

Journal of Surgery Concepts & Practice ›› 2023, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (04): 371-377.doi: 10.16139/j.1007-9610.2023.04.014
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHU Qiaoli1, MIAO Yiming2*, CHEN Xiaosong2( )
)
Received:2022-08-24
Online:2023-07-25
Published:2023-10-24
CLC Number:
ZHU Qiaoli, MIAO Yiming, CHEN Xiaosong. Prognostic analysis of breast-conserving surgery or mastectomy in patients with stage Ⅰ-Ⅲ triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Journal of Surgery Concepts & Practice, 2023, 28(04): 371-377.
Tab 1
Clinicopathological characteristics for stage Ⅰ-Ⅲ TNBC patients [$\bar{x}±s$/n(%)]
| Factors | BCS(n=311) | M(n=533) | F/x2 value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age(years) | 53.68±13.05 | 57.23±11.85 | 16.3 | <0.001 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 23.10±3.01 | 23.01±2.79 | 0.2 | 0.671 |
| Menopause status[n(%)] | ||||
| Pre-menopause | 128 (41.16) | 167 (31.33) | 8.3 | 0.004 |
| Post-menopause | 183 (58.84) | 366 (68.67) | ||
| pT[n(%)] | ||||
| T1 | 192 (61.74) | 226 (42.40) | 29.4 | <0.001 |
| T2-3 | 119 (38.26) | 307 (57.60) | ||
| pN[n(%)] | ||||
| Negative | 250 (80.39) | 358 (67.17) | 17.0 | <0.001 |
| Positive | 61 (19.61) | 175 (32.83) | ||
| HER2[n(%)] | ||||
| HER2-0 | 135 (43.41) | 182 (34.15) | 7.2 | 0.007 |
| HER2 low | 176 (56.59) | 351 (65.85) | ||
| Ki-67[n(%)] | ||||
| ≤14% | 42 (13.50) | 90 (16.89) | 1.7 | 0.192 |
| >14% | 269 (86.50) | 443 (83.11) | ||
| Pathologic typing[n(%)] | ||||
| DCIS | 5 (1.61) | 11 (2.07) | ||
| IDC | 290 (93.25) | 490 (91.93) | 0.5 | 0.776 |
| Others[n(%)] | 16 (5.14) | 32 (6.00) | ||
| Grading | ||||
| Ⅰ-Ⅱ | 59 (18.97) | 129 (24.20) | ||
| Ⅲ | 200 (64.31) | 322 (60.41) | 3.1 | 0.211 |
| Unknown | 52 (16.72) | 82 (15.39) | ||
| Chemotherapy[n(%)] | ||||
| No | 41 (13.18) | 63 (11.82) | 0.3 | 0.561 |
| Yes | 270 (86.82) | 470 (88.18) |
Tab 2
Logistic regression analysis for mastectomy in stage Ⅰ-Ⅲ TNBC patients
| Factors | OR | 95%CI | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age(years) ≥60 vs. <60 | 1.02 | 1.01-1.04 | 0.013 |
| Menopause status post-menopause vs. pre-menopause | 0.99 | 0.63-1.57 | 0.967 |
| pT T2-3 vs. T1 | 2.17 | 1.61-2.91 | <0.001 |
| pN N positive vs. N negative | 1.84 | 1.30-2.59 | <0.001 |
| HER2 HER2 low vs. HER2-0 | 1.42 | 1.05-1.92 | 0.023 |
