

Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice ›› 2025, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (01): 27-34.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2025.01.005
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Ke, ZHANG Weiyi, SUN Haitian, CAO Mingfeng, ZHANG Xinhuan( )
)
Received:2024-11-12
Accepted:2025-02-08
Online:2025-02-25
Published:2025-02-05
Contact:
ZHANG Xinhuan
E-mail:kathy0418@163.com
CLC Number:
ZHANG Ke, ZHANG Weiyi, SUN Haitian, CAO Mingfeng, ZHANG Xinhuan. Anoikis-related gene PDK4 and pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A bioinformatics-based study[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2025, 24(01): 27-34.
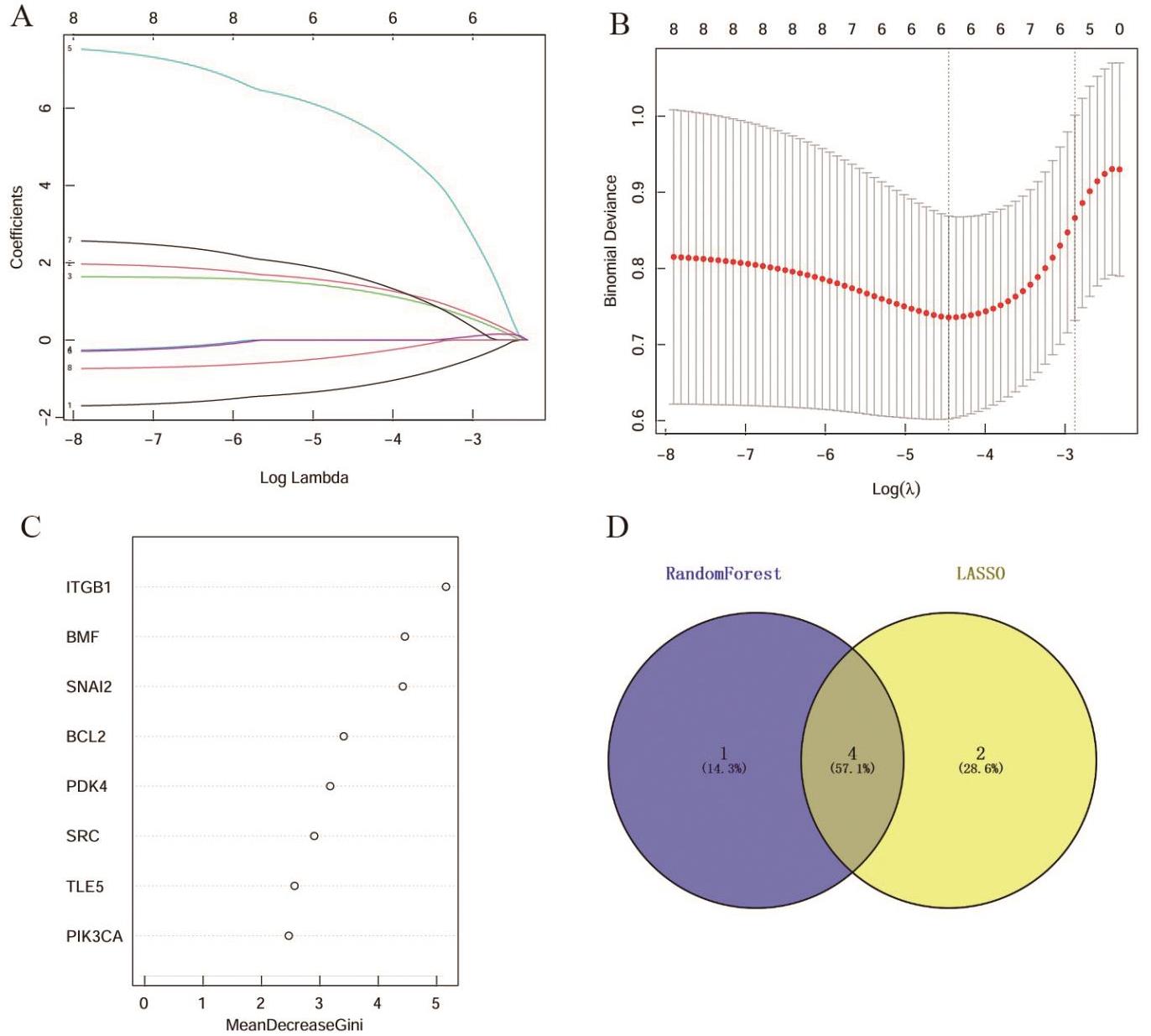
Figure 2
Machine learning algorithm for screening key genesA: LASSO regression coefficient plot with each curve representing a gene; B: LASSO cross-validation curve with 6 genes most consistent with the diagnosis; C: Mean Decrease Gini of the RF model for the genes; D: Wayne's plots of the intersections of the characterized genes obtained from LASSO and RF.
