

Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice ›› 2023, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (03): 247-254.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2023.03.07
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
XU Li, GAO Huajie, YANG Mengge, LI Yue, JI Suqiong( )
)
Received:2023-02-02
Online:2023-06-25
Published:2023-11-17
CLC Number:
XU Li, GAO Huajie, YANG Mengge, LI Yue, JI Suqiong. Clinical characteristics of anti-SRP antibody positive immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy with anti-TRIM21/Ro52 antibody positive[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(03): 247-254.
Table 1
Comparison of the indicators and clinical characteristics between the two anti-SRP IMNM groups
| Items | anti-TRIM21/Ro52 positive group (n=23) | anti-TRIM21/Ro52 negative group (n=34) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male | 10(43.5%) | 10(29.4%) | 0.718 |
| Female | 13(56.5%) | 24(70.6%) | |
| Age at myositis diagnosis (years) | 44.9±10.1 | 44.3±18.4 | 0.868 |
| Disease duration (months) | 6 | 5.5 | 0.345 |
| Clinical manifestation | |||
| Upper promixal limbs weakness (≤3,MRC) | 7(30%) | 16(47%) | 0.275 |
| Upper distal limbs weakness (≤3,MRC) | 2(9%) | 10(29%) | 0.097 |
| Lower promixal limbs weakness(≤3,MRC) | 8(35%) | 19(56%) | 0.177 |
| Lower distal limbs weakness (≤3,MRC) | 7(30%) | 11(32%) | >0.999 |
| Atrophy | 10(43.5%) | 9(26.4%) | 0.253 |
| Dyspnea | 1(4.3%) | 2(5.9%) | >0.999 |
| Dysphagia | 5(21.7%) | 7(20.6%) | >0.999 |
| Myalgia | 12(52.1%) | 15(44.1%) | 0.597 |
| Rash | 2(8.7%) | 2(5.9%) | >0.999 |
| Thyroid dysfunction | 10(43.5%) | 15(44.1%) | 0.563 |
| Tumor marker abnormality | 8(34.8%) | 13(38.2%) | 0.752 |
| Laboratory examinations | |||
| CK (U/L) | 2629 | 1795 | 0.49 |
| LDH (U/L) | 541 | 534 | 0.79 |
| ALT (U/L) | 97 | 83 | 0.626 |
| AST (U/L) | 83 | 88 | 0.771 |
| Cr (umol/L) | 35 | 43±15 | 0.141 |
| Myoglobin (ng/mL) | 605±460 | 284±307 | 0.071 |
| CK-MB (ng/mL) | 98±90 | 54.4 | 0.877 |
| cTnI (pg/mL) | 31±41 | 28.4 | 0.339 |
| WBC (×109/L) | 11.685 | 6.98 | 0.044 |
| Neutro (×109/L) | 8.18 | 3.93 | 0.034 |
| Lym (×109/L) | 2.18 | 2.11 | 0.864 |
| ASS antibody | 3 (13%) | 2 (5.9%) | 0.384 |
| ANA (titer 1∶1000) | 6 (42.9%) | 4 (26.7%) | 0.008 |
| ANA (titer 1∶3200) | 4 (28.6%) | 5 (33.3%) | |
| ILD | 5 (21.7%) | 1 (2.9%) | 0.034 |
| Cardiac dysfunction | 5 (21.7%) | 10(29.4%) | 0.542 |
| Treatment | |||
| Symptomatic treatment | 1 (4.3%) | 5(14.7%) | |
| Glucocorticoid monotherapy | 10(43.5%) | 14(41.2%) | |
| Glucocorticoid and Immunosuppressant | 12(52.2%) | 15(44.1%) | |
| Outcome | |||
| Basically normal | 4 (17.4%) | 4 (11.8%) | 0.076 |
| Marked improvement | 18 (78.3%) | 24(70.6%) | |
| No improvement | 0 | 5(14.7%) | |
| Relapse | 1(4.3%) | 1(2.9%) |

Figure 1
Distribution characteristics of serum myositis antibodies in two groups of anti-SRP (+) IMNM patients Anti-TRIM21/Ro52 positive group (n=23) Anti-TRIM21/Ro52 negative group (n=34) MSAs: anti-SRP, anti-HMGCR, anti-Jo-1, anti-PL-7, anti-Mi-2 and anti-NXP antibody; