

Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice ›› 2023, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (03): 277-282.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2023.03.11
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
WEI Jian1, SUN Jie2( ), CUI Shishuang3,4(
), CUI Shishuang3,4( )
)
Received:2023-05-05
Online:2023-06-25
Published:2023-11-17
CLC Number:
WEI Jian, SUN Jie, CUI Shishuang. Development of a Nomogram model for early diagnosis of Parkinson disease[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(03): 277-282.
Table 1
General information of training and validation sets[n(%)]
| Characteristics | Training set (n=300) | Validation set (n=102) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.633 | ||
| Female | 167 (41.5%) | 54 (13.4%) | |
| Male | 133 (33.1%) | 48 (11.9%) | |
| Agedness | 0.278 | ||
| Yes | 219 (54.5%) | 80 (19.9%) | |
| No | 81 (20.1%) | 22 (5.5%) | |
| diabetes | 0.310 | ||
| Yes | 38 (9.5%) | 17 (4.2%) | |
| No | 262 (65.2%) | 85 (21.1%) | |
| Cognitive decline | 0.830 | ||
| Yes | 218 (54.2%) | 73 (18.2%) | |
| No | 82 (20.4%) | 29 (7.2%) | |
| RBD | 0.840 | ||
| Yes | 212 (52.7%) | 71 (17.7%) | |
| No | 88 (21.9%) | 31 (7.7%) | |
| Constipation | 0.814 | ||
| Yes | 214 (53.2%) | 74 (18.4%) | |
| No | 86 (21.4%) | 28 (7%) | |
| Hyposmia | 0.136 | ||
| Yes | 212 (52.7%) | 64 (15.9%) | |
| No | 88 (21.9%) | 38 (9.5%) | |
| CER | 195.95 (±15.15) | 202 (±51.42) | 0.109 |
| Hypertension | 0.440 | ||
| Yes | 38 (9.5%) | 16 (4%) | |
| No | 262 (65.2%) | 86 (21.4%) | |
| Postural hypotension | 0.542 | ||
| Yes | 238 (59.2%) | 78 (19.4%) | |
| No | 62 (15.4%) | 24 (6%) | |
| Smoking | 0.570 | ||
| Yes | 73 (18.2%) | 22 (5.5%) | |
| No | 227 (56.5%) | 80 (19.9%) | |
| Drinking | 0.333 | ||
| Yes | 76 (18.9%) | 21 (5.2%) | |
| No | 224 (55.7%) | 81 (20.1%) |
Table 2
Univariate regression analysis of risk factors for PD
| Characteristics | OR | 95% CI | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.703 | 0.445-1.111 | 0.131 |
| Agedness | 2.979 | 1.732-5.122 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 1.274 | 0.643-2.523 | 0.488 |
| Cognitive decline | 2.280 | 1.348-3.856 | 0.002 |
| RBD | 1.919 | 1.156-3.187 | 0.012 |
| Constipation | 2.383 | 1.418-4.005 | <0.001 |
| Hyposmia | 1.795 | 1.083-2.975 | 0.023 |
| CER | 2.389 | 1.477-3.866 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 0.785 | 0.396-1.556 | 0.488 |
| Postural hypotension | 1.562 | 0.890-2.741 | 0.120 |
| Smoking | 1.296 | 0.759-2.211 | 0.342 |
| Drinking | 0.732 | 0.422-1.268 | 0.266 |
Table 3
Multivariate regression analysis of risk factors for PD
| Characteristics | regression coefficient | OR | OR(95% CI) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agedness | 1.228 | 3.413 | 1.884 - 6.182 | <0.001 |
| Cognitive decline | 0.951 | 2.588 | 1.444 - 4.642 | <0.001 |
| RBD | 0.665 | 1.945 | 1.090- 3.471 | 0.024 |
| Constipation | 1.064 | 2.897 | 1.623 - 5.169 | <0.001 |
| Hyposmia | 0.751 | 2.120 | 1.208 - 3.722 | 0.009 |
| CER | 1.211 | 3.356 | 1.923 - 5.855 | <0.001 |
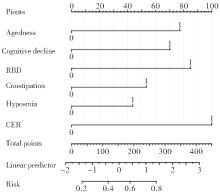
Figure 1
The nomogram early diagnostic model for PD The length of the line for each predictor variable represents the predicted risk of that factor for PD and corresponds to the single score at the top; the total score corresponding to the individual scores corresponding to all the variables taking values added together corresponds to the predicted risk of PD.
| [1] |
BLOEM B R, OKUN M S, KLEIN C. Parkinson's disease[J]. Lancet, 2021, 397(10291):2284-2303.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00218-X pmid: 33848468 |
| [2] |
ARMSTRONG M J, OKUN M S. Diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease: a review[J]. JAMA, 2020, 323(6):548-560.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.22360 pmid: 32044947 |
| [3] |
HAYES M T. Parkinson's Disease and Parkinsonism[J]. Am J Med, 2019, 132(7):802-807.
doi: S0002-9343(19)30235-9 pmid: 30890425 |
| [4] |
CEBALLOS-BAUMANN A. Parkinson-Syndrom [Parkinson's Disease - What is New?][J]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 2022, 147(6):337-343.
doi: 10.1055/a-1646-6321 URL |
| [5] | DORSEY E R, SHERER T, OKUN M S, et al. The emerging evidence of the Parkinson pandemic[J]. J Parkinsons Dis, 2018, 8(s1):S3-S8. |
| [6] |
TONG C, MIAO Q, ZHENG J, et al. A novel nomogram for predicting the decision to delayed extubation after thoracoscopic lung cancer surgery[J]. Ann Med, 2023, 55(1):800-807.
doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2160490 pmid: 36869647 |
| [7] |
ABDULHALEEM M, RUIZ J, CRAMER C, et al. Brain metastasis prognostic nomograms and brain metastasis velocity: a narrative review[J]. Chin Clin Oncol, 2022, 11(2):10.
doi: 10.21037/cco URL |
| [8] |
ZHANG L, TANG L, CHEN S, et al. A nomogram for predicting the 4-year risk of chronic kidney disease among Chinese elderly adults[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2023, 55(6):1609-1617.
doi: 10.1007/s11255-023-03470-y |
| [9] | 石红, 杨彦辉, 张亚萍, 等. Nomogram预测乳腺浸润性导管癌Ki-67表达水平[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2023, 39(1):17-21. |
| SHI H, YANG Y H, ZHANG Y P, et al. Nomogram to Predict Ki-67 Expression levels in invasive ductal breast cancer[J]. Chin J Ultrasound Med, 2023, 39(1):17-21. | |
| [10] |
YE H, ROBAK L A, YU M, et al. Genetics and Pathoge-nesis of Parkinson's Syndrome[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2023, 18:95-121.
doi: 10.1146/pathmechdis.2023.18.issue-1 URL |
| [11] | 王刚, 崔海伦. 帕金森病临床诊断和治疗现状及进展[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2019, 44(4):464-467. |
| WANG G, CUI H L. Clinical diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson's disease in China:Current status and research advances[J]. J Chongqing Med Univ, 2019, 44(4):464-467. | |
| [12] | 孙雪婷, 张志伟, 余刚. 磁敏感加权成像黑质“燕尾征”在帕金森病中的诊断价值[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2021, 46(7):823-827. |
| SUN X T, ZHANG Z W, YU G. Diagnostic value of “swallow tail” appearance in the substantia nigra using susceptibility weighted imaging in Parkinson's disease[J]. J Chongqing Med Univ, 2021, 46(7):823-827. | |
| [13] |
AMBROSIO L, PORTILLO M C, RODRIGUEZ-BLAZQUEZ C, et al. Influencing factors when living with Parkinson's disease: a cross-sectional study[J]. J Clin Nurs, 2019, 28(17-18):3168-3176.
doi: 10.1111/jocn.14868 pmid: 30938889 |
| [14] |
SIMON D K, TANNER C M, BRUNDIN P. Parkinson disease epidemiology, pathology, genetics, and pathophysiology[J]. Clin Geriatr Med, 2020, 36(1):1-12.
