

Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice ›› 2025, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (02): 212-219.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2025.02.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
LÜ Haiying, LU Yong, HE Naying( )
)
Received:2025-01-03
Accepted:2025-03-27
Online:2025-04-25
Published:2025-07-11
Contact:
HE Naying
E-mail:i@nayinghe.com
CLC Number:
LÜ Haiying, LU Yong, HE Naying. Clinical applications of photon-counting CT in neuroimaging[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2025, 24(02): 212-219.
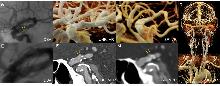
Figure 1
Comparative visualization of a small intracranial aneurysm on the left internal carotid artery (LICA) in a 68-year-old malePanels A & E: digital subtraction angiography, clearly demonstrates the left internal carotid artery (LICA) small aneurysm. Panels B, D & F: UHR-PCCTA multiplanar reconstructions (MPR) and volume renderings (VR) vividly depict the aneurysm and the parent vessel's fine details. Panels C & G: standard-resolution PCCTA, MPR reveals the aneurysm only faintly and it is not discernible on VR. The orange arrow in panels A-D and F-G indicates the location of the aneurysm. The orange line in panel E indicates the outline of the aneurysm.
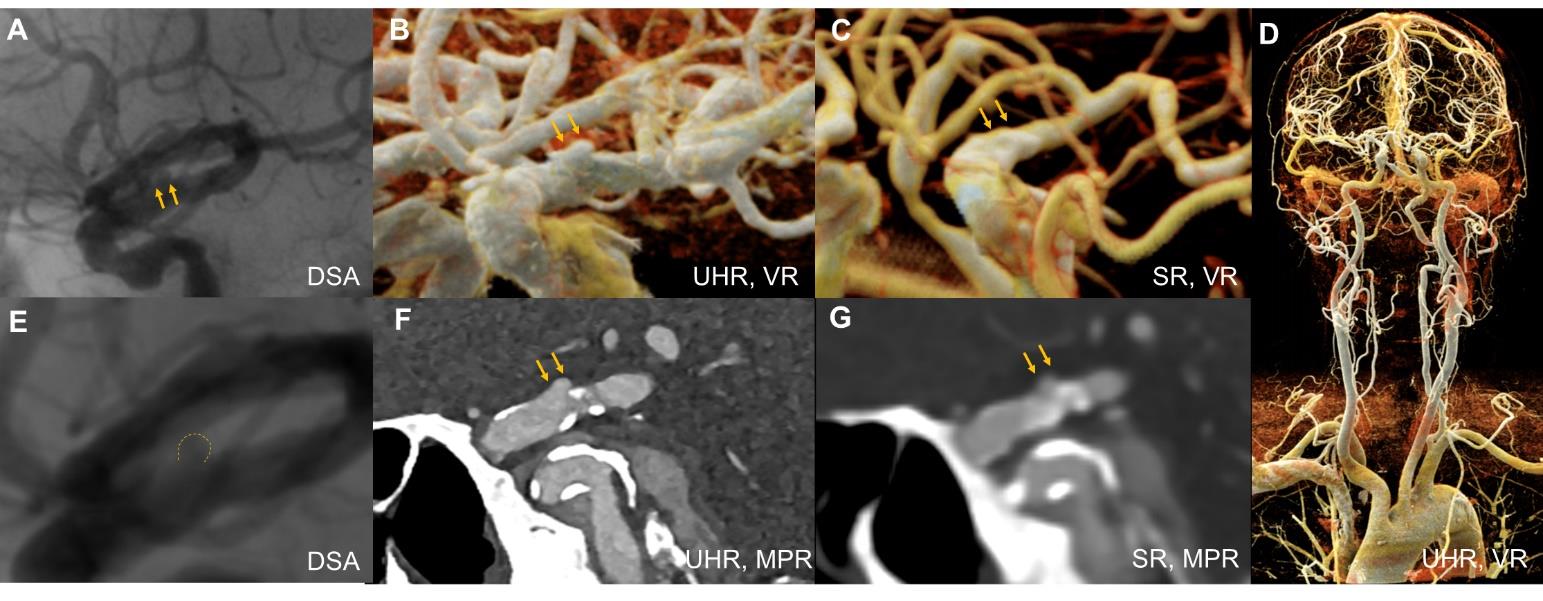
Figure 2
Comparative visualization of a basilar artery aneurysm and posterior cerebral artery branches in a 74-year-old femalePanels A-C、H [Standard-resolution (SR) PCCTA]: multiplanar reconstruction (MPR), maximum intensity projection (MIP), and volume rendering (VR) depict the aneurysm and its feeding artery, providing adequate delineation of aneurysm morphology and PCA branch anatomy. Panels E, J (DSA): DSA and its VR reconstruction clearly demonstrate the aneurysm sac, feeding artery, and PCA branch details. Panels D, F, G, I (UHR-PCCTA): MPR images reveal fine structural details of the aneurysm and PCA branches, with visualization comparable to DSA. The orange arrow indicates the location of the aneurysm.