| [1] |
ZHENG Y, LEY S H, HU F B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2018, 14(2):88-98.
doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.151 pmid: 29219149 |
| [2] |
FORBES J M, COOPER M E. Mechanisms of diabetic complications[J]. Physiol Rev, 2013, 93(1):137-188.
doi: 10.1152/physrev.00045.2011 pmid: 23303908 |
| [3] | XOURAFA G, KORBMACHER M, RODEN M. Interor-gan crosstalk during development and progression of type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Na Rev Endocrinol, 2023, 20(1):27-49. |
| [4] | 李延兵. 2024年美国糖尿病学会《糖尿病诊疗标准》解读——糖尿病诊断和分型[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2024, 23(5):467-473. |
| LI Y B. Interpretation of 2024 American Diabetes Association’s Standards of Care in Diabetes — diabetes diagnosis and classification[J]. J Diagnost Concept Pract, 2024, 23(5):467-473. | |
| [5] | SU J, LUO Y, HU S,et al. Advances in Research on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Targets and Therapeutic Agents[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(17):13381. |
| [6] | ZHANG J-S, PAN R-S, LI G-L,et al. Comprehensive analysis of anoikis-related genes in diagnosis osteoarthritis: based on machine learning and single-cell RNA sequencing data[J]. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology, 2024, 52(1):156-174. |
| [7] | MEI J, JIANG X Y, TIAN H X,et al. Anoikis in cell fate, physiopathology, and therapeutic interventions[J]. MedComm, 2024, 5(10):e718. |
| [8] |
DOBLER D, AHMED N, SONG L,et al. Increased dicarbonyl metabolism in endothelial cells in hyperglycemia induces anoikis and impairs angiogenesis by RGD and GFOGER motif modification[J]. Diabetes, 2006, 55(7):1961-1969.
doi: 10.2337/db05-1634 pmid: 16804064 |
| [9] |
CHAQOUR B, SCHUTZE N, CHOUDHRY A,et al. Cysteine-rich protein 61 and connective tissue growth factor induce deadhesion and anoikis of retinal pericytes[J]. Endocrinology, 2008, 149(4):1666-1677.
doi: 10.1210/en.2007-1415 pmid: 18187544 |
| [10] | SU N, WANG J, ZHANG H,et al. Identification and clinical validation of the role of anoikis-related genes in diabetic foot [J]. Int Wound J, 2024, 21(3):e14771. |
| [11] | LIN J, LIN Y, LI X,et al. Uncovering the role of anoikis-related genes in modulating immune infiltration and pathogenesis of diabetic kidney disease[J]. J Inflam Res, 2024, 17:4975-4991. |
| [12] | 付林, 杨杨, 张同存. 2型糖尿病免疫发病机制研究进展[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志, 2021, 29(5):393-396. |
| FU L, YANG Y, ZHANG T C. Research progress on the immune pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Chin J Diabetes, 2021, 29(5):393-396. | |
| [13] | RITCHIE M E, PHIPSON B, WU D,et al. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2015, 43(7):e47. |
| [14] |
FRIEDMAN J, HASTIE T, TIBSHIRANI R. Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent[J]. J Stat Softw, 2010, 33(1):1-22.
pmid: 20808728 |
| [15] | WARDE-FARLEY D, DONALDSON S L, COMES O,et al. The GeneMANIA prediction server: biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2010, 38(Web Server issue):W214-220. |
| [16] | TANG D, CHEN M, HUANG X,et al. SRplot: a free online platform for data visualization and graphing[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18(11):e0294236. |
| [17] | ZENG D, YE Z, SHEN R,et al. IOBR: multi-omics immuno-oncology biological research to decode tumor microenvironment and signatures[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12:687975. |
| [18] | HAN Y H, WANG Y, LEE S J,et al. Regulation of anoikis by extrinsic death receptor pathways[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2023, 21(1):227. |
| [19] | JIANG A, SONG A, ZHANG C. Modes of podocyte death in diabetic kidney disease: an update[J]. J Nephrol, 2022, 35(6):1571-1584. |
| [20] |
DOU X, FU Q, LONG Q,et al. PDK4-dependent hypercatabolism and lactate production of senescent cells promotes cancer malignancy[J]. Nature Metabolism, 2023, 5(11):1887-1910.