Tab 3
Univariate COX regression analysis for OS and DFS in stage Ⅰ-Ⅲ TNBC patients
| Factors | OS | DFS |
|---|---|---|
| P value | P value | |
| Age(years) ≥60 vs. <60 | 0.07 | 0.158 |
| Menopause status post-menopause vs. pre-menopause | 0.09 | 0.061 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 0.773 | 0.605 |
| ≥24 vs. ≥18.5,<24 | 0.473 | 0.698 |
| <18.5 vs. ≥18.5,<24 | 0.967 | 0.375 |
| Pathologic typing | 0.589 | 0.507 |
| IDC vs. DCIS | 0.78 | 0.725 |
| Others vs. DCIS | 0.723 | 0.333 |
| pT T2-3 vs. T1 | 0.001 | <0.001 |
| pN N positive vs. N negative | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Grading | 0.291 | 0.733 |
| Ⅲ vs. Ⅰ-Ⅱ | 0.981 | 0.566 |
| Unknown vs. Ⅰ-Ⅱ | 0.156 | 0.897 |
| HER2 HER2 low vs. HER2-0 | 0.362 | 0.749 |
| Ki-67 >14% vs. ≤14% | 0.119 | 0.045 |
| Chemotherapy Yes vs. No | 0.112 | 0.049 |
| Surgical approach M vs. BCS | 0.002 | 0.005 |
Tab 4
Multivariate COX regression analysis for OS and DFS in stage Ⅰ-Ⅲ TNBC patients
| Factors | OS | DFS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | P value | HR | 95%CI | P value | ||
| Age(years) ≥60 vs. <60 | 1.37 | 0.64-2.91 | 0.419 | / | / | / | |
| Menopause status Post-menopause vs. pre-menopause | 1.23 | 0.53-2.84 | 0.626 | 1.33 | 0.9-1.97 | 0.155 | |
| Surgical approach M vs. BCS | 2.02 | 1.04-3.91 | 0.038 | 1.42 | 0.94-2.15 | 0.100 | |
| pT T2-3 vs. T1 | 2.02 | 1.17-3.48 | 0.011 | 1.82 | 1.25-2.65 | 0.002 | |
| Chemotherapy Yes vs. No | / | / | / | 0.58 | 0.35-0.94 | 0.026 | |
| pN N Positive vs. N Negative | 3.22 | 1.96-5.30 | <0.001 | 2.12 | 1.48-3.05 | 0.001 | |
| Ki-67 >14% vs. ≤14% | / | / | / | 0.67 | 0.44-1.04 | 0.076 | |
Tab 5
Clinical-pathological characteristics for stage Ⅰ-Ⅲ TNBC patients underwent BCS or M after PSM [$\bar{x}±s$/n(%)]
| Factors | BCS (n=257) | M (n=257) | F/x2 value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age(years) | 54.79±12.76) | 56.02±11.67) | 1.3 | 0.253 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 23.11±3.00) | 23.14±2.82) | 0.0 | 0.912 |
| Menopause status[n(%)] | ||||
| Pre-menopause | 100 (38.91) | 87 (33.85) | 1.4 | 0.233 |
| Post-menopause | 157 (61.09) | 170 (66.15) | ||
| pT[n(%)] | ||||
| T1 | 148 (57.59) | 145 (56.42) | 0.7 | 0.789 |
| T2-3 | 109 (42.41) | 112 (43.58) | ||
| pN[n(%)] | ||||
| Negative | 202 (78.60) | 208 (80.93) | 0.4 | 0.51 |
