

Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice ›› 2025, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (02): 204-211.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2025.02.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Jinghao1, GUO Haiyan1, GAN Guifang1, CHEN Fuxiang1,2( )
)
Received:2025-01-13
Accepted:2025-04-02
Online:2025-04-25
Published:2025-07-11
Contact:
CHEN Fuxiang
E-mail:chenfxsh@163.com
CLC Number:
LIU Jinghao, GUO Haiyan, GAN Guifang, CHEN Fuxiang. Value of miR-2355-3p,miR-337-3p and miR-99a-5p detection in early screening of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2025, 24(02): 204-211.
Table 1
miRNA primer sequences
| Primer | Primer sequence(5’→3’) |
|---|---|
| miR-2355-5p RT | 5’-GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTA TTCGCACTGGATACGACATCTCC-3’ |
| miR-2355-5p Forward | 5’-AAGCGCCTATTGTCCTTGCTGT-3’ |
| miR-2355-5p Reverse | 5’-ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG-3’ |
| miR-337-3p RT | 5’-GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT ATTCGCACTGGATACGACGAAGAA-3’ |
| miR-337-3p Forward | 5’-AAGCGACCCTCCTATATGATGC-3’ |
| miR-337-3p Reverse | 5’-GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGT-3’ |
| miR-99a-5p RT | 5’-GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT ATTCGCACTGGATACGACCACAAG-3’ |
| miR-99a-5p Forward | 5’-AACACGTGAACCCGTAGATCCG-3’ |
| miR-99a-5p Reverse | 5’-ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG-3’ |
| U6 Forward | 5’-CTACTCTTTCTTCAAATCCC-3’ |
| U6 Reverse | 5’-GCTCTACCACCACATCCT-3’ |
Table 2
Comparison of relative expression levels of miR-2355-3p, miR-337-3p and miR-99a-5p between the HNSCC and the normal control group
| Groups | N | miR-2355-3p | miR-337-3p | miR-99a-5p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 60 | 0.062±0.051 | 0.070±0.044 | 0.311±0.202 |
| HNSCC | 60 | 0.222±0.142 | 0.190±0.103 | 0.207±0.152 |
| NC vs HNSCC | P<0.001(t=-8.211) | P<0.001(t=-8.264) | P=0.002(t=3.190) |
Table 3
Relationship between miR-2355-3p, miR-337-3p, miR-99a-5p and clinical pathological characteristics of HNSCC patients
| Indice | N | miR-2355-3p | miR-337-3p | miR-99a-5p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $\bar{x}\pm s$ | P value(t) | $\bar{x}\pm s$ | Pvalue(t) | $\bar{x}\pm s$ | P value(t) | ||||
| Sex | 0.858(-0.180) | 0.861(0.176) | 0.471(0.726) | ||||||
| Male | 33 | 0.219±0.144 | 0.192±0.113 | 0.220±0.146 | |||||
| Female | 27 | 0.226±0.142 | 0.187±0.092 | 0.191±0.160 | |||||
| Age | 0.947(-0.066) | 0.710(-0.373) | 0.211(-1.266) | ||||||
| ≥60 | 35 | 0.221±0.133 | 0.185±0.098 | 0.186±0.138 | |||||
| <60 | 25 | 0.223±0.156 | 0.196±0.112 | 0.236±0.168 | |||||
| TNM Stage | |||||||||
| Stage Ⅰ-Ⅱ | 36 | 0.128±0.055 | <0.001(-9.704) | 0.136±0.067 | <0.001(-5.997) | 0.219±0.165 | 0.446(0.767) | ||
| Stage Ⅲ-Ⅳ | 24 | 0.363±0.110 | 0.271±0.096 | 0.188±0.131 | |||||
| Lymph nodes metastasis | <0.001(9.773) | <0.001(5.782) | 0.597(-0.532) | ||||||
| With | 23 | 0.369±0.108 | 0.272±0.098 | 0.193±0.131 | |||||
| Without | 37 | 0.130±0.057 | 0.138±0.068 | 0.215±0.164 | |||||
| Tumor size | <0.001(4.484) | <0.001(5.331) | 0.595(0.535) | ||||||
| >2 cm | 35 | 0.282±0.123 | 0.239±0.082 | 0.216±0.146 | |||||
| ≤2 cm | 25 | 0.138±0.123 | 0.120±0.090 | 0.194±0.161 | |||||
Figure 1
ROC Curves of Single and Combined Detection of miR-2355-3p, miR-337-3p and miR-99a-5p for Diagnosing HNSCCA: ROC curves of single miRNA in the differential diagnosis of HNSCC; B: ROC curves of two miRNAs combined determinations in the differential diagnosis of HNSCC; C: ROC curve of three miRNAs combined determination in the differential diagnosis of HNSCC.