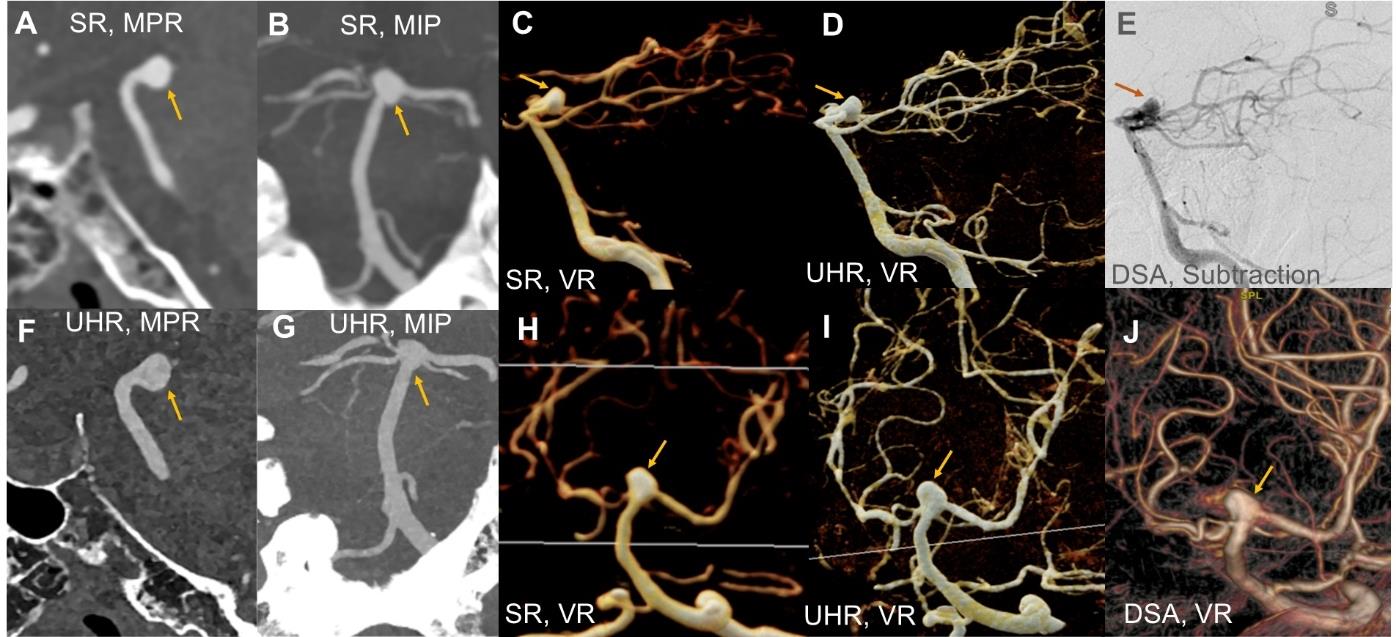
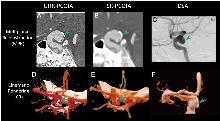
Figure 3
Comparative detailed visualization of an intracranial aneurysm in a 51-year-old malePanels A, D: UHR-PCCTA multiplanar reconstruction (MPR) + cinematic rendering (CR), reveal a linear high-density signal along the aneurysm wall, indicating calcification, and a subjacent low-density signal suggestive of possible thrombus. Panels B, E: standard-resolution PCCTA show only the high-density calcified wall; pronounced blooming artifacts obscure the internal wall structures. Panels C, F: DSA clearly delineate intra-aneurysmal details but depict the external wall only indirectly. The green arrowhead indicates the location of the aneurysm.
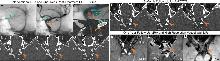
Figure 4
A 64 year old female patient with left internal carotid artery ocular segment (C6 segment) vesicular aneurysmNote: Follow-up ultra-high-resolution photon-counting CT angiography (UHR-PCCTA) and MRI of a blister aneurysm in the C6 segment of the left internal carotid artery treated with a flow diverter. Panels A-B (Immediate Post-Operation DSA): Digital subtraction angiography shows the flow-diverter in correct position (green arrow), with optimal stent deployment and patent parent artery; contrast pooling within the aneurysm sac (orange arrow) indicates residual filling. Panels C-D: DSA measurements of aneurysm remnant size closely match those obtained on 1-week UHR-PCCTA. Panels E-G (1-Week UHR-PCCTA): Follow-up demonstrates the device in place and clearly visualizes the residual aneurysm. Panels H-J (6-Month UHR-PCCTA): Follow-up shows the device in place and a marked reduction in aneurysm size. Panels K-M (1-Year MRI): Non-contrast MRA is degraded by stent artifacts, with only faint residual aneurysm visible; black-blood T1W/T2W vessel-wall MRI reveals a thickened aneurysm wall showing slightly hyperintense signal on T2W and hyperintense signal on T1W, suggestive of mural thrombus formation. The orange arrowhead indicates the location of the aneurysm.
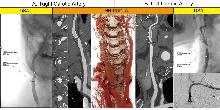
Figure 5
Atherosclerotic plaque in the neck (68 year old male)Note: Right internal carotid artery post-stent placement (Panel A) and severe luminal stenosis at the left common carotid artery bifurcation (Panel B); images shown from outer to inner: digital subtraction angiography (DSA), ultra-highresolution PCCTA (UHR-PCCTA) curved planar reconstruction (CPR), and cinematic rendering (CR). UHR-PCCTA clearly demonstrates the patency of stented head and neck arteries and the degree of vascular stenosis, while also accurately visualizing wall-adherent plaques. In contrast, DSA is limited in its ability to depict vessel walls and plaque composition, and can only infer such features indirectly based on luminal narrowing.
