

Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice ›› 2025, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (01): 51-58.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2025.01.008
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHE Guanhua1, ZENG Chang2, CHEN Xiaoyan3( )
)
Received:2023-10-07
Accepted:2024-06-03
Online:2025-02-25
Published:2025-02-25
Contact:
CHEN Xiaoyan
E-mail:cxy11832@rjh.com.cn
CLC Number:
CHE Guanhua, ZENG Chang, CHEN Xiaoyan. Micronodular thymoma with lymphoid stroma: a clinicopathologic analysis of five cases and literature review[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2025, 24(01): 51-58.
Table 1
Clinical data of 5 cases with micronodular thymoma with lymphoid stroma
| Case | Gender | Age (years) | Clinical symptoms | Maximum size (cm) | Cystic change | Location | Diagnose | Group | Follow-up (months) | Recurrence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Male | 63 | No Special | 4.5 | Yes | Anterior mediastinum | MAMNT | Ⅰ | 39 | No |
| 2 | Male | 57 | No Special | 2.3 | Yes | Anterior upper mediastinum | MNT | Ⅱ | 30 | No |
| 3 | Female | 68 | No Special | 1.3 | No | Right upper mediastinum | MNT | Ⅰ | 25 | No |
| 4 | Male | 55 | No Special | 2.0 | No | Anterior mediastinum | MNT | Ⅰ | 8 | No |
| 5 | Female | 65 | No Special | 3.2 | No | Anterior mediastinum | MNT | Ⅱ | 7 | No |

Figure 1
Pathological images of MNT patients(Hematoxylin Eosin)A: MNT invaded fibrous capsule(×10); B: The luminal monolayer and basal lamina cells in cystic area(×400); C: Short fusiform and oval epithelial cells with relatively rich eosinophilic cytoplasm(×400); D: Epithelial nodules and lymphoid stroma(×40).
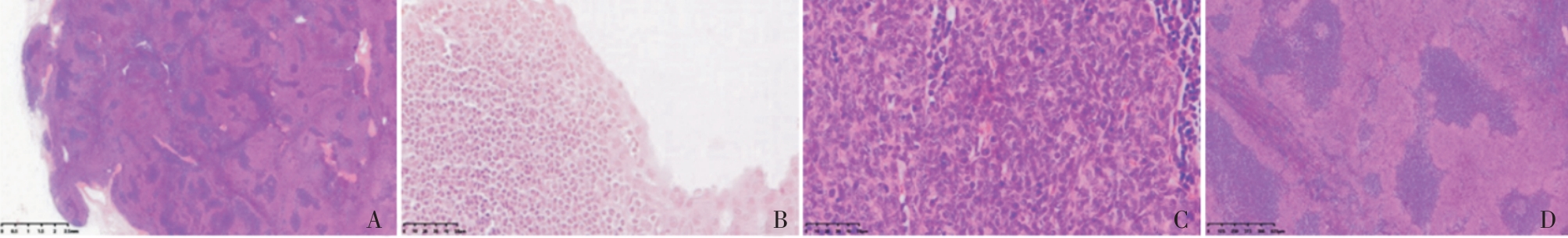
Figure 2
Immunohistochemical images of MNT patients(Bench Mark)A: The luminal monolayer cells were positive for EMA while the basal lamina cells and epithelial nodules werenegative(×200); B: Both luminal cells and epithelial nodules were positive for CK19(×200); C: The basal lamina cells and epithelial nodules werepositive for P63, but the luminal monolayer cells were negative(×100); D: The luminal monolayer cells were negative for Bcl-2 while the other basal lamina cells, epithelial nodules and stromal lymphocytes were allpositive(×400); E: The B lymphocytes were positive for CD20(×20 );F: Theimmature T lymphocytes around epithelial nodules were positive for TdT(×40);G: The lymphoid follicle germinal center was positive for CD10(×40)(Top right corner ×400); H: The langerhans cells among epithelial nodules were positive for CD1α(×100).