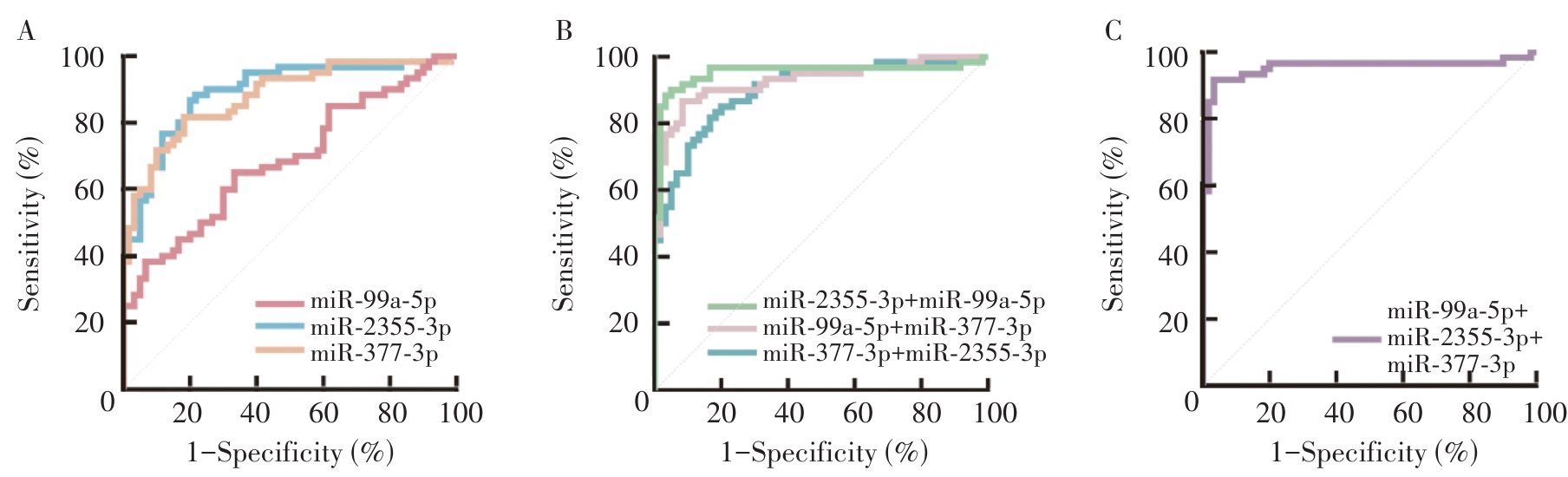
Table 4
Diagnostic efficacy of single and combined detection of miR-2355-3p, miR-337-3p and miR-99a-5p for HNSCC
| Indice | Combined detection equation | AUC(95%CI) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Youden index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-2355-3p | 0.892(0.822-0.941) | 86.67 | 80.00 | 0.6667 | |
| miR-337-3p | 0.877(0.805-0.930) | 81.67 | 81.67 | 0.6333 | |
| miR-99a-5p | 0.686(0.595-0.768) | 38.33 | 93.33 | 0.3167 | |
| miR-2355-3p + miR-337-3p | Logit(P)=-2.925 + 13.398*miR-2355-3p + 12.424*miR-337-3p | 0.898(0.830-0.946) | 85.00 | 80.00 | 0.6500 |
| miR-337-3p + miR-99a-5p | Logit(P)=-1.680 + 36.809*miR-337-3p - 9.040*miR-99a-5p | 0.927(0.865-0.967) | 86.67 | 91.67 | 0.7833 |
| miR-2355-3p + miR-99a-5p | Logit(P)=-1.456 + 43.541*miR-2355-3p - 11.258*miR-99a-5p | 0.952(0.897-0.983) | 90.00 | 95.00 | 0.8500 |
| miR-2355-3p + miR-99a-5p + miR-337-3p | Logit(P)=-1.796 + 33.979*miR-2355-3p + 12.457*miR-337-3p - 11.262*miR-99a-5p | 0.954(0.899-0.984) | 91.67 | 96.67 | 0.8833 |
Figure 2
ROC curves for screening early-stage HNSCC (TNM stage Ⅰ-Ⅱ) based on the individual and combined detection of serum miR-2355-3p, miR-337-3p and miR-99a-5p.A: ROC curves of single miRNA in the differential screening of early-stage HNSCC; B: ROC curves of two miRNAs combined determinations in the differential screening of early-stage HNSCC; C: ROC curve of three miRNAs combined determination in the differential screening of early-stage HNSCC.
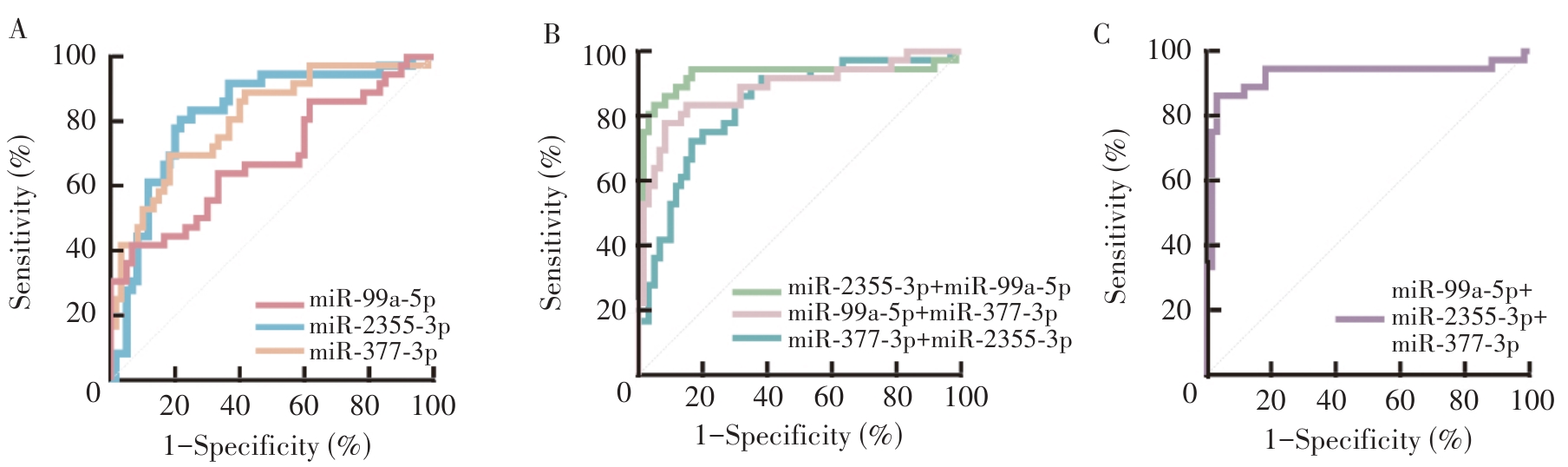
Table 5
The screening efficacy of single and combined detection of serum miR-2355-3p, miR-337-3p and miR-99a-5p for early-stage HNSCC (TNM stage Ⅰ-Ⅱ)