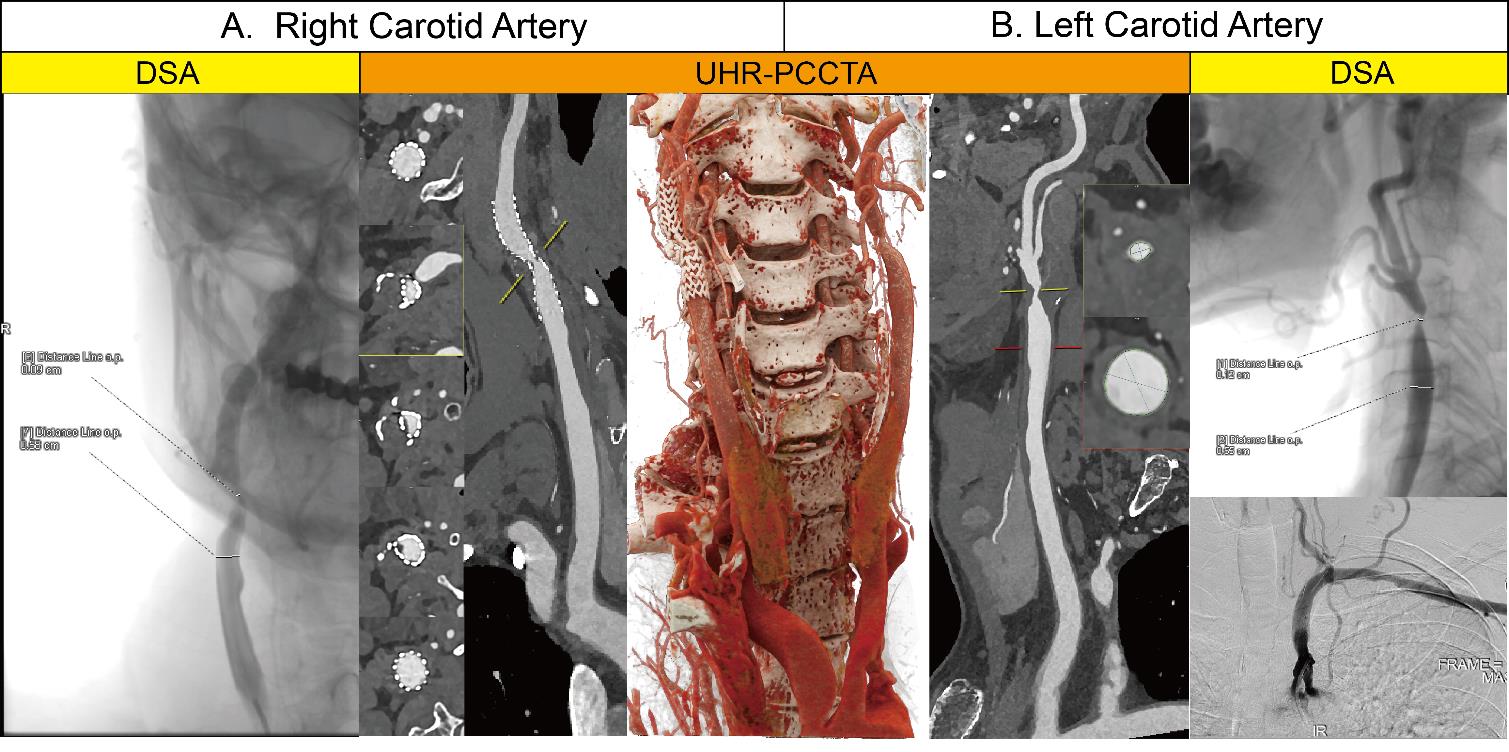
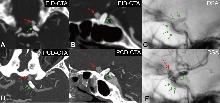
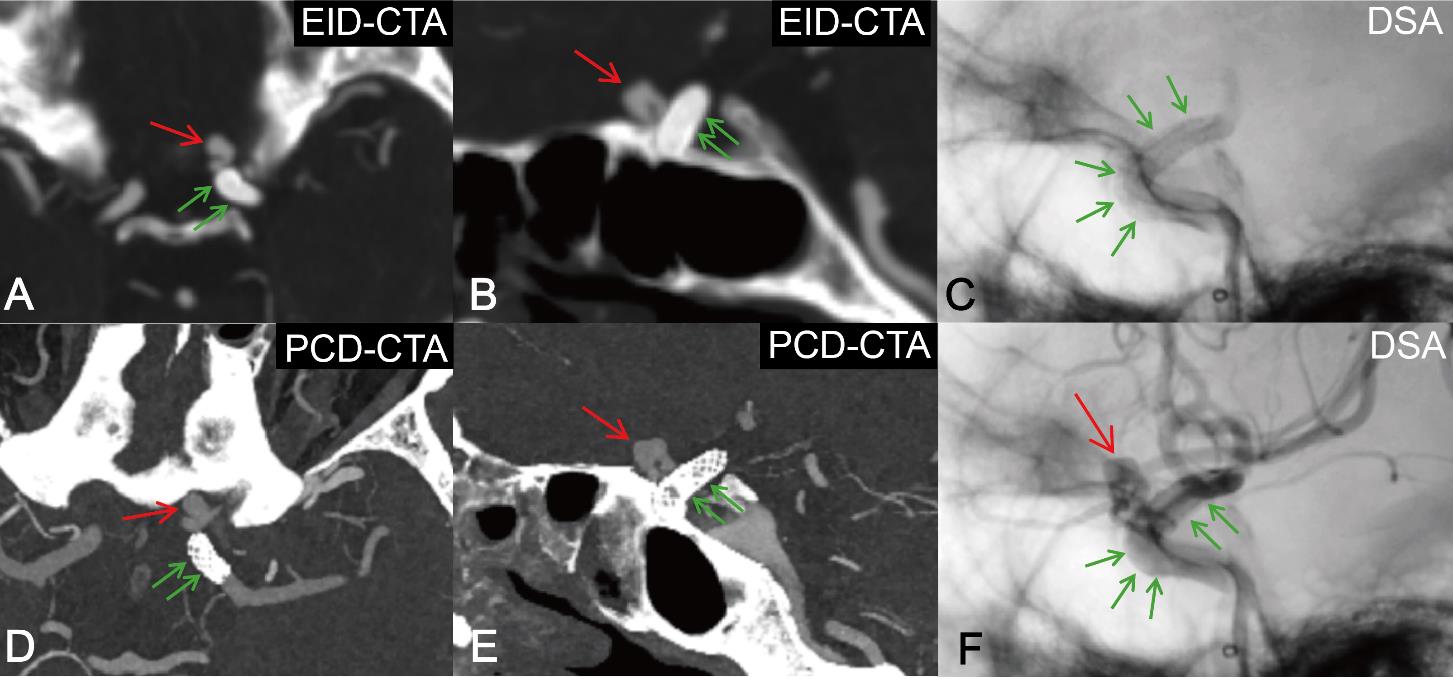
Figure 6
A 68 year old male patient with left internal carotid artery ocular segment (C6 segment) vesicular aneurysmNote:Imaging follow-up after DSA-guided flow-diverter deployment for a blister aneurysm in the C6 segment of the left internal carotid artery. Immediate post-procedure digital subtraction angiography (DSA), one-week follow-up energy-integrating detector CT angiography (EID-CTA)[0.6 mm slice thickness, presented as maximum intensity projection (MIP)], and three-month follow-up ultra-high-resolution photon-counting CT angiography (UHR-PCCTA)(0.2 mm slice thickness, MIP). UHR-PCCTA clearly visualized the detailed structure of the flow-diverter device and the residual aneurysm, whereas EID-CTA demonstrated limited visualization. Red arrows indicate the aneurysm; green arrows indicate the flow-diverter device.
| [1] | 中华医学会放射学分会,《中华放射学杂志》光子计数CT临床应用协作组. 光子计数CT临床应用专家共识[J]. 中华放射学杂志,2025,59(4):364-383. |
| Chinese Society of Radiology Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Journal of Radiology Photon-Counting CT Clinical Application Collaborative Group. Expert consensus on clinical application of photon-counting CT[J]. Chin J Radiol,2025,59(4):364-383. | |
| [2] | 陈海燕, 杨永波, 刘璐璐, 等. 光子计数探测器CT初步临床应用的研究进展[J]. 中华放射学杂志,2022,56(2):213-216. |
| CHEN H Y, YANG Y B, LIU L L, et al. Research progress of clinical application of spectrum CT based on photon-counting detector[J]. Chin J Radiol,2022,56(2):213-216. | |
| [3] |
张龙江, 卢光明. 勇立潮头,努力提升我国光子计数CT的临床研究和应用水平[J]. 国际医学放射学杂志,2024,47(6):629-630, 635.
