

诊断学理论与实践 ›› 2025, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (01): 35-42.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2025.01.006
陈洪卫1,2, 朱婷1, 刘燕1, 侯彦强2, 范广建1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-15
接受日期:2024-12-31
出版日期:2025-02-25
发布日期:2025-02-05
通讯作者:
范广建 E-mail:gjfan@shsmu.edu.cn基金资助:
CHEN Hongwei1,2, ZHU Ting1, LIU Yan1, HOU Yanqiang2, FAN Guangjian1( )
)
Received:2024-10-15
Accepted:2024-12-31
Published:2025-02-25
Online:2025-02-05
摘要:
目的 寻找代谢相关脂肪性肝病(metabolic associated fatty liver disease,MAFLD)进展为肝硬化的诊断生物标志物,为肝硬化疾病的早诊、早治提供诊断依据。方法 选用健康雄性SD(Sprague Dawley)大鼠,随机分为正常对照(normal control,NC)组(15只)、高脂饮食(high-fat diet,HFD)组(15只)和肝纤维化(liver fibrosis,LF)组(15只)。NC组大鼠接受普通饲料喂养,HFD组持续高脂饲料喂养以诱导脂肪肝和轻度肝纤维化,LF组持续高脂饲料喂养同时注射四氯化碳诱导肝硬化。饲养41周后,采集大鼠血液和肝脏组织。肝脏组织采用苏木精-伊红(hematoxylin and eosin,HE)染色、油红O染色和天狼星红染色,以评价肝脏组织形态、脂肪浸润及肝纤维化程度。利用mRNA测序技术分析血液样本筛选差异表达基因,采用反转录实时荧光定量聚合酶链式反应(reverse transcription quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, RT-qPCR)技术验证测序筛选的差异基因表达情况。另收集2025年1月至2月来自上海交通大学医学院附属松江医院的健康体检者、MAFLD和肝硬化患者的血液样本各10例,验证筛选出的差异基因的mRNA表达情况。结果 大鼠外周血细胞mRNA测序筛选出17个差异基因,包括Rab3ip、Gprasp2、Emid1、Hbq1b、Scimp、Wipf3、Scrn1、Sez6、Bglap、Bhlhb9、Ranbp10、Ubd、Plekhb1、Nup210l、Gp1bb、Cpne8和Oscar;RT-qPCR验证结果表明,Scimp基因在NC组、HFD组、LF组的mRNA表达水平依次呈上调趋势,与测序结果一致,各组间两两比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。人外周血细胞RT-qPCR验证结果与大鼠外周血Scimp基因的mRNA测序和RT-qPCR验证表达趋势一致。在体检人群、MAFLD患者及肝硬化患者间,Scimp存在同样的表达差异(P<0.05)。结论 外周血细胞Scimp基因的mRNA表达水平可作为早期肝硬化的潜在无创诊断标志物。
中图分类号:
陈洪卫, 朱婷, 刘燕, 侯彦强, 范广建. 外周血Scimp可作为代谢相关脂肪性肝病肝硬化的生物诊断标志物——基于动物实验的研究[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2025, 24(01): 35-42.
CHEN Hongwei, ZHU Ting, LIU Yan, HOU Yanqiang, FAN Guangjian. Study on exploring Scimp in peripheral blood as a biodiagnostic marker for MAFLD-related cirrhosis based on animal experiments[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2025, 24(01): 35-42.