| Indice | Combined detection equation | AUC(95%CI) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Youden index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-2355-3p | 0.820(0.728-0.891) | 80.56 | 78.33 | 0.5889 | |
| miR-337-3p | 0.806(0.712-0.879) | 69.44 | 81.67 | 0.5111 | |
| miR-99a-5p | 0.658(0.554-0.752) | 38.89 | 93.33 | 0.3222 | |
| miR-2355-3p + miR-337-3p | Logit(P)=-2.925 + 13.398*miR-2355-3p + 12.424*miR-337-3p | 0.832(0.742-0.901) | 86.11 | 70.00 | 0.5611 |
| miR-337-3p + miR-99a-5p | Logit(P)=-1.680 + 36.809*miR-337-3p - 9.040*miR-99a-5p | 0.880(0.798-0.937) | 77.78 | 91.67 | 0.6944 |
| miR-2355-3p + miR-99a-5p | Logit(P)=-1.456 + 43.541*miR-2355-3p - 11.258*miR-99a-5p | 0.920(0.846-0.965) | 83.33 | 95.00 | 0.7833 |
| miR-2355-3p + miR-99a-5p + miR-337-3p | Logit(P)=-1.796 + 33.979*miR-2355-3p + 12.457*miR-337-3p - 11.262*miR-99a-5p | 0.923(0.850-0.967) | 86.11 | 96.67 | 0.8278 |
| [1] |
BRAY F, LAVERSANNE M, SUNG H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. Ca-Cancer J Clin,2024,74(3):229-263.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21834 pmid: 38572751 |
| [2] | HAN B, ZHENG R, ZENG H, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022[J]. J Natl Cancer Ctr,2024,4(1):47-53. |
| [3] | PAN X, XU X, WANG L, et al. BASP1 is a prognostic biomarker associated with immunotherapeutic response in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2023,13:1021262. |
| [4] |
OLIVA M, SPREAFICO A, TABERNA M, et al. Immune biomarkers of response to immune-checkpoint inhibitors in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Ann Oncol, 2019,30(1):57-67.
doi: S0923-7534(19)31004-X pmid: 30462163 |
| [5] |
KIM T, CROCE C M. MicroRNA: trends in clinical trials of cancer diagnosis and therapy strategies[J]. Exp Mol Med,2023,55(7):1314-1321.
doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-01050-9 pmid: 37430087 |
| [6] | LEE Y S, DUTTA A. MicroRNAs in Cancer[J]. Annu Rev Pathol-Mech,2009,4(1):199-227. |
| [7] |
ZHAO Y, ZHANG W, YANG Y, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of microRNA-2355-3p and contribution to the progression in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Bioengineered, 2021,12(1):4747-4756.
doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1952367 pmid: 34334103 |
| [8] | MOHAMED F S, JALAL D, FADEL Y M, et al. Profiling of the serum MiRNAome in pediatric egyptian patients with wilms tumor[J]. Front Mol Biosci,2024,11:1453562. |
| [9] |
ZHUANG Q, SHEN J, CHEN Z, et al. MiR-337-3p suppresses the proliferation and metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells via modulating Capn4[J]. Cancer Biomark,2018,23(4):515-525.
doi: 10.3233/CBM-181645 pmid: 30452399 |
| [10] | ZUO X L, CHEN Z Q, WANG J F, et al. miR-337-3p suppresses the proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through targeting JAK2[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2018,8(4):662-674. |
| [11] | CAO X M. Role of miR-337-3p and its target Rap1A in modulating proliferation, invasion, migration and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells[J]. Cancer Biomark,2019,24(3):257-267. |
| [12] | ZHANG R, LENG H, HUANG J, et al. miR-337 regulates the proliferation and invasion in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by targeting HOXB7[J]. Diagn Pathol,2014,9(1):171. |
| [13] | REGEV K, HEALY B C, PAUL A, et al. Identification of MS-specific serum miRNAs in an international multicenter study[J]. Neurol-Neuroimmunol,2018,5(5):e491. |
| [14] |
SAITO R, MARUYAMA S, KAWAGUCHI Y, et al. miR-99a-5p as Possible Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker in Patients With Gastric Cancer[J]. J Surg Res,2020,250:193-199.