doi: 10.19300/j.2024.S21750 |
| ZHANG L J, LU G M. Standing at the forefront:striving to improve the clinical research and application of photon counting CT in China[J]. Int J Med Radiol,2024,47(6):629-630, 635. | |
| [4] |
ABEL F, SCHUBERT T, WINKLHOFER S. Advanced neuroimaging with photon-counting detector CT[J]. Invest Radiol,2023,58(7):472-481.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000984 pmid: 37158466 |
| [5] | CADEMARTIRI F, MELONI A, PISTOIA L, et al. Dual source photon-counting computed tomography-part Ⅱ: clinical overview of neurovascular applications[J]. J Clin Med,2023,12(11):3626. |
| [6] |
BENSON J C, CAMPEAU N G, DIEHN F E, et al. Photon-counting CT in the head and neck: current applications and future prospects[J]. Am J Neuroradiol,2024,45(8):1000-1005.
doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A8265 pmid: 38964861 |
| [7] | 中国医师协会神经介入专业委员会中国颅内动脉瘤计划研究组. 颅内动脉瘤影像学判读中国指南(2024版)[J]. 中华神经外科杂志,2024,40(8):757-773. |
| The Chinese Intracranial Aneurysm Program Research Group of the Neurointerventional Professional Committee of the Chinese Medical Association. Chinese guidelines for imaging interpretation of intracranial aneurysms (2024 edition)[J]. Chin J Neurosurg,2024,40(8):757-773. | |
| [8] |
BENDER M T, WENDT H, MONARCH T, et al. Small aneurysms account for the majority and increasing percentage of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A 25-year, single institution study[J]. Neurosurgery,2018,83(4):692-699.
doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyx484 pmid: 29029314 |
| [9] | HE N, LYU H, ZHANG Y, et al. Increased diagnostic accuracy and better morphology characterization of unruptured intracranial aneurysm by ultra-high-resolution photon-counting detector CT angiography[J/OL]. J Neurointerv Surg,2025[2025-04-05].https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40185624/. |
| [10] | HE N, ZHANG Y, LI Z, et al. Ultrahigh-resolution photon-counting detector CTA of the head and neck: image quality assessment and vascular kernel optimization[J]. Am J Roentgenol,2025,224(1):e2431763. |
| [11] | 中华医学会神经外科学分会, 中国卒中学会脑血管外科分会, 国家神经系统疾病医学中心, 等. 中国未破裂颅内动脉瘤临床管理指南(2024版)[J]. 中华医学杂志,2024,104(21):1918-1939. |
| Society of Neurosurgery of Chinese Medical Association, Society of Cerebrovascular Surgery of Chinese Stroke Association, National Center for Neurological Disorders, et al. Chinese guideline for the clinical management of patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms (2024)[J]. Natl Med J China,2024,104(21):1918-1939. | |
| [12] | BYL A, KLEIN L, SAWALL S, et al. Photon-counting normalized metal artifact reduction (NMAR) in diagnostic CT[J]. Med Phys,2021,48(7):3572-3582. |
| [13] | SCHMITT N, WUCHERPFENNIG L, ROTKOPF L T, et al. Metal artifacts and artifact reduction of neurovascular coils in photon-counting detector CT versus energy-integrating detector CT - in vitro comparison of a standard brain imaging protocol[J]. Eur Radiol,2023,33(2):803-811. |
| [14] | TÓTH A, CHO JY, WILSON E, O'DOHERTY J, et al. Photon-counting CT imaging of a patient with coiled and untreated intracranial saccular aneurysms[J/OL]. Neuroradiol J,2025[2025-04-05].https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39881477/. |
| [15] | PALLASCH F B, RAU A, REISERT M, et al. Impact of different metal artifact reduction techniques in photon-counting computed tomography head and neck scans in patients with dental hardware[J]. Eur Radiol,2024,34(6):3742-3749. |
