

Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice ›› 2025, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (03): 268-278.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2025.03.005
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHI Manman1, MA Yuhua1, ZHENG Jinxin2,3, KE Yanrong1, WANG Yuxin1, LIU Jian2( ), WANG Weiming2(
), WANG Weiming2( )
)
Received:2025-01-28
Accepted:2025-06-09
Online:2025-06-25
Published:2025-06-25
Contact:
LIU Jian, WANG Weiming
E-mail:wwm11120@rjh.com.cn;lewis_963@163.com
CLC Number:
SHI Manman, MA Yuhua, ZHENG Jinxin, KE Yanrong, WANG Yuxin, LIU Jian, WANG Weiming. Global and Chinese burden of chronic kidney disease due to type 2 diabetes and associated risk factors from 1990 to 2021[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2025, 24(03): 268-278.
Table 1
Incidence,prevalence,mortality,and disability-adjusted life years of chronic kidney disease due to type 2 diabetes globally in 1990,2019,and 2021 [n(95%UI)]
| Items | Incidence | Prevalence | Mortality | DALYs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | ||||
| Number(×1 000) | 2 012.024 (1 857.800-2 154.288) | 107 559.955 (99 170.797-115 994.732) | 477.273 (401.541-565.951) | 11 278.935 (9 682.785-13 103.871) |
| ASRs(/100 000) | 23.074 (21.403-24.724) | 1 259.627 (1 161.985-1 359.917) | 5.723 (4.826-6.792) | 131.082 (112.752-152.492) |
| 2019 | ||||
| Number(×1 000) | 1 898.285 (1 756.086-2 033.895) | 103 692.703 (95 804.213-111 877.535) | 452.842 (384.289-535.796) | 10 649.449 (9 179.491-12 417.895) |
| ASRs(/100 000) | 22.903 (21.208-24.569) | 1 261.314 (1 164.900-1 360.483) | 5.731 (4.833-6.798) | 130.187 (112.440-151.504) |
| 1990 | ||||
| Number(×1 000) | 753.106 (680.930-826.928) | 58 105.268 (53 056.992-63 286.818) | 147.970 (124.179-176.413) | 4 122.919 (3 498.980-4 818.958) |
| ASRs(/100 000) | 19.073 (17.285-20.835) | 1 327.225 (1 223.256-1 439.418) | 4.154 (3.504-4.936) | 105.710 (90.677-122.672) |
| Percent change (2021 vs 2019) | ||||
| Number | 6.0% (5.4%-6.6%) | 3.7% (3.4%-4.1%) | 5.4% (0.2%-10.9%) | 5.9% (1.3%-10.9%) |
| ASRs | 0.7% (0.2%-1.3%) | -0.1% (-0.5%-0.2%) | -0.1 (-4.9%-5.0%) | 0.7% (-3.7%-5.4%) |