doi: S0022-4804(20)30049-4 pmid: 32078828 |
| [15] | SUN X, YAN H. MicroRNA-99a-5p suppresses cell proli-feration, migration, and invasion by targeting isoprenylcysteine carboxylmethyltransferase in oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. J Int Med Res,2021,49(5):0300060520939031. |
| [16] | 武燃, 刘辉, 郑深, 等. MCU通过LETM1维持线粒体钙稳态调节口腔鳞状细胞癌细胞转移[J].重庆医科大学学报,2023,48(4):411-416. |
| WU R, LIU H, ZHENG S, et al. MCU regulates metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by maintaining mitochondrial calcium homeostasis through LETM1[J]. J Chong-qing Med Univ,2023,48(04):411-416. | |
| [17] |
MASTRONIKOLIS N S, DELIDES A, KYRODIMOS E, et al. Insights into metastatic roadmap of head and neck cancer squamous cell carcinoma based on clinical, histopathological and molecular profiles[J]. Mol Biol Rep,2024,51(1):597.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09476-8 pmid: 38683372 |
| [18] | FORTERRE A, KOMURO H, AMINOVA S, et al. A Comprehensive Review of Cancer MicroRNA Therapeutic Delivery Strategies[J]. Cancers,2020,12(7):1852. |
| [19] | MUNKER R, CALIN G A. MicroRNA profiling in cancer[J]. Clin Sci,2011,121(4):141-158. |
| [20] | ALAHDAL M, ELKORD E. Non-coding RNAs in cancer immunotherapy: Predictive biomarkers and targets[J]. Clin Transl Med,2023,13(9):e1425. |
| [21] | CHAKRABORTTY A, PATTON D J, SMITH B F, et al. miRNAs: potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets for cancer[J]. Genes-Basel,2023,14(7):1375. |
| [22] | HAO L, ZHANG Q, QIAO H Y, et al. TRIM29 alters bioe-nergetics of pancreatic cancer cells via cooperation of miR-2355-3p and DDX3X recruitment to AK4 transcript[J]. Mol Ther-Nucl Acids,2021,24:579-590. |
| [23] | 陆开睿, 潘树矿, 胡梦甜,等. miR-2355-3p通过靶向SERPINA3增强口腔鳞状细胞癌细胞的放射敏感性[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2024,40(7):387-392. |
| LU K R, PAN S K, HU M T, et al. miR-2355-3p enhances radiosensitivity of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting SERPINA3[J]. J Clin Stomatol,2024,40(7):387-392. | |
| [24] | DU L, SUBAUSTE M C, DESEVO C, et al. miR-337-3p and its targets STAT3 and RAP1A modulate taxane sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancers[J]. Plos One,2012,7(6):e39167. |
| [25] | WANG Z, WANG J, YANG Y, et al. Loss of has-miR-337-3p expression is associated with lymph node metastasis of human gastric cancer[J]. J Exp Clin Canc Res,2013,32(1):76. |
| [26] |
TAMAI M, TATARANO S, OKAMURA S, et al. microRNA-99a-5p induces cellular senescence in gemcitabine-resistant bladder cancer by targeting SMARCD1[J]. Mol Oncol, 2022,16(6):1329-1346.
doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13192 pmid: 35148461 |
| [27] | CHEN Y, YAO J, QIN Y, et al. Biological role and clinical value of miR-99a-5p in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma ( HNSCC ): A bioinformatics-based study[J]. Febs Open Bio,2018,8(8):1280-1298. |
| [28] | HUANG Q, SHEN Y J, HSUEH C Y, et al. Plasma extracellular vesicles-derived miR-99a-5p: A potential biomarker to predict early head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Pathol Oncol Res,2022,28:1610699. |
| [29] | FEKETE J T, WELKER Á, GYŐRFFY B. miRNA expression signatures of therapy response in squamous cell carcinomas[J]. Cancers,2020,13(1):63. |
| [30] | LUO H, YE Z. Identification of Serum miR-337-3p, miR-484, miR-582, and miR-3677 as promising biomarkers for osteosarcoma[J]. Clin Lab,2021,67(4). |
| [31] |
CHENG C, ZHANG H, DAI Z, et al. Circular RNA circVRK1 suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by regulating zinc finger protein ZNF652 expression via microRNA miR-337-3p[J]. Bioengineered,2021,12(1):5411-5427.
doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1965695 pmid: 34424826 |
| [32] |
PAN Y, LIU G, WANG D, et al. Analysis of lncRNA-mediated ceRNA crosstalk and identification of prognostic signature in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Front Pharmacol,2019,10:150.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00150 pmid: 30886579 |
| [33] |
ZHAO H, LI G, MA Q, et al. MicroRNA-99a-5p in circulating immune cells as a potential biomarker for the early diagnosis of ischemic stroke[J]. Brain Circ,2017,3(1):21.
doi: 10.4103/bc.bc_1_17 pmid: 30276300 |
| [34] | SASANO T, IHARA K, TANAKA T, et al. Risk stratification of atrial fibrillation and stroke using single nucleotide polymorphism and circulating biomarkers[J]. Plos One, 2023,18(10):e0292118. |
| [35] |
TOWLE R, DICKMAN C T D, MACLELLAN S A, et al. Identification of a serum-based microRNA signature that detects recurrent oral squamous cell carcinoma before it is clinically evident[J]. Brit J Cancer,2023,129(11):1810-1817.
doi: 10.1038/s41416-023-02405-9 pmid: 37798371 |
| [36] |
SHI J, BAO X, LIU Z, et al. Serum miR-626 and miR-5100 are promising prognosis predictors for oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Theranostics,2019,9(4):920-931.
doi: 10.7150/thno.30339 pmid: 30867806 |
| [37] |
TORRES A, TORRES K, PESCI A, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of miRNA signatures in tissues and plasma of endometrioid endometrial carcinoma patients[J]. Int J Cancer, 2013, 132(7): 1633-1645.
doi: 10.1002/ijc.27840 pmid: 22987275 |
| [38] | SCHIFFMAN J D, FISHER P G, GIBBS P. Early detection of cancer: past, present, and future[J]. Am Soc of Cli Oncol Educ Book,2015(35):57-65. |
| [39] | LAW H K W, YIM H C H. Early diagnosis of cancer using circulating microbial DNA[J]. Cell Rep Med,2024,5(4): 101502. |
| [1] | WANG Yiyang, LÜ Liangjing. Potential biomarkers for prediction of the efficacy and safety of CAR T cell treatment in systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(03): 263-269. |
| [2] | CHEN Guoqun, CAI Jiaodi. Interpretation of the Clinical Practice Guidelines for Non-small Lung Cancer (version 4 and version 5) of 2022 National Comprehensive Cancer Nerwork(NCCN) [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(01): 8-13. |
| [3] | ZHOU Sifeng, XU Haishu, FAN Xinsheng. Application of metabolomics of different biological samples in study of OSAHS biomarkers [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2022, 21(04): 535-540. |
| [4] | DU Kun, YANG Xi, BIAN Binxian, REN Yiqian, ZHANG Guanghui. Comparison of diagnostic value of new infection biomarker presepsin with procalcitonin, C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 in diagnosis of bacterial infection [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2018, 17(05): 581-585. |
| [5] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2014, 13(06): 588-592. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||