| [16] | 中华医学会神经病学分会神经血管介入协作组, 中国医师协会神经内科医师分会神经介入专业委员会, 中国研究型医院学会介入神经病学专业委员会. 中国颅内外大动脉非急性闭塞血管内介入治疗专家共识[J]. 中华内科杂志,2020,59(12):932-941. |
| Neurovascular Intervention Group of Chinese Society of Neurology, Chinese Medical Association, Professional Committee of Neurological Intervention, Society of Neurology, Chinese Medical Doctor Association, Professional Committee of Interventional Neurology, Chinese Research Hospital Association. Expert consensus: endovascular treatment in non-acute occlusion of intracranial and extracranial large vessel in China[J]. Chin J Intern Med,2020,59(12):932-941. | |
| [17] | 刘翔宇, 王嵇, 所世腾, 等. 超高分辨率光子计数探测器CT评估颈动脉支架经皮置入术后再狭窄1例[J]. 中华放射学杂志,2025,59(1):103-104. |
| LIU X Y, WANG J, SUO S T, et al. Evaluation of in-stent restenosis after carotid artery stent implantation with ultra-high-resolution photon-counting detector CT: a case report[J]. Chin J Radiol,2025,59(1):103-104. | |
| [18] |
SHAMI A, SUN J, GIALELI C, et al. Atherosclerotic plaque features relevant to rupture-risk detected by clinical photon-counting CT ex vivo: a proof-of-concept study[J]. Eur Radiol Exp,2024,8(1):14.
doi: 10.1186/s41747-023-00410-4 pmid: 38286959 |
| [19] | CAU R, SABA L, BALESTRIERI A, et al. Photon-counting computed tomography in atherosclerotic plaque characterization[J]. Diagnostics (Basel),2024,14(11):1065. |
| [20] | DAHAL S, RAJA A Y, SEARLE E, et al. Components of carotid atherosclerotic plaque in spectral photon-counting CT with histopathologic comparison[J]. Eur Radiol,2023,33(3):1612-1619. |
| [21] | MELONI A, CAU R, SABA L, et al. Photon-counting computed tomography angiography of carotid arteries: a topical narrative review with case examples[J]. Diagnostics (Basel),2024,14(18):2012. |
| [22] | FARNSWORTH P J, CAMPEAU N G, DIEHN F E, et al. High-resolution computed tomography angiography of the orbit using a photon-counting computed tomography scanner[J/OL]. Interv Neuroradiol,2023[2025-04-05].https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37401156/. |
| [23] | HARVEY E C, FENG M, JI X, et al. Impacts of photon counting CT to maximum intensity projection (MIP) images of cerebral CT angiography: theoretical and experimental studies[J]. Phys Med Biol,2019,64(18):185015. |
| [24] | 中国卒中学会神经介入分会. 症状性颅内动脉粥样硬化性狭窄血管内治疗中国专家共识2022[J]. 中国卒中杂志,2022,17(8):863-888. |
| Chinese Stroke Association, Chinese Interventional Neuroradiology Society. Chinese experts consensus on endovascular treatment for symptomatic intracranial Atherosclderotic Stenosis 2022[J]. Chin J Stroke,2022,17(8):863-888. | |
| [25] | LUDOVICHETTI R, GORUP D, KREPUSKA M, et al. Ultra-high resolution CT angiography for the assessment of intracranial stents and flow diverters using photon counting detector CT[J/OL]. J Neurointerv Surg,2025[2025-04-05].https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39438133/. |
| [26] | DACHS T M, HAUCK S R, KERN M, et al. In-stent restenosis in peripheral arterial disease: ultra-high-resolution photon-counting versus third-generation dual-source energy-integrating detector CT phantom study in seven different stent types[J]. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol,2025,48(1):65-74. |
| [27] | DECKER J A, O'DOHERTY J, SCHOEPF U J, et al. Stent imaging on a clinical dual-source photon-counting detector CT system-impact of luminal attenuation and sharp kernels on lumen visibility[J]. Eur Radiol,2023,33(4):2469-2477. |