表1
基因real-time引物序列
| Primer | 5'-F | 5'-R |
|---|---|---|
| Hbq1b | AGCAATGTTGGAATCTACACGA | TTTAACCTGGCTGGAACCT |
| Scrn1 | TGGTGGACCGGAGAGGAT | AGAATCTATGCAAACGCCACT |
| Ranbp10 | CTCTGTACGAGCCACCCAC | CAGAAGGAATGCCCATCATCG |
| Sez6 | ATTGCTATGAGCCCTTTGTCAA | GCTGGTTCTGTCTCATTCCAC |
| Scimp | CGGTCTCCACTGATCCAGA | CTGTGTAAGCCCGTTTCAGC |
| Wipf3 | CTGCCACCCATACCACCT | GTGGCTCTCTCACGTCCT |
| Cpne8 | TGTACGGGCCAACCAACTTT | TCCGTCACAATGAGGAGCAC |
| Bglap | CTCAACAATGGACTTGGAGCCC | CACATGCCCTAAACGGTGGT |
| Nup210l | TTGCCATACAGCCTTTATACGAA | ATTCAGCAACAAGAACTGCC |
| Rab3ip | GTGAGAGAGGCGAACGTCAA | AGGCGATGTTGGAGAACTGG |
| Gp1bb | CCTGAGCGCGAGTTCTACC | CTCATCCTCCGCCACGTA |
| Bhlhb9 | ATCCCCTTATTCATAAAATAGCACAG | GGAAGAGTTCAGAGTAATAACAGCC |
| Emid1 | CTCAGTCCCAGCTACCCC | GAAGCTCCCAAGAATCAACTCT |
| Ubd | AAATGATCGAGAATGTGACTGC | GATCTTTCCATCTTCCAGCCTC |
| Gprasp2 | GCTAAACATCAGGCTAACACCA | CCAGCCCAAAAGCAAAACG |
| Plekhb1 | GTTTGCCCTAAGGTCAGGTG | TACCCAGATCCGCCTCTCAA |
| Oscar | GTTATCACTGCCGCTACCG | TACCAGCAGTTCCAGAGCA |
| GAPDH | TCAACGACCCCTTCATTGAC | GTTTCCCGTTGATGACCAG |
图1
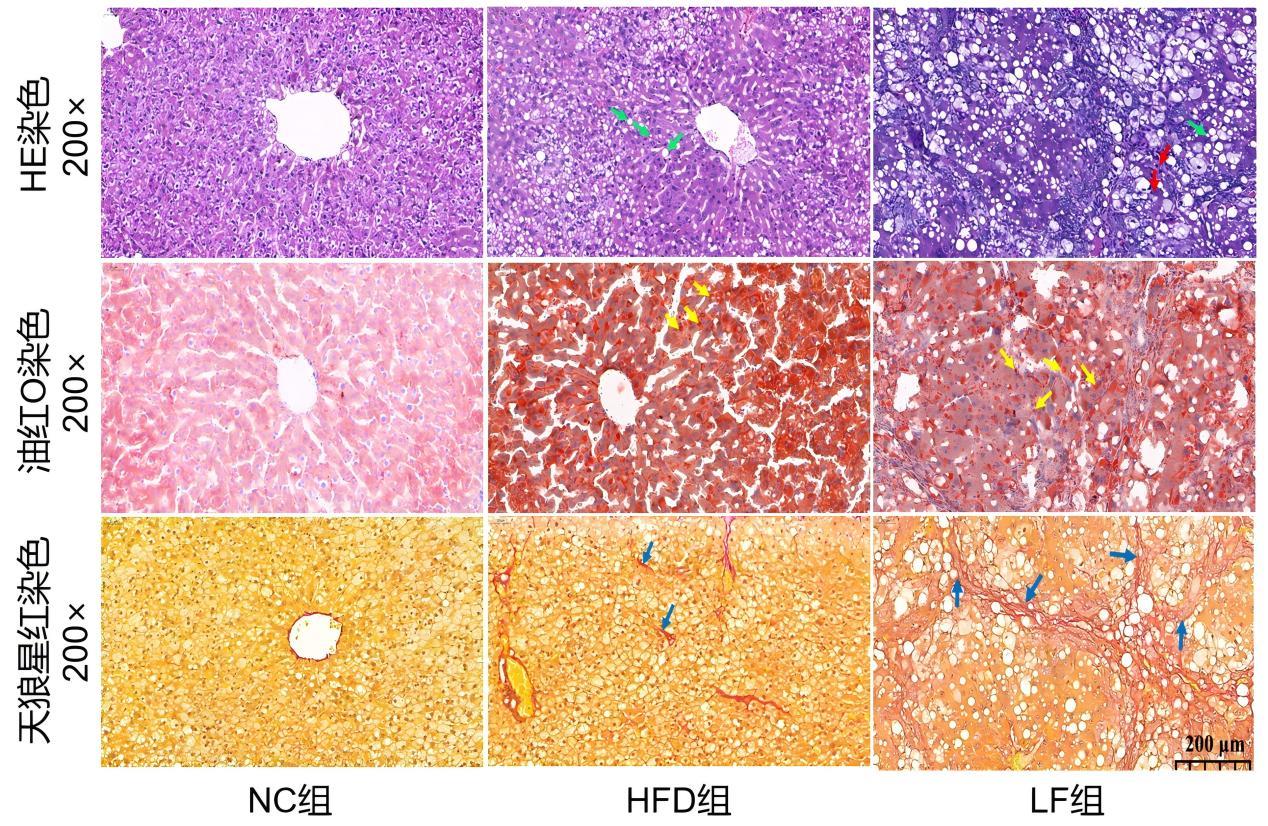
SD大鼠肝脏组织病理染色注:SD大鼠肝脏组织经HE染色、油红O染色及天狼星红染色处理,于200倍放大条件下观测(标尺200 μm)。NC组3种染色结果均显示肝组织结构正常。HFD组大鼠自然进展为轻度肝纤维化,染色结果显示,HE染色下细胞质可见大小不等的空泡;油红O染色呈现大量红色脂滴;天狼星红染色显示肝组织存在少量胶原纤维增生。LF组大鼠已发展为肝硬化,HE染色可见纤维组织增生、假小叶形成,细胞质内存在大量形态各异的脂肪空泡;油红O染色下细胞质中红色脂滴大小不均;天狼星红染色显示肝组织出现大量胶原纤维增生,并伴有假小叶形成。图中绿色箭头指示脂肪空泡,红色箭头指示假小叶,黄色箭头指示脂滴;蓝色箭头指示胶原纤维。
| [1] |
LI X Y, WANG J, GONG X,et al. Upregulation of BCL-2 by acridone derivative through gene promoter i-motif for alleviating liver damage of NAFLD/NASH[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(15):8255-8268.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa615 pmid: 32710621 |
| [2] | YUAN M, HE J, HU X,et al. Hypertension and NAFLD risk: Insights from the NHANES 2017-2018 and Mendelian randomization analyses[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2024, 137(4):457-464. |
| [3] | SONG C W, LV W, LI Y H,et al. Alleviating the effect of quinoa and the underlying mechanism on hepatic steatosis in high-fat diet-fed rats[J]. Nutrition & Metabolism, 2021, 18(1):106. |
| [4] | DINIZ T A, JUNIOR E A D L, TEIXEIRA A A,et al. Aerobic training improves NAFLD markers and insulin resistance through AMPK-PPAR-α signaling in obese mice[J]. Life Sciences, 2021, 266:118868. |
| [5] |
