002, 26(2):257-261.
pmid: 11884783 |
| [18] |
COHEN AUBART F, IDBAIH A, EMILE J F, et al. Histiocytosis and the nervous system: from diagnosis to targeted therapies[J]. Neuro Oncol, 2021, 23(9):1433-1446.
doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noab107 URL |
| [19] |
ALLEN T C, CHEVEZ-BARRIOS P, SHETLAR D J, et al. Pulmonary and ophthalmic involvement with Erdheim-Chester disease: a case report and review of the literature[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2004, 128(12):1428-1431.
doi: 10.5858/2004-128-1428-PAOIWE pmid: 15578889 |
| [20] |
ARNAUD L, PIERRE I, BEIGELMAN-AUBRY C, et al. Pulmonary involvement in Erdheim-Chester disease: a single-center study of thirty-four patients and a review of the literature[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2010, 62(11):3504-3512.
doi: 10.1002/art.v62:11 URL |
| [21] |
PAPO M, DIAMOND E L, COHEN-AUBART F, et al. High prevalence of myeloid neoplasms in adults with non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis[J]. Blood, 2017, 130(8):1007-1013.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-01-761718 pmid: 28679734 |
| [22] |
DIAMOND E L, DAGNA L, HYMAN D M, et al. Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and clinical management of Erdheim-Chester disease[J]. Blood, 2014, 124(4):483-492.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-03-561381 pmid: 24850756 |
| [23] |
VAGLIO A, SALVARANI C, BUZIO C. Retroperitoneal fibrosis[J]. Lancet, 2006, 367(9506):241-251.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)68035-5 pmid: 16427494 |
| [24] | COHEN-AUBART F, EMILE J F, CARRAT F, et al. Phenotypes and survival in Erdheim-Chester disease: Results from a 165-patient cohort[J]. Am J Hematol, 2018, 93(5):E114-E117. |
| [25] |
FAN X, LIU T, ZHANG Z, et al. Comparison of neuroi-maging features of histiocytic neoplasms with central nervous system involvement: a retrospective study of 121 adult patients[J]. Eur Radiol, 2023, 33(11):8031-8042.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09724-8 |
| [26] | AGGARWAL A, TAYCHERT M, HASANIN L, et al. Erdheim-Chester disease: a case report of BRAF V600E-negative, MAP2K1-positive ECD diagnosed by blood next-generation sequencing assay and a brief literature review[J]. Oncology (Williston Park), 2023, 37(7):298-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||