| Percent change (2021 vs 1990) | ||||
| Number | 167.2% (153.5%-182.6%) | 85.1% (78.1%-91.4%) | 222.5% (177.4%-253.8%) | 173.6% (140.5%-194.3%) |
| ASRs | 21.0% (15.0%-27.5%) | -5.1% (-7.5%-3.0%) | 37.8% (19.2%-49.6%) | 24.0% (9.3%-33.0%) |
Table 2
Incidence,prevalence,mortality,and disability-adjusted life years of chronic kidney disease due to type 2 diabetes in China in 1990,2019,and 2021
| Items | Incidence | Prevalence | Mortality | DALYs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | ||||
| Number(×1 000) | 354.157 (321.265-382.784) | 20 911.520 (19 184.463-2 2605.470) | 107.652 (84.626-134.047) | 2 537.070 (2 044.338-3 072.897) |
| ASRs(/100 000) | 16.287 (14.921-17.529) | 1 053.915 (971.106-1 139.636) | 5.637 (4.462-6.998) | 122.149 (99.621-146.989) |
| 2019 | ||||
| Number(×1 000) | 324.557 (293.012-350.843) | 20 100.997 (18 473.868-21 752.987) | 100.313 (81.544-119.984) | 2 376.638 (1 935.101-2 779.215) |
| ASRs(/100 000) | 15.939 (14.489-17.164) | 1 051.714 (969.074-1 137.546) | 5.692 (4.573-6.835) | 122.509 (100.078-143.707) |
| 1990 | ||||
| Number(×1 000) | 127.561 (112.718-142.654) | 11 890.522 (10 790.476-1 3078.708) | 43.537 (35.988-53.065) | 1 231.518 (1 022.061-1 492.725) |
| ASRs(/100 000) | 15.109 (13.452-16.795) | 1 214.763 (1 109.345-1 320.704) | 6.825 (5.739-8.340) | 155.940 (131.157-188.264) |
| Percent change(2021 vs 2019) | ||||
| Number | 9.1% (6.9%-1.0%) | 4.0% (3.3%-4.8%) | 7.3% (-11.4%-31.0%) | 6.8% (-10.0%-26.2%) |
| ASRs | 2.2% (0.5%-3.9%) | 0.2% (-0.4%-0.7%) | -1.0% (-17.5%-19.6%) | -0.3% (-15.8%-17.7%) |
| Percent change(2021 vs 1990) | ||||
| Number | 177.6% (154.8%-205.5%) | 75.9% (66.4%-85.1%) | 147.3% (89.3%-209.3%) | 106.0% (65.6%-148.7%) |
| ASRs | 7.8% (-0.1%-17.8%) | -13.2%(-15.9%-10.9%) | -17.4%(-37.4%-1.9%) | -21.7% (-37.0%-5.7%) |
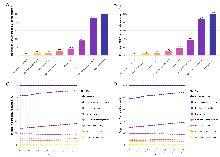
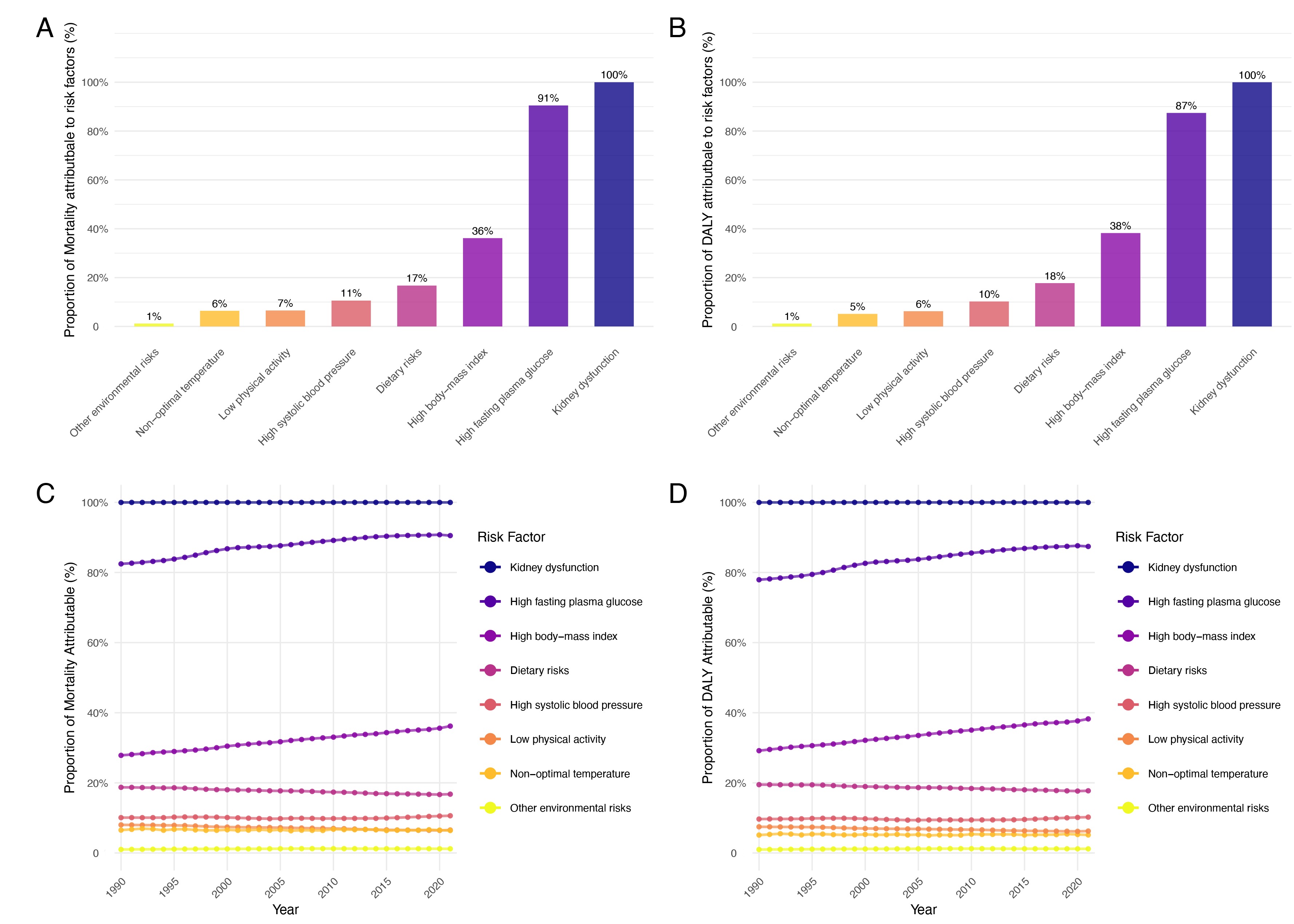
Figure 6
Contributions of major risk factors to age-standardized mortality (A) and DALYs (B) of chronic kidney disease due to type 2 diabetes in 2021, and temporal changes in impacts of risk factors on age-standardized mortality (C) and DALYs (D), 1990-2021 Data source: Global Burden of Disease Study 2021 (GBD 2021).