| [28] | DE BEUKELAER F, HALAL M EL, DE BEUKELAER S, et al. Photon-counting ct-angiography to assess intracranial stents and flow diverters in comparison to digital subtraction angiography[J/OL]. Clin Neuroradiol,2025[2025-04-05].https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40343459/. |
| [29] | VERELST E, BULS N, DE MEY J, et al. Stent appeara-nce in a novel silicon-based photon-counting CT prototype: ex vivo phantom study in head-to-head comparison with conventional energy-integrating CT[J]. Eur Radiol Exp,2023,7(1):23. |
| [30] | HIGAKI F, HIRAMATSU M, YASUHARA T, et al. Cranial and spinal computed tomography (CT) angiography with photon-counting detector CT: comparison with angiographic and operative findings[J]. Jpn J Radiol,2025,43(2):143-151. |
| [31] |
HE N, LYU H, LU Y, et al. Accurate detection of spinal dural arteriovenous fistula with spinal photon-counting computed tomography angiography: a report of two cases[J]. Stroke,2025,56(2):e44-e46.
doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.124.049475 pmid: 39676653 |
| [32] |
BENSON J C, RAJENDRAN K, LANE J I, et al. A new frontier in temporal bone imaging: photon-counting detector CT demonstrates superior visualization of critical anatomic structures at reduced radiation dose[J]. Am J Neuroradiol,2022,43(4):579-584.
doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A7452 pmid: 35332019 |
| [33] | 孙钢. 光子计数CT成像技术的临床应用[J]. 中国研究型医院,2023,10(6):23-27. |
| SUN G. Clinical applications of photon counting CT ima-ging technology[J]. Chin Res Hosp,2023,10(6):23-27. |
| [1] | CHANG Rui, LI Jiqiang, YANG Yanzhao, CHAI Weimin, YAN Fuhua, DONG Haipeng.. Evaluation value of single-phase images from photon-counting CT-based low-dose pancreatic dynamic volume perfusion scanning for pancreatic cancer imaging [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2025, 24(02): 155-162. |
| [2] | CAI Xinxin, DENG Rong, XU Xinxin, XU Zhihan, CHANG Rui, DONG Haipeng, LIN Huimin, YAN Fuhua. Study on consistency between liver fat fraction quantification based on photon-counting CT and MRI proton density fat fraction [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2025, 24(02): 146-154. |
| [3] | HUANG Ruikun, YANG Yanzhao, CHAI Weimin. Advances in application of photon-counting CT for pancreatic imaging [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2025, 24(02): 111-117. |
| [4] | XU Pengyu, CHI Cheng, ZHANG Xiaoxia. Application progress of BLUE and modified protocols in diagnosing and monitoring pulmonary lesions in EICU patients [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(05): 542-549. |
| [5] | FENG Yuan, HE Zhao, SUN Qingfang, SUN Bomin, YAN Fuhua, YANG Guangzhong. Advances in interventional magnetic resonance imaging and its clinical applications [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(02): 108-113. |
| [6] | Aging and Cognitive Impairment Branch of Shanghai Society of Aging and Degenerative Diseases. Expert consensus on neuroimaging diagnosis of dementia and cognitive impairment (2023) [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(01): 30-39. |
| [7] | WANG Yanchun, LU Renquan. The application value of determination of hemostasis and thrombosis in tumor patients [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(04): 341-347. |
| [8] | CHEN Chen, ZHANG Yue, HU Xiaobo. The clinical evaluation and optimization of alarm Threshold setting for Sysmex UF5000 UTI [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2020, 19(02): 168-171. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||