| Positive | 55 (21.40) | 49 (19.07) | ||
| HER2[n(%)] | ||||
| HER2 0 | 103 (40.08) | 107 (41.63) | 0.1 | 0.72 |
| HER2 low | 154 (59.92) | 150 (58.37) | ||
| Ki-67[n(%)] | ||||
| ≤14% | 34 (13.23) | 42 (16.34) | 1.0 | 0.32 |
| >14% | 223 (86.77) | 215 (83.66) | ||
| Pathologic typing[n(%)] | ||||
| DCIS | 5 (1.95) | 6 (2.34) | 0.3 | 0.854 |
| IDC | 242 (94.16) | 243 (94.55) | ||
| Others | 10 (3.89) | 8 (3.11) | ||
| Grading[n(%)] | ||||
| Ⅰ-Ⅱ | 52 (20.23) | 47 (18.29) | 1.3 | 0.528 |
| Ⅲ | 168 (65.37) | 164 (63.81) | ||
| Unknown | 37 (14.40) | 46 (17.90) | ||
| Chemotherapy[n(%)] | ||||
| No | 30 (11.67) | 39 (15.18) | 1.4 | 0.244 |
| Yes | 227 (88.33%) | 218 (84.82%) |
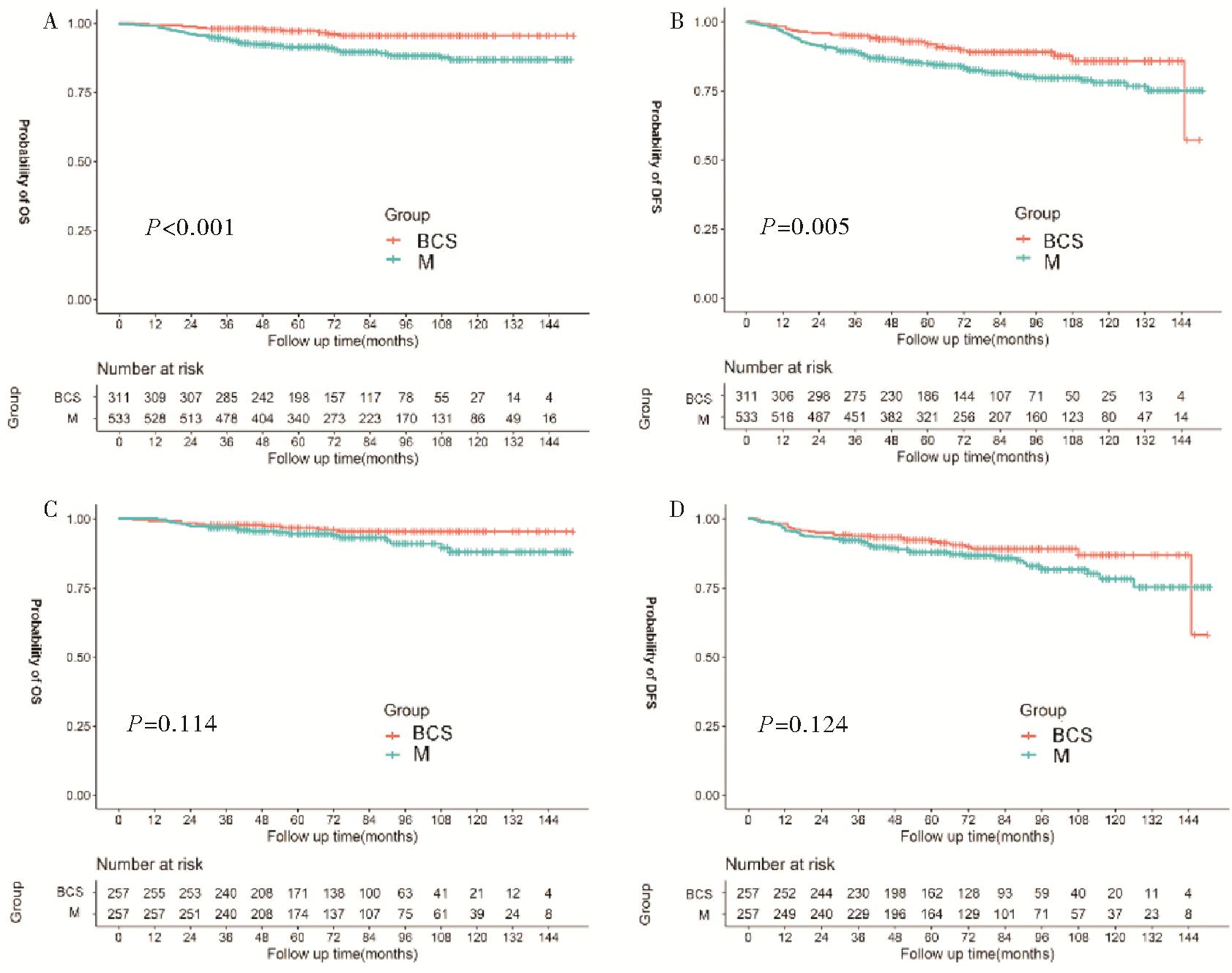
Fig1
The relationship between different surgical approach and survival outcome in stage Ⅰ-Ⅲ TNBC patients before and after PSM Kaplan-Meier survival analysis for early stage TNBC patients underwent BCS or M before and after PSM A: OS before PSM; B: DFS before PSM; C: OS after PSM; D: DFS after PSM.
| [1] |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3):209-249.
doi: 10.3322/caac.v71.3 URL |
| [2] | DASS S A, TAN K L, SELVA RAJAN R, et al. Triple negative breast cancer: a review of present and future diagnostic modalities[J]. Medicina(kaunas), 2021, 57(1):62. |
| [3] | LI Y, MU L, RUAN Y X, et al. The influence of molecular classification of breast cancer on the safety of breast-conserving surgery[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2018, 40(5):341-346. |
| [4] | 陈春明, 孔灵芝. 中国成人超重和肥胖症预防控制指南[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2006:3. |
| CHEN C M, KONG L Z. Guidelines for the prevention and control of overweihgt and obesity in Chinese adults[M]. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2006:3. | |
| [5] | AMIN M B, EDGE S B, GREENE F L, et al. AJCC cancer staging manual. 8th ed[M]. NewYork: Springer, 2016:589-628. |
| [6] |
GU J, GROOT G, BODEN C, et al. Review of factors influencing women's choice of mastectomy versus breast conserving therapy in early stage breast cancer: a syste-matic review[J]. Clin Breast Cancer, 2018, 18(4):e539-e554.
doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2017.12.013 URL |
| [7] |
BOERO I J, PARAVATI A J, HOU J, et al. The impact of surgeons on the likelihood of mastectomy in breast cancer[J]. Ann Surg, 2019, 269:951-958.
doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002698 pmid: 29465454 |
| [8] |
CHEN Q X, WANG X X, LIN P Y, et al. The different outcomes between breast-conserving surgery and mastectomy in triple-negative breast cancer: a population-based study from the SEER 18 database[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(3):4773-4780.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v8i3 URL |
| [9] |
LI P, LI L, XIU B, et al. The prognoses of young women with breast cancer (≤35 years) with different surgical options: a propensity score matching retrospective cohort study[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12:795023.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.795023 URL |
| [10] |
FISHER B, ANDERSON S, BRYANT J, et al. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing total mastectomy, lumpectomy, and lumpectomy plus irradiation for the treatment of invasive breast cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2002, 347(16):1233-1241.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022152 URL |
| [11] |
SINNADURAI S, KWONG A, HARTMAN M, et al. Breast-conserving surgery versus mastectomy in young women with breast cancer in Asian settings[J]. BJS Open, 2018, 3(1):48-55.
doi: 10.1002/bjs5.2019.3.issue-1 URL |
| [12] |
AGARWAL S, PAPPAS L, NEUMAYER L, et al. Effect of breast conservation therapy vs. mastectomy on disease-specific survival for early-stage breast cancer[J]. JAMA Surg, 2014, 149(3):267-274.
doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2013.3049 URL |
| [13] |
HARTMANN-JOHNSEN O J, KÅRESEN R, SCHLICHTING E, et al. Survival is better after breast conserving therapy than mastectomy for early stage breast cancer: a registry-based follow-up study of Norwegian women primary ope-rated between 1998 and 2008[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2015, 22(12):3836-3845.
doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4441-3 URL |
| [14] |
WANG J, YANG S P, ZHOU P, et al. Additional radiotherapy to breast-conserving surgery is an optional treatment for de novo stage Ⅳ breast cancer: a population-based analysis[J]. Cancer Med, 2021, 10(5):1634-1643.
doi: 10.1002/cam4.v10.5 URL |
| [15] |
WANG J, WANG S, TANG Y, et al. Comparison of treatment outcomes with breast-conserving surgery plus radiotherapy versus mastectomy for patients with stage Ⅰ breast cancer: a propensity score-matched analysis[J]. Clin Breast Cancer, 2018, 18(5):e975-e984.
doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2018.06.002 URL |
| [16] |
DE LA CRUZ KU G, KARAMCHANDANI M, CHAMBERGO-MICHILOT D, et al. Does breast-conserving surgery with radiotherapy have a better survival than mastectomy? A meta-analysis of more than 1,500,000 patients[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2022, 29(10):6163-6188.
doi: 10.1245/s10434-022-12133-8 |
| [17] |
VAN MAAREN M C, DE MUNCK L, DE BOCK G H, et al. 10 year survival after breast-conserving surgery plus radiotherapy compared with mastectomy in early breast cancer in the Netherlands: a population-based study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2016, 17(8):1158-1170.
doi: S1470-2045(16)30067-5 pmid: 27344114 |
| [18] | 刘晓静, 杨柳春, 进淑娟, 等. 乳腺癌患者生存与复发的随访报告:一项单中心回顾性研究[J]. 中华乳腺病杂志(电子版), 2019, 13(5):270-276. |
| LIU X J, YANG L C, JIN S J, et al. Survival and recurrence of breast cancer patients:a single-center retrospective study[J]. Chin J Breast Dis(Electronic Edition), 2019, 13(5):270-276. | |
| [19] | 刘晓静, 朱明华, 左思, 等. 不同治疗方式对三阴性乳腺癌预后的影响[J]. 国际肿瘤学杂志, 2022, 49(1):33-38. |
|
LIU X J, ZHU M H, ZUO S, et al. Effects of different treatments on prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer[J]. J Int Oncol, 2022, 49(1):33-38.
doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3516 URL |
|
| [20] | 吕文芝, 丁波泥, 钱立元, 等. 保留乳房手术对比乳房根治术治疗三阴性乳腺癌疗效的Meta分析[J]. 中华乳腺病杂志(电子版), 2018, 12(5):276-281. |
| LYU W Z, DING B N, QIAN L Y, et al. Efficacy comparison of breast conserving surgery versus radical mastectomy in triple negative breast cancer patients:a meta-analysis[J]. Chin J Breast Dis(Electronic Edition), 2018, 12(5):276-281. | |
| [21] | DOMINICI L S, HU J, KING T A, et al. Abstract GS6-06: local therapy and quality of life outcomes in young women with breast cancer[J]. Cancer Research, 2019, 79(4 Supplement):GS6-06-GS6-06. |
| [1] | LI Hui, YIN Yu, LI Chunxiao, et al. Research progress on rehabilitation effect of respiratory training on breast cancer-related lymphedema [J]. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Reconstructive Surgery, 2023, 19(4): 430-. |
| [2] | ZHU Danli, BAO Wanting, WEI Hao, et al. Advances in breast reconstruction after breast cancer surgery [J]. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Reconstructive Surgery, 2023, 19(2): 201-. |
| [3] | YANG Yi, YANG Xingxia, JIN Sili, ZHANG Xu, ZHU Juanying, CHEN Xiaosong. Clinical application of preoperative MRI examination in breast-conserving surgery for ductal carcinoma in situ [J]. Journal of Surgery Concepts & Practice, 2023, 28(04): 378-382. |
| [4] | DONG Jun, CUI Fengming, LIU Jun. Effects of silencing Ki-67 gene on doxorubicin resistance of breast cancer MCF-7/DOX cells [J]. Journal of Surgery Concepts & Practice, 2023, 28(03): 254-259. |
| [5] | GAO Weiqi, ZHANG Xu, WANG Zheng, ZHU Yifei, HUANG Jiahui, HONG Jin, ZHU Siji, CHEN Xiaosong, HUANG Ou, HE Jianrong, CHEN Weiguo, LI Yafen, SHEN Kunwei, XU Hua, WU Jiayi. Safety analysis of immediate breast reconstruction with deep inferior epigastric perforator after neoadjuvant treatment [J]. Journal of Surgery Concepts & Practice, 2023, 28(02): 147-151. |
| [6] |
ZHANG Xiaoli, LI Zan, SONG Dajiang, et al.
Clinical application of the pedicled lateral thoracic artery perforation flap in breast reconstruction immediately after breast-conserving surgery [J]. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Reconstructive Surgery, 2022, 18(5): 382-. |
| [7] |
SONG Dajiang, LI Zan, ZHANG Yixin.
Surgical strategy of huge chest wall defect reconstruction using pedicled rectus abdominis musculocutaneous flap combined with free deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap [J]. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Reconstructive Surgery, 2022, 18(5): 386-. |
| [8] |
CHEN Kuo, SONG Dajiang, MU Lan, et al.
Repair of abdominal wall donor site defect of TRAM by freeing the anterior rectus sheath of superior rectus abdominis -- An attempt to make patch with autologous tissue [J]. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Reconstructive Surgery, 2022, 18(5): 393-. |
| [9] | LIU Min (刘 敏), YI Ming (易 鸣), WU Minghu∗ (武明虎), WANG Juan (王 娟), HE Yu (何 宇). Breast Pathological Image Classification Based on VGG16 Feature Concatenation [J]. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ Sci, 2022, 27(4): 473-484. |
| [10] |
YAO Chengcai, CHEN Ming, LIU Changchun, et al.
Application of silicone gel breast prosthesis combined with titanium polypropylene mesh in immediate breast reconstruction for early breast cancer [J]. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Reconstructive Surgery, 2022, 18(3): 247-. |
| [11] |
LIAO Xiaoming, JIANG Yi, TANG Wei, et al.
Application of thin vascularized lymph node transfer combined with reverse mapping in the treatment of secondary upper extremity lymphedema [J]. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Reconstructive Surgery, 2022, 18(1): 8-. |
| [12] |
SONG Jingyong, TANG Peng, ZHONG Xiaojie, et al.
Quantitative analysis of anastomosis stoma in prophylactic lymphaticovenous anastomosis immediately after axillary lymph node dissection of breast caner: A case report [J]. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Reconstructive Surgery, 2022, 18(1): 34-. |
| [13] | YANG Cuiyan, WANG Haoyu, CHEN Xiaosong, SHEN Kunwei. Study on tumour suppressor gene TP53 mutation and prognosis in patients with triple-negative breast cancer [J]. Journal of Surgery Concepts & Practice, 2022, 27(05): 421-428. |
| [14] | PAN Ruixin, CHEN Xiaosong, SHEN Kunwei. Study on circulating tumor DNA and circulating tumor cell detecting minimal residual disease in breast cancer [J]. Journal of Surgery Concepts & Practice, 2022, 27(05): 463-467. |
| [15] | ZHU Siyi, CHEN Xiaosong, SHEN Kunwei. Study on obesity associated with prognosis of early breast cancer and efficacy of adjuvant therapy [J]. Journal of Surgery Concepts & Practice, 2022, 27(05): 468-472. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||