| [1] | JHA R, LOPEZ-TREVINO S, KANKANAMALAGE H R, et al. Diabetes and renal complications: an overview on pathophysiology, biomarkers and therapeutic interventions[J]. Biomedicines, 2024, 12(5):1098. |
| [2] | OOI Y G, SARVANANDAN T, HEE N K Y, et al. Risk prediction and management of chronic kidney disease in people living with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Diabetes Metab J, 2024, 48(2):196-207. |
| [3] |
VAN RAALTE D H, BJORNSTAD P, CHERNEY D Z I, et al. Combination therapy for kidney disease in people with diabetes mellitus[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2024, 20(7):433-446.
doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00827-z pmid: 38570632 |
| [4] | DING X, LI X, YE Y, et al. Epidemiological patterns of chronic kidney disease attributed to type 2 diabetes from 1990-2019[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2024,15:1383777. |
| [5] | Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. Global health data exchange[EB/OL]. 2021. http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool. |
| [6] | GBD 2021 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021[J]. Lancet,2024, 403(10440):2133-2161. |
| [7] |
GBD 2021 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021[J]. Lancet, 2024, 403(10440):2100-2132.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00367-2 pmid: 38582094 |
| [8] | Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. Global Burden of Disease Study 2021 (GBD 2021) data resources[EB/OL]. 2024. https://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-2021. |
| [9] | Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease[J]. Kidney Int, 2024, 105(4S):S117-S314. |
| [10] |
GBD 2021 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden and strength of evidence for 88 risk factors in 204 countries and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021[J]. Lancet, 2024, 403(10440):2162-2203.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00933-4 pmid: 38762324 |
| [11] | SOBAMOWO H, PRABHAKAR S S. The kidney in aging: physiological changes and pathological implications[J]. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci, 2017,146:303-340. |
| [12] | LYTVYN Y, BJORNSTAD P, VAN RAALTE D H, et al. The new biology of diabetic kidney disease-mechanisms and therapeutic implications[J]. Endocr Rev, 2020, 41(2):202-231. |
| [13] | CLOTET-FREIXAS S, ZASLAVER O, KOTLYAR M, et al. Sex differences in kidney metabolism may reflect sex-dependent outcomes in human diabetic kidney disease[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2024, 16(737):eabm2090. |
| [14] | PIANI F, MELENA I, TOMMERDAHL K L, et al. Sex-related differences in diabetic kidney disease: A review on the mechanisms and potential therapeutic implications[J]. J Diabetes Complications, 2021, 35(4):107841. |
| [15] | LOEFFLER I, ZILLER N. Sex-related aspects in diabetic kidney disease-an update[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 12(8):2834. |
| [16] | BOWE B, XIE Y, LI T, et al. Changes in the US burden of chronic kidney disease from 2002 to 2016: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2018, 1(7):e184412. |
| [17] | SARAN R, ROBINSON B, ABBOTT K C, et al. US Renal Data System 2016 annual data report: epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2017, 69(3Suppl 1):A7-A8. |
| [18] | SINDHU D, SHARMA G S, KUMBALA D. Management of diabetic kidney disease: where do we stand? A narrative review[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2023, 102(13):e33366. |
| [19] |
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in underweight and obesity from 1990 to 2022: a pooled analysis of 3663 population-representative studies with 222 million children, adolescents, and adults[J]. Lancet, 2024, 403(10431):1027-1050.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)02750-2 pmid: 38432237 |
| [20] | ZU C, LIU M, SU X, et al. Association of body weight time in target range with the risk of kidney outcomes in patients with overweight/obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Diabetes Care, 2024, 47(3):371-378. |
| [21] | RUZE R, LIU T, ZOU X, et al. Obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: connections in epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatments[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2023,14:1161521. |
| [22] | ROSENFELD R M, KELLY J H, AGARWAL M, et al. Dietary interventions to treat type 2 diabetes in adults with a goal of remission: An expert consensus statement from the American College of Lifestyle Medicine[J]. Am J Lifestyle Med, 2022, 16(3):342-362. |
| [23] | GALLARDO-GÓMEZ D, SALAZAR-MARTÍNEZ E, ALFONSO-ROSA R M, et al. Optimal dose and type of physical activity to improve glycemic control in people diagnosed with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Diabetes Care, 2024, 47(2):295-303. |
| [24] | GBD 2017 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Di-sease Study 2017[J]. Lancet, 2018, 392(10159):1736-1788. |
| [25] |
NCD Countdown 2030 collaborators. NCD Countdown 2030: worldwide trends in non-communicable disease mortality and progress towards Sustainable Development Goal target 3.4[J]. Lancet, 2018, 392(10152):1072-1088.
