

诊断学理论与实践 ›› 2024, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (05): 517-523.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2024.05.008
冯国伟, 黄新韵, 孟宏平, 江旭峰, 陈克敏, 林晓珠( )
)
收稿日期:2024-06-08
接受日期:2024-10-08
出版日期:2024-10-25
发布日期:2025-02-25
通讯作者:
林晓珠 E-mail: lxz11357@rjh.com.cn基金资助:
FENG Guowei, HUANG Xinyun, MENG Hongping, JIANG Xufeng, CHEN Kemin, LIN Xiaozhu( )
)
Received:2024-06-08
Accepted:2024-10-08
Published:2024-10-25
Online:2025-02-25
摘要:
目的:评估18F-氟脱氧葡萄糖正电子发射断层扫描/磁共振成像(18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/magnetic resonanceimaging,18F-FDG PET/MRI)在胰腺癌术后复发诊断中的价值。方法:连续纳入2018年4月至2023年12月期间86例胰腺癌切除术后的患者,在2024年8月至9月行18F-FDG PET/MRI检查。回顾性分析18F-FDG PET/MRI检测胰腺癌术后复发的效能,比较PET/MRI和血清糖类抗原19-9(CA19-9)水平在诊断复发的效能。结果:经随访证实,86例患者中有67.4%(58/86)发生了肿瘤复发。复发组的原发肿瘤直径大于未复发组[(3.4±1.3)cm比(2.7±1.2)cm]。复发的患者中,87.9%(51/58)为系统性复发,最常见的是肝脏转移和腹膜转移。PET/MRI检查结果改变了30.2%(26/86)患者的治疗方案。86例中,有79例患者同时检查了PET/MRI和血清CA19-9,在诊断胰腺癌术后复发中,PET/MRI显示出比血清CA19-9更高的诊断效能(AUC:0.847对0.719)。PET/MRI检出9/12例血清CA19-9正常的胰腺癌复发,排除了5/8例血清CA19-9升高的未复发患者。结论:PET/MRI在胰腺癌术后复发诊断中具有较大的临床价值,其不仅能诊断是否复发,还能提供肿瘤复发的具体部位,对于血清CA19-9正常的患者,PET/MRI检查更有意义,为下一步治疗方案的制定提供全面的信息。
中图分类号:
冯国伟, 黄新韵, 孟宏平, 江旭峰, 陈克敏, 林晓珠. 18F-氟脱氧葡萄糖正电子发射断层扫描/磁共振成像(18F-FDG PET/MRI)在诊断胰腺癌术后复发中的价值[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2024, 23(05): 517-523.
FENG Guowei, HUANG Xinyun, MENG Hongping, JIANG Xufeng, CHEN Kemin, LIN Xiaozhu. Value of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging (18F-FDG PET/MRI) in diagnosis of postoperative recurrence of pancreatic cancer[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(05): 517-523.
表1
86例胰腺癌切除术后18F-FDG PET/MRI检查患者一般情况
| Indice | Recurrence group | Non-recurrence group | Statistics value | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender(male/female) | 40/18 | 22/6 | χ2=0.866 | 0.446 |
| Age(mean±standard deviation,year) | 62.2±10.1 | 61.4±8.2 | t=0.332 | 0.740 |
| Height(mean±standard deviation,cm) | 168.2±7.7 | 167.9±7.3 | t=0.160 | 0.873 |
| Body weight(mean±deviation,Kg) | 57.4±9.5 | 58.5±11.2 | t=-0.464 | 0.644 |