ZHANG L J, LIU C H, YIN L F,et al. Mangiferin relieves CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1):4172.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30582-3 pmid: 36914687 |
| [6] |
LIAO S L, HE H, ZENG Y P,et al. A nomogram for predicting metabolic steatohepatitis: The combination of NAMPT, RALGDS, GADD45B, FOSL2, RTP3, and RASD1[J]. Open Medicine, 2021, 16(1):773-785.
doi: 10.1515/med-2021-0286 pmid: 34041361 |
| [7] |
WU X Z, YUAN C B, PAN J X,et al. CXCL9, IL2RB, and SPP1, potential diagnostic biomarkers in the co-morbidity pattern of atherosclerosis and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1):16364.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66287-4 pmid: 39013959 |
| [8] | YAN J Y, FENG Y Y, FANG X W,et al. Anti-liver fibrosis effects of the total flavonoids of litchi semen on CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats associated with the upregulation of retinol metabolism[J]. Pharmaceutical Biology, 2022, 60(1):1264-1277. |
| [9] | 沈颖筱, 施惠海, 罗家乐,等.非酒精性脂肪性肝病肝纤维化风险预测模型的应用与进展[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2023, 27(9):131-136, 142. |
| SHEN Y X, SHI H H, LUO J L,et al. Application and progress of liver fibrosis risk prediction model for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Med Pract, 2023, 27(9):131-136, 142. | |
| [10] | 赵梓硕, 朱玉光, 马燕山,等.不同高脂饲料配方对建立非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠模型的影响[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2024, 29(5):543-553. |
| ZHAO Z S, ZHU Y G, MA Y S,et al. Effects of different formulations of high-fat diet on establishment of a non-alcoholic fatty liver model in rats[J]. Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2024, 29(5):543-553. | |
| [11] | 张垚, 叶嘉豪, 范星宇,等.基于数据挖掘的肝硬化动物模型分析[J]. 湖北民族大学学报(医学版), 2024, 41(2):28-32. |
| ZHANG Y, YE J H, FAN X Y,et al.Analysis of Animal Models of Cirrhosis Based on Data Mining[J]. J Hubei Minzu Univ Med Ed, 2024, 41(2):28-32. | |
| [12] |
PEI X L, LIU L, WANG J R,et al. Exosomal secreted SCIMP regulates communication between macrophages and neutrophils in pneumonia[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1):691.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44714-4 pmid: 38263143 |
| [13] |
LI Q S, FRANCKE S, SNOEYS J,et al. Genome-wide association study of abnormal elevation of ALT in patients exposed to atabecestat[J]. BMC Genomics, 2023, 24(1):513.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09625-6 pmid: 37658353 |