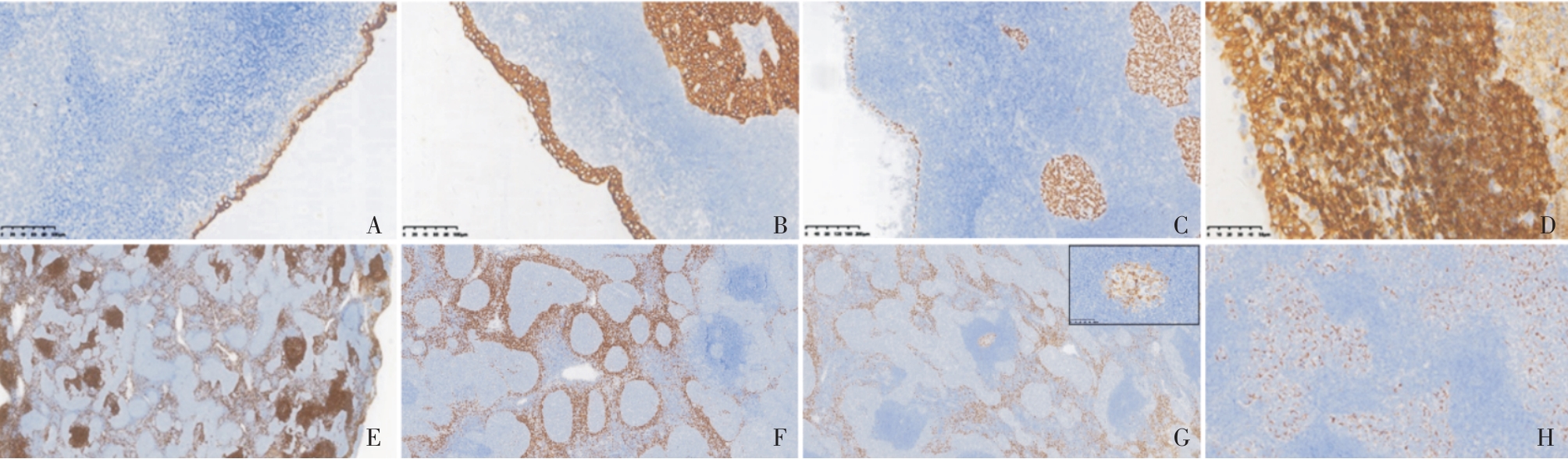
Table 2
Clinical data of 211 cases with micronodular thymoma with lymphoid stroma in literature and this study
| Literature | Cases (male:female) | Ages (median,years) | Location | Maximum size(cm) | Clinical symptoms | Macroscopically | Follow-up(months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang[ | 107(1.3∶1.0) | 45-83 (Not detailed) | 103 cases occurred in the thymus, 4 cases occurred in the neck | 1.0-10.7 | 6 cases of severe myasthenia gravis, 3 cases of ptosis, 6 cases of chest discomfort, 1 case ofsternal pain, and the rest were found during physical examination or incidentally | 12 cystic, 30 solid, 7 cystic and solid, others not specified | 68 cases (4-190 months), 1 case died of esophageal cancer, 1 case of rectal cancer, and the rest had no recurrence |
| Zhang[ | 4(2∶2) | 5-62(52) | mediastinum | 3.3-5.0 | 1 case of severe myasthenia gravis, 3 cases found during physical examination | Not specified | 4 cases (19-32 months), disease-free survival |
| Yagi[ | 8(1∶1) | 47-76(60.5) | thymus | 1.8-6.0 | Not detailed | Not specified | 8 cases (14-120 months), 1 case recurred 10 years after surgery, and the rest had no recurrence |
| Oramas[ | 25(13∶12) | 38-69(57) | anterior mediastinum | 2.5-8.0 | Most presented with non-specific symptoms such as cough, chest pain, and dyspnea, and 4 cases were asymptomatic | Multilocular cystic | 19 cases (12-24 months), no recurrence |
| Hulme[ | 5(1∶4) | 58-70(65) | anterior mediastinum | 2.2-6.0 | Incidentally found | 1 solid, 4 cystic and solid | 5 cases (1-96 months), no recurrence |
| Zhao[ | 5(3∶2) | 49-68(64) | anterior mediastinum | 0.5-6.0 | 1 case of thyroid cancer, 1 case of emphysema, 1 case of bullae, 1 case of cough, 1 case asymptomatic | 4 solid, 1 multilocular cystic | 4 cases (9-29 months), no recurrence |
| Jiang[ | 5(3∶2) | 49-64(53) | anterior mediastinum | 3.5-8.2 | 1 case of repeated cough and chest distress, 4 cases asymptomatic | 1 solid, 4 cystic and solid | 5 cases (8-35 months), no recurrence |
| Bakshi[ | 3(2∶1) | 70-76(71) | thymus | 4.5-7.5 | 1 case of chest discomfort, 1 case of intermittent dry cough, 1 case asymptomatic | 2 solid, 1 cystic and solid | 3 cases(19-34 months), no recurrence |
| Yu[ | 8(5∶3) | 36-74(64.5) | anterior mediastinum | 2.1-12.0 | Found during physical examination or when seeking medical attention for other diseases (lung adenocarcinoma, chest discomfort) | 3 solid, 5 with cystic areas (3 multilocular cystic) | 8 cases (4-77 months), no recurrence |
| He[ | 7(4∶3) | 18-75(62) | 6 cases were located in the anterior mediastinum, 1 case was located in the middle mediastinum | 1.2-6.5 | 1 case of right upper eyelid ptosis,6 cases found during physical examination | 3 solid, 1 slightly solid 2 cystic and solid, 1 cystic | 7 cases (10-56 months), no recurrence |