| Blood glucose(mean±deviation,mmol/L) | 6.9±2.2 | 7.2±3.1 | t=-0.518 | 0.606 |
| Time between operation and PET/MRI(median,day) | 306 | 365 | U=666.000 | 0.180 |
| Location of tumor(pancreatic head and uncinate process/body and tail) | 27/31 | 12/16 | χ2=0.104 | 0.819 |
| Tumor size(mean±standard deviation,cm) | 3.4±1.3 | 2.7±1.2 | 2.419 | 0.018 |
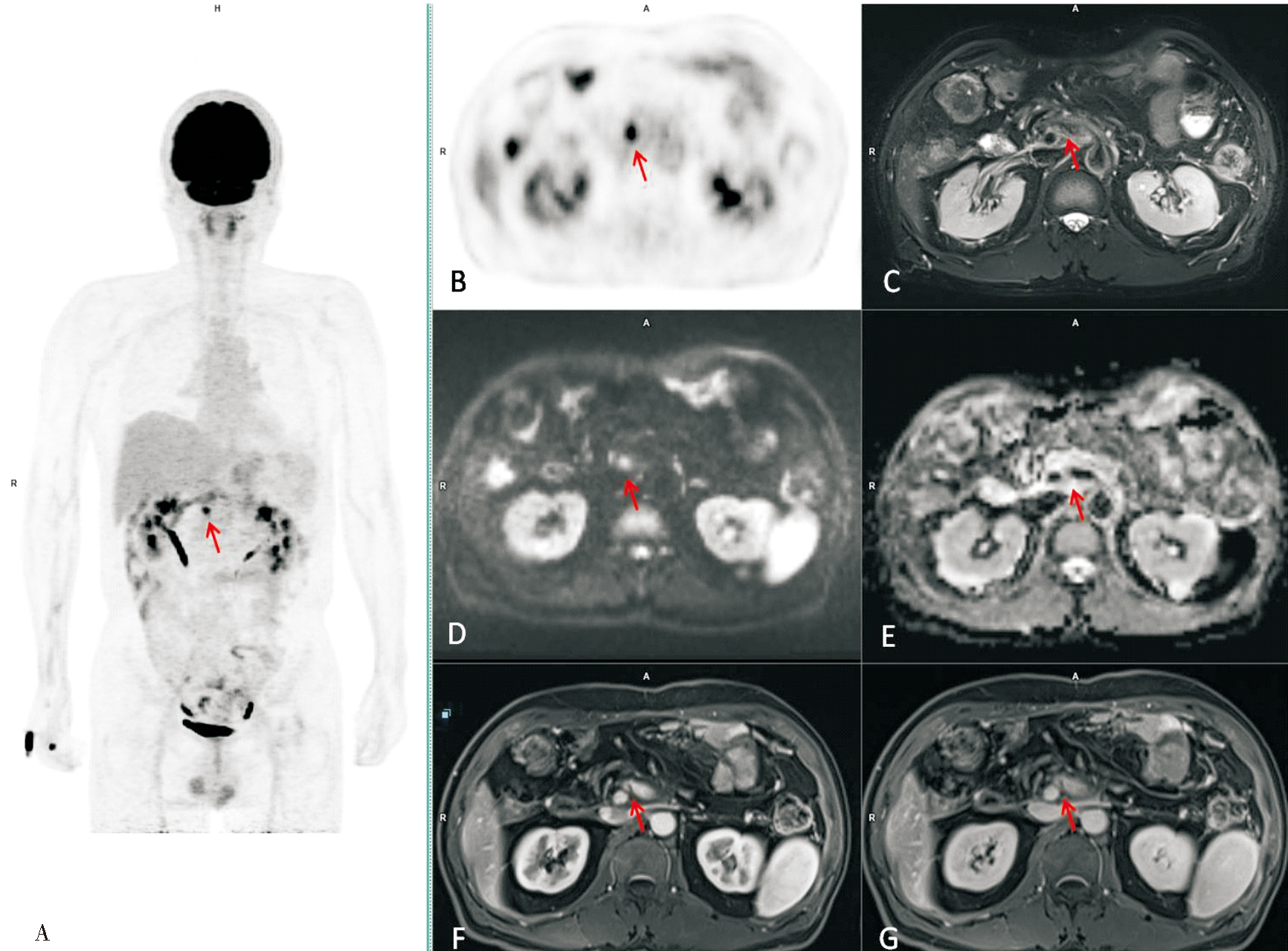
图1
胰头癌术后16个月余随访PET/MRI示手术区复发 男性,56岁,胰十二指肠根治术后16个月余,术后随访,CA19-9不高,PET/MRI提示手术区复发,随后患者进行了化疗(白蛋白紫杉醇+吉西他滨)。A:全身PET MIP图,可见上腹中部高代谢灶(红色箭头);B:上腹部PET横断面图像,腹主动脉右前方高代谢灶,SUVmax12.5;C:上腹部MRI T2WI脂肪抑制横断面,肠系膜上静脉、肠系膜上动脉周围毛糙;D、E:上腹部MRI-DWI横断面及ADC图,腹主动脉右前方DWI高信号灶、ADC不高;F、G:上腹部MRI T1:WI脂肪抑制增强动脉晚期和门脉期横断面图像,肠系膜上动脉增粗,肠系膜上静脉旁点状异常信号。
| [1] | MIZRAHI J D, SURANA R, VALLE J W, et al. Pancrea-tic cancer[J]. Lancet, 2020, 395(10242):2008-2020. |
| [2] | HAN B, ZHENG R, ZENG H, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022[J]. J Natl Cancer Cent, 2024, 4(1):47-53. |
| [3] | TEMPERO M A, MALAFA M P, AL-HAWARY M, et al. 2021, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2021, 19(4):439-457. |
| [4] | 朱琳熙, 毛谅, 杜娟, 等. 胰腺癌新辅助转化治疗后根治性切除术的临床疗效[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2023, 22(7):916-923. |
| ZHU L X, MAO L, DU J, et al. Clinical efficacy of radical resection after neoadjuvant transformation therapy for pancreatic cancer[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2023, 22(7):916-923. | |
| [5] | 朱凌宇, 高绥之, 吴欣乾, 等. 胰腺癌转化手术后辅助治疗的临床价值[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2024, 23(5):694-702. |
| ZHU L Y, GAO S Z, WU X Q, et al. Clinical value of adjuvant therapy after pancreatic cancer transformation surgery[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2024, 23(5):694-702. | |
| [6] | JUNG W, JANG J Y, KANG M J, et al. The clinical usefulness of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) in follow-up of curatively resected pancreatic cancer patients[J]. HPB (Oxford), 2016, 18(1):57-64. |
| [7] |