| [14] | SUN X L, TIAN A X, LI P,et al. SCIMP:A Novel Targeted Gene for Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Progression[J]. Orthopaedic Surgery, 2023, 15(5):1375-1383. |
| [15] | 朱海伟, 梁琳琅. 2型糖尿病合并非酒精性脂肪性肝病患者维生素D水平与肝纤维化的关系[J]. 中国临床研究, 2023, 36(5):670-674. |
| ZHU H W, LIANG L L. Correlation between 25 Hydroxyvitamin D level and liver fibrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chin J Clin Res, 2023, 36(5):670-674. |
| [1] | 杨铭康, 刘禹, 许冠群, 王剑飚, 王学锋, 梁茜. vWF相关指标在诊断乙肝患者肝硬化进展中的价值[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2024, 23(06): 574-579. |
| [2] | 刘悦, 吴翰林, 佟武强, 许静. 自身抗体和D-二聚体检测评估慢性乙型肝炎及乙型肝炎肝硬化患者预后的价值[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2024, 23(02): 173-179. |
| [3] | 杨文康, 张俊, 王淑秋, 祥巴央宗, 杨翠萍. 我国云南香格里拉地区104例肝硬化患者的病因及临床特征分析[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2022, 21(06): 730-734. |
| [4] | 赵英妹, 聂红明, 张珏, 黄燕. 肝硬化患者凝血五项的测定及其临床意义[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2021, 20(05): 480-483. |
| [5] | 王丽娟, 潘自来, 苏文婷, 徐敬慈, 饶敏, 刘宵. 非对比剂增强磁共振血管成像流入反转恢复序列在肝硬化门静脉高压患者门静脉系统成像的可行性研究[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2020, 19(05): 494-498. |
| [6] | 王虹. 肝硬化门静脉高压性胃病的分类和诊断认识[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2016, 15(05): 446-450. |
| [7] | 谷雷雷, 朱时燕, 忻笑容, 谢玲, 周郁芬, 俞骁君, 吴云林. 门静脉高压性胃病急性出血的临床诊断[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2016, 15(05): 459-463. |
| [8] | 王晓瑜, 徐艳, 王利兵, 吴云林, 陈平, 张国华. 肝硬化食管静脉曲张内镜下皮圈结扎术对门静脉高压性胃病的影响及研究[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2016, 15(05): 468-471. |
| [9] | 吴瑛婷, 张军, 陈慧芬,. 原发性胆汁性肝硬化合并妊娠的研究进展[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2015, 14(06): 573-576. |
| [10] | 陈凌, 钱锋, 叶玲英, 林丽, 吴歆, 李梦梦, 刘晓, 张志国, 张倜, 王赓, 徐沪济,. 抗CD74抗体不是汉族人群强直性脊柱炎患者的血清标志物[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2015, 14(04): 338-342. |
| [11] | 赵春华, 耿烨芳,. 肝脏储备功能评估方法的研究现状[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2015, 14(04): 371-374. |
| [12] | 尚佳, 李威,. 肝硬化并发症的诊断[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2015, 14(04): 304-307. |
| [13] | 李越, 魏玲, 安云鹤, 武会娟,. 循环microRNA在人类疾病诊断标志物筛选中的研究进展[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2014, 13(06): 632-635. |
| [14] | 许峰,. 血清抗线粒体抗体M_2亚型检测在原发性胆汁性肝硬化临床诊断中的价值[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2013, 12(05): 556-558. |
| [15] | 谈绮文, 郭玮, 张春燕, 吴炯, 宋斌斌, 王蓓丽, 潘柏申,. 血清高尔基体蛋白73在肝硬化诊断及分级中的价值[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2013, 12(05): 516-521. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||