doi: S0140-6736(18)31992-5 pmid: 30264707 |
| [26] |
NUGENT R, BERTRAM M Y, JAN S, et al. Investing in non-communicable disease prevention and management to advance the Sustainable Development Goals[J]. Lancet, 2018, 391(10134):2029-2035.
doi: S0140-6736(18)30667-6 pmid: 29627167 |
| [1] | ZHANG Ke, ZHANG Weiyi, SUN Haitian, CAO Mingfeng, ZHANG Xinhuan. Anoikis-related gene PDK4 and pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A bioinformatics-based study [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2025, 24(01): 27-34. |
| [2] | SHEN Xiaoyu, SHA Sha, YIN Lei, ZHOU Wei, MAO Youying, WANG Zhangjuan, SUN Yan, WU Yan. Clinical study of ambulatory blood pressure changes in children with stage Ⅰ-Ⅱ chronic kidney disease combined with proteinuria [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(05): 531-536. |
| [3] | PEI Zhou, LUO Feihong. Progress in diagnosis and treatment of pediatric diabetes in China [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(05): 461-466. |
| [4] | FAN Bonan, LI Yan. Trends in global major disease burden and health conditions—interpretation of the Global Burden of Disease Study 1990-2021 [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(05): 474-483. |
| [5] | MIAO Jie, WANG Wei, ZHAO Yajie, ZHANG Fengru, SHEN Linhui. The correlation between free T3 level and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in elderly male patients with T2DM [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(02): 155-161. |
| [6] | TANG Chunhua, GUO Lu, LI Qiong, ZHANG Lili. Interpretation on the report of global stroke data 2022 [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(03): 238-246. |
| [7] | QIAN Ying, MA Xiaobo, GAO Chenni, ZHANG Chunli, MA Jun, ZHANG Wen, CHEN Xiaonong. Association between hyperuricemia and hypertension in chronic kidney disease [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(02): 160-165. |
| [8] | QIAN Ying, MA Xiaobo, GAO Chenni, CHEN Zijin, MA Jun, YU Haijin, ZHANG Wen, CHEN Xiaonong. The diagnostic efficiency and application value of fracture risk assessment tools in maintenance hemodialysis patients [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(01): 50-57. |
| [9] | HUANG Juan, ZHU Xiaolei, LI Xiao, CHEN Kemin, YAN Fuhua, XU Xueqin. Study on blood oxygen level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of early renal hypoxia in chronic kidney disease [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2022, 21(03): 385-389. |
| [10] | WANG Yuanyuan, FAN Qiuling. Clinical value of serum procalcitonin in patients of chronic kidney disease with bacterial infection [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2019, 18(03): 353-359. |
| [11] | TAN Jiaorong, TIAN Dongmei, YANG Xin, ZHANG Lijuan, WANG Fang, SU Yuxia. Study on relationship between vitamin D deficiency and incidence of diabetic nephropathy: A prospective follow-up study of three years [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2018, 17(02): 176-180. |
| [12] | JI Ri, ZHOU Chun, ZHAN Weiwei, YANG Zhifang, GUO Wenjia. Evaluation of foot microcirculation by contrast-enhanced ultrasound in elderly male type 2 DM and IGT patients [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2017, 16(03): 287-291. |
| [13] | LIN Anhua, WANG Chenxiu, HUO Yanan, CHEN Zhixiong, SONG Wei, LIU Jingdong, HU Yaqin. Correlation of blood pressure level with development and progression of chronic kidney disease in Chinese community diabetes patients [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2017, 16(02): 178-182. |
| [14] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2014, 13(03): 321-324. |
| [15] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2014, 13(03): 276-279. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||