doi: S0749-0690(19)30063-1 pmid: 31733690 |
| [15] |
PAN L, LI C, MENG L, et al. Tau accelerates α-synuclein aggregation and spreading in Parkinson's disease[J]. Brain, 2022, 145(10):3454-3471.
doi: 10.1093/brain/awac171 pmid: 35552614 |
| [16] | LEWITT P A, CHAUDHURI K R. Unmet needs in Parkinson disease: motor and non-motor[J]. Parkinsonism Relat Disord, 2020, 80 Suppl 1:S7-S12. |
| [17] |
BANG Y, LIM J, CHOI H J. Recent advances in the pathology of prodromal non-motor symptoms olfactory deficit and depression in Parkinson's disease: clues to early diagnosis and effective treatment[J]. Arch Pharm Res, 2021, 44(6):588-604.
doi: 10.1007/s12272-021-01337-3 pmid: 34145553 |
| [18] |
DU Y, LI Y, XU X, et al. Probiotics for constipation and gut microbiota in Parkinson's disease[J]. Parkinsonism Relat Disord, 2022, 103:92-97.
doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2022.08.022 URL |
| [19] |
CHEN Z, LI G, LIU J. Autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson's disease: Implications for pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2020, 134:104700.
doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104700 URL |
| [20] | 阿地拉·艾尼瓦尔, 张拉, 蒋森, 等. α-突触核蛋白基因多态性与帕金森病的关联分析[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2021, 46(7):844-848. |
| ADILA·A, ZHANG L, JIANG S, et al. Correlation between polymorphism of α-synuclein gene and Parkinson's disease[J]. J Chongqing Med Univ, 2021, 46(7):844-848. | |
| [21] |
DAUVILLIERS Y, SCHENCK C H, POSTUMA R B, et al. REM sleep behaviour disorder[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2018, 4(1):19.
doi: 10.1038/s41572-018-0016-5 pmid: 30166532 |
| [22] |
HU M T. REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD)[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2020, 143:104996.
doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104996 URL |
| [23] |
LIN Y Q, CHEN S D. RBD: a red flag for cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease?[J]. Sleep Med, 2018, 44:38-44.
doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2018.01.006 URL |
| [24] |
ZHAO X, SHAO Z, ZHANG Y, et al. Ceruloplasmin in Parkinson's disease and the nonmotor symptoms[J]. Brain Behav, 2018, 8(6):e00995.
doi: 10.1002/brb3.2018.8.issue-6 URL |
| [25] |
WANG B, WANG X P. Does ceruloplasmin defend against neurodegenerative diseases?[J]. Curr Neuropharmacol, 2019, 17(6):539-549.
doi: 10.2174/1570159X16666180508113025 pmid: 29737252 |
| [26] |
GARDNER B, DIERIKS B V, CAMERON S, et al. Metal concentrations and distributions in the human olfactory bulb in Parkinson's disease[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1):10454.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10659-6 pmid: 28874699 |
| [27] |
ZUZUÁRREGUI J R P, DURING E H. Sleep issues in Parkinson's disease and their management[J]. Neurotherapeutics, 2020, 17(4):1480-1494.
doi: 10.1007/s13311-020-00938-y pmid: 33029723 |
| [28] |
HELLMAN N E, GITLIN J D. Ceruloplasmin metabolism and function[J]. Annu Rev Nutr, 2002, 22:439-458.
pmid: 12055353 |
| [29] | 张忠伟, 李杨飞, 潘璟琍, 等. 扩散峰度成像参数在帕金森病诊断中的价值研究[J]. 中华全科医学, 2020, 18(2):273-276. |
| ZHANG Z W, LI Y F, PAN J L, et al. The value research of diffusion kurtosis imaging parameters in diagnosing Parkinson's disease[J]. Chin J General Pract, 2020, 18(2):273-276. |
| [1] | WU Dongdong, LI Shuhua, SU Wen, LIU Yinghong, CHEN Haibo, CHEN Di. Serotonin syndrome induced by anti-parkinsonism drugs:a case report [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(03): 303-305. |
| [2] | HE Xin, CHEN Hui, FENG Weiwei. Research progress on the application of machine learning in assisted ultrasound diagnosis of adnexal masses [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2022, 21(04): 541-546. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||