JOO I, LEE J M, LEE D H, et al. Preoperative assessment of pancreatic cancer with FDG PET/MR imaging versus FDG PET/CT plus contrast-enhanced multidetector CT: a prospective preliminary study[J]. Radiology, 2017, 282(1):149-159.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2016152798 pmid: 27556273 |
| [8] | ZHANG Z, ZHOU N, GUO X, et al. Pretherapeutic assessment of pancreatic cancer: comparison of FDG PET/CT plus delayed PET/MR and contrast-enhanced CT/MR[J]. Front Oncol, 2022,11:790462. |
| [9] | SEELEN L W F, FLOORTJE VAN OOSTEN A, BRADA L J H, et al. Early recurrence after resection of locally advanced pancreatic cancer following induction therapy: an international multicenter study[J]. Ann Surg, 2023, 278(1):118-126. |
| [10] |
RAYAMAJHI S, BALACHANDRAN A, KATZ M, et al. Utility of (18) F-FDG PET/CT and CECT in conjunction with serum CA 19-9 for detecting recurrent pancreatic adenocarcinoma[J]. Abdom Radiol (NY), 2018, 43(2):505-513.
doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1316-z pmid: 28900703 |
| [11] |
LUO G, LIU C, GUO M, et al. Potential biomarkers in lewis negative patients with pancreatic cancer[J]. Ann Surg, 2017, 265(4):800-805.
doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001741 pmid: 28267695 |
| [12] |
RUF J, LOPEZ HÄNNINEN E, OETTLE H, et al. Detection of recurrent pancreatic cancer: comparison of FDG-PET with CT/MRI[J]. Pancreatology, 2005, 5(2-3):266-272.
pmid: 15855825 |
| [13] | 张淼, 李彪, 王华枫, 等. 18F-FDG PET-CT与增强CT在胰腺癌诊断和分期中的价值比较[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2009, 8(1):50-54. |
| ZHANG M, LI B, WANG H F, et al. Comparison of 18F-FDG PET-CT and enhanced CT in the diagnosis and sta-ging of pancreatic cancer[J]. J Diagn Concepts Pract, 2009, 8(1):50-54. | |
| [14] | DAAMEN L A, GROOT V P, GOENSE L, et al. The diagnostic performance of CT versus FDG PET-CT for the detection of recurrent pancreatic cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2018,106:128-136. |
| [15] |
SPERTI C, PASQUALI C, BISSOLI S, et al. Tumor relapse after pancreatic cancer resection is detected earlier by 18-FDG PET than by CT[J]. J Gastrointest Surg, 2010, 14(1):131-140.
doi: 10.1007/s11605-009-1010-8 pmid: 19777315 |
| [16] | KANG M J, JANG J Y, LEE S E, et al. Comparison of the long-term outcomes of uncinate process cancer and non-uncinate process pancreas head cancer: poor prognosis accompanied by early locoregional recurrence[J]. Langenbecks Arch Surg, 2010, 395(6):697-706. |
| [17] | ZHANG Z, GUO S, SU W, et al. Preoperative assessment of pancreatic cancer with [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/MR versus [18F]-FDG PET/CT plus contrast-enhanced CT: a prospective preliminary study[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2025, 52(3):1017-1027. |
| [18] | LI X, LU N, LIN L, et al. 18F-FAPI-04 outperforms 18F-FDG PET/CT in clinical assessments of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma[J]. J Nucl Med, 2024, 65(2):206-212. |
| [1] | 孔晓晓, 陈萍, 牛建梅, 吕明丽, 王慧. 自身免疫相关复发性流产子宫动脉及子宫内膜超声参数分析[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2023, 22(06): 550-554. |
| [2] | 谢吻, 梁怀予, 董磊, 袁菲, 王朝夫, 郭滟. 胰腺导管腺癌重要驱动基因突变与临床病理特征、预后间相关性的分析[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2022, 21(05): 581-587. |
| [3] | 顾炫, 柳俊. 超声筛查鉴别胰腺实性假乳头状瘤与胰腺导管腺癌的研究分析[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2022, 21(04): 504-508. |
| [4] | 王晨琛, 方跃华, 施仲伟, 屈雪蒸. 25例主动脉瓣成形术后一年的超声心动图评价[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2022, 21(03): 395-398. |
| [5] | 罗晓颖, 许燕, 张凤如, 吴立群, 戚文航. P波离散度和N端脑钠肽前体预测房颤冷冻球囊导管消融术后复发的价值[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2020, 19(1): 32-36. |
| [6] | 高燕婷, 赵金艳, 王娟, 李佳, 许雯, 李莉, 蔺丽慧. 急性髓细胞性白血病患者骨髓淋巴细胞亚群分析及其临床意义[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2020, 19(04): 407-413. |
| [7] | 吕良敬, 倪若柠. 重视复发性流产患者中未分化结缔组织病的诊断[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2018, 17(03): 235-237. |
| [8] | 王晨琛, 詹维伟. 甲状腺癌术后复发转移灶的超声特征及超声引导下细针穿刺的应用价值[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2018, 17(01): 111-114. |
| [9] | 董育玮, 李郑红, 汪佩文, 陆伦根. 良性复发性肝内胆汁淤积伴先天性黄疸一例报道[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2017, 16(04): 434-436. |
| [10] | 陈颖, 李翠, 应春妹. 复发性自然流产患者T细胞中T细胞免疫球蛋白和免疫受体酪氨酸抑制基序的表达[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2017, 16(03): 273-276. |
| [11] | 吴瑛婷, 张军, 陈慧芬,. 原发性胆汁性肝硬化合并妊娠的研究进展[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2015, 14(06): 573-576. |
| [12] | 罗晓颖, 权薇薇, 许燕, 张风如, 吴立群, 戚文航,. C反应蛋白与房颤冷冻球囊导管消融术后房颤复发的相关性研究[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2015, 14(03): 219-222. |
| [13] | 张俊, 瞿晴, 费晓春, 陈小松, 任若冰, 徐昊平, 许赪, 沈坤炜,. 乳腺癌转移病灶再活检对于指导治疗的价值[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2013, 12(03): 304-308. |
| [14] | 张芳, 李本尚, 王翔, 马亚妮, 薛惠良, 潘慈, 叶启东, 江华, 周敏, 汤燕静, 陈静,. 流式细胞术检测微小残留病预测儿童急性B淋巴细胞白血病复发的意义[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2012, 11(02): 141-144. |
| [15] | 吴瑛婷, 陈慧芬, 王学锋, 王鸿利,. 复发性自然流产与免疫因素和遗传性凝血缺陷关系的研究[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2010, 9(03): 290-293. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||