doi: 10.1038/s42255-023-00912-w pmid: 37903887 |
| [21] | TIAN S, YANG X, LIN Y,et al. PDK4-mediated Nrf2 inactivation contributes to oxidative stress and diabetic kidney injury[J]. Cell Signal, 2024:121. |
| [22] |
THOUDAM T, HA C M, LEEM J,et al. PDK4 augments ER-mitochondria contact to dampen skeletal muscle insulin signaling during obesity[J]. Diabetes, 2019, 68(3):571-586.
doi: 10.2337/db18-0363 pmid: 30523025 |
| [23] | WANG S, LU Y, CHI T,et al. Identification of ferroptosis-related genes in type 2 diabetes mellitus based on machine learning[J]. Immun Inflamm Dis, 2023, 11(10):e1036. |
| [24] |
CHYLIKOVA J, DVORACKOVA J, CIZKOVA K,et al. Macrophages of the subcutaneous and omental fatty tissue in obese patients: Immunohistochemical phenotyping of M2 subtypes in relation to type 2 diabetes[J]. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub, 2020, 164(2):133-137.
doi: 10.5507/bp.2019.011 pmid: 30967686 |
| [25] |
NAM H W, CHO Y J, LIM J A,et al. Functional status of immune cells in patients with long-lasting type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2018, 194(1):125-136.
doi: 10.1111/cei.13187 pmid: 30022471 |
| [26] |
WINER D A, WINER S, CHNG M H,et al. B Lymphocytes in obesity-related adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2014, 71(6):1033-1043.
doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1486-y pmid: 24127133 |
| [27] |
BUTCHER M J, HALLINGER D, GARCIA E,et al. Association of proinflammatory cytokines and islet resident leucocytes with islet dysfunction in type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetologia, 2014, 57(3):491-501.
doi: 10.1007/s00125-013-3116-5 pmid: 24429578 |
| [28] | EGUCHI K, MANABE I. Macrophages and islet inflammation in type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2013, 15():152-158. |
| [1] | PEI Zhou, LUO Feihong. Progress in diagnosis and treatment of pediatric diabetes in China [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(05): 461-466. |
| [2] | MIAO Jie, WANG Wei, ZHAO Yajie, ZHANG Fengru, SHEN Linhui. The correlation between free T3 level and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in elderly male patients with T2DM [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(02): 155-161. |
| [3] | OU Dan, CAI Gang, CHEN Jiayi. Bioinformatics analysis for expression of RAD51AP1 in triple negative breast cancer with brain metastasis [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(02): 146-154. |
| [4] | WANG Tao, DENG Yu, ZHAO Ping, YÜ Baohua, WANG Xiang, WANG Chaofu. Identification of genes associated with distinguished Gleason patterns of prostate cancer by analyzing TCGA database [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2018, 17(06): 694-700. |
| [5] | TAN Jiaorong, TIAN Dongmei, YANG Xin, ZHANG Lijuan, WANG Fang, SU Yuxia. Study on relationship between vitamin D deficiency and incidence of diabetic nephropathy: A prospective follow-up study of three years [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2018, 17(02): 176-180. |
| [6] | JI Ri, ZHOU Chun, ZHAN Weiwei, YANG Zhifang, GUO Wenjia. Evaluation of foot microcirculation by contrast-enhanced ultrasound in elderly male type 2 DM and IGT patients [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2017, 16(03): 287-291. |
| [7] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2014, 13(03): 321-324. |
| [8] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2014, 13(03): 276-279. |
| [9] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2011, 10(05): 479-481. |
| [10] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2009, 8(06): 647-649. |
| [11] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2009, 8(03): 273-275. |
| [12] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2009, 8(03): 269-272. |
| [13] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2007, 6(02): 111-114. |
| [14] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2007, 6(02): 115-118. |
| [15] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2007, 6(02): 123-126. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||