| Liu[ | 4(1∶1) | 40-70(55) | thymus | 4.0-10.0 | 1 case of severe myasthenia gravis, 1 case of anemia, 1 case of cough, 1 found during physical examination | Not specified | 4 cases (4-51 months), 1 case died of other reasons 4 months later, the rest had no recurrence |
| Qin[ | 15(8∶7) | 5-73(61) | mediastinum | 1.4-6.0 | 4 cases of severe myasthenia gravis, 3 cases of chest distress and shortness of breath, 8 cases found during examination | 10 solid, 5 cystic and solid | 15 cases (3-97 months), no recurrence |
| Hsieh[ | 10(3∶7) | 53-80(70) | thymus | 2.0-16.5 | Not detailed | Not specified | 10 cases (3-124 months), no recurrence |
| The group | 5(3∶2) | 55-68(58) | 4 cases were located in the anterior mediastinum, 1 case was located in the superior mediastinum | 1.3-4.5 | Found during physical examination | 3 solid, 2 cystic and solid | 5 cases (7-39 months), no recurrence |
| [1] |
SUSTER S, MORAN C A. Micronodular thymoma with lymphoid B-cell hyperplasia: clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of eighteen cases of a distinctive morphologic variant of thymic epithelial neoplasm[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 1999, 23(8):955-962.
doi: 10.1097/00000478-199908000-00014 pmid: 10435566 |
| [2] |
ISHIKAWA Y, TATEYAMA H, YOSHIDA M,et al. Micronodular thymoma with lymphoid stroma: an immunohistochemical study of the distribution of Langerhans cells and mature dendritic cells in six patients[J]. Histopathology, 2015, 66(2):300-307.
doi: 10.1111/his.12428 pmid: 24702632 |
| [3] | SUSTER S. The WHO 2021 thymoma classification: a work in progress[J]. J Cancer Metastasis Treat, 2022, 8:7. |
| [4] | 倪亚平, 笪倩, 袁菲,等. 混合性A型胸腺瘤与伴有淋巴样间质的微结节型胸腺瘤1例临床病理分析及文献复习[J]. 诊断病理学杂志, 2021, 28(7):557-561. |
| NI Y P, DA Q, YUAN F,et al. Mixed type A thymoma and micronodular thymoma with lymphoid stroma: a clinicopathologic analysis of one case and review of literature[J]. J Diag Pathol, 2021, 28(7):557-561. | |
| [5] | 王立娟, 曹友德, 曾敏, 等. 伴有淋巴样间质的微结节型胸腺瘤临床病理特征及文献复习[J]. 重庆医学, 2019, 48(17):2983-2987. |
| WANG L J, CAO Y D, ZENG M,et al. Clinicopathological features and literature review of micronodular thymoma with lymphoid stroma[J]. Chongqing Med, 2019, 48(17):2983-2987. | |
| [6] | 张冬梅, 魏建国, 方三高, 等. 4例伴淋巴样间质的微结节性胸腺瘤的临床病理分析[J]. 诊断病理学杂志, 2019, 26(9):562-565. |
| ZHANG D M, WEI J G, FANG S G,et al. Micronodular thymoma with lymphoid stroma: a clinicopathological study of four cases[J]. J Diag Pathol, 2019, 26(9):562-565. | |
| [7] | YAGI H, NAKAGURO M, ITO M,et al. Difference in the distribution of tumor infiltrating CD8+ T cells and FOXP3+ T cells between micronodular thymoma with lym-phoid stroma and micronodular thymic carcinoma with lymphoid stroma[J]. Pathol Int, 2021, 71(7):453-462. |
| [8] |
ORAMAS D M, MORAN C A. Micronodular thymomas with prominent cystic changes: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of 25 cases[J]. Int J Surg Pathol, 2021, 29(4):352-357.
doi: 10.1177/1066896920963803 pmid: 33026263 |
| [9] | HULME K R, MAHAR A, CAO C,et al. Micronodular thymoma with lymphoid stroma: a clinicopathological study of five cases[J]. Pathology, 2021, 53(7):930-933. |
| [10] | 赵丽娜, 袁静萍, 黄亚冰, 等. 伴淋巴间质的微结节型胸腺肿瘤5例临床病理特征[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志, 2021, 37(7):855-858. |
| ZHAO L N, YUAN J P, HUANG Y B,et al. Micronodular thymoma with lymphoid stroma: a clinicopathologic features of five cases[J]. J Clin Exp Pathol, 2021, 37(7):855-858. | |
| [11] | 江美辰, 郑巧灵, 杨映红. 伴淋巴样间质的微结节型胸腺瘤5例临床病理分析[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志, 2021, 37(10):1234-1236. |
| JIANG M C, ZHENG Q L, YANG Y H. Micronodular thymoma with lymphoid stroma: a clinicopathologic analysis of five cases[J]. J Clin Exp Pathol, 2021, 37(10):1234-1236. | |
| [12] | BAKSHI N, DHAWAN S, RAO S,et al. Micronodular thymoma with lymphoid stroma: a trio of cases, with diverse-associated histological features[J]. Int J Surg Pathol, 2021, 29(6):693-697. |
| [13] | 余昶, 孙文勇. 伴淋巴样间质的微结节型胸腺瘤8例临床病理分析[J]. 肿瘤学杂志, 2022, 28(7):602-606. |
| YU C, SUN W Y. Micronodular thymoma with lymphoid stroma: a clinicopathologic analysis of eight cases[J]. J Chin Oncol, 2022, 28(7):602-606. | |
| [14] | 何晓顺, 詹升华, 黄山, 等. 伴淋巴样间质的微结节型胸腺瘤7例临床病理分析[J]. 临床肿瘤学杂志, 2022, 27(7):638-642. |
| HE X S, ZHAN S H, HUANG S,et al. Micronodular thymoma with lymphoid stroma: a clinicopathologic analysis of seven cases [J]. Chin Clin Oncol, 2022, 27(7):638-642. | |
| [15] | LIU P P, SU Y C, NIU Y,et al. Comparative clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of micronodular thymoma and micronodular thymic carcinoma with lymphoid stroma[J]. J Clin Pathol, 2021, 75(10):702-705. |
| [16] | 秦积龙, 何萍, 范蕾, 等. 伴淋巴样间质的微结节型胸腺肿瘤17例临床病理与形态学分化谱系分析[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志, 2023, 1(1):23-28. |
| QIN J L, HE P, FAN L,et al. Spectrum of morphological differentiation of micronodular thymic neoplasms with lymphoid stroma: a clinical and pathological analysis of seventeen cases[J]. J Clin Exp Pathol, 2023, 1(1):23-28. | |
| [17] | HSIEH M S, KAO H L, HUANG W C,et al. L424H mutation in GTF2I in micronodular thymomas with lymphoid stroma: evidence supporting close relationship with type A and AB thymomas[J]. Mod Pathol, 2023, 36(2):100008. |
| [18] | YOON J C, HAN J, KIM J,et al. A rare case of mixed type A thymoma and micronodular thymoma with lymphoid stroma[J]. Pathol Transl Med, 2015, 49(1):75-77. |
| [19] |
RADOVICH M, PICKERING C R, FELAU I,et al. The integrated genomic landscape of thymic epithelial tumors[J]. Cancer Cell, 2018, 33(2):244-258.
doi: S1535-6108(18)30003-5 pmid: 29438696 |
| [20] | 陈骏, 陈亭亭, 吴鸿雁, 等. 伴淋巴样间质的微结节型胸腺瘤2例并文献复习[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志, 2014, 30 (7):766-770. |
| CHEN J, CHEN T T, WU H Y,et al. Micronodular thymoma with lymphoid stroma:two cases of report and lite-rature review[J]. J Clin Exp Pathol, 2014, 30(7):766-770. | |
| [21] |
STRÖBEL P, MARINO M, FEUCHTENBERGER M,et al. Micronodular thymoma: an epithelial tumour with abnormal chemokine expression setting the stage for lymphoma development[J]. J Pathol, 2005, 207 (1):72-82.
pmid: 15965907 |
| [22] | WELLS K, LAMRCA A, PAPAXOINIS G,et al. Unique correlation between GTF2I mutation and spindle cell morphology in thymomas (type A and AB thymomas)[J]. J Clin Pathol, 2023, 76(7):463-466. |
| [1] | GU Xiaohong, SUN Aimin, WANG Qian, ZHU Ming, ZHONG Yumin. The three-dimensional balanced steady state free precession magnetic resonance imaging sequence in diagnosis of anomalous origin of the coronary artery from the pulmonary artery in children [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2020, 19(02): 145-150. |
| [2] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2015, 14(01): 58-61. |
| [3] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2010, 9(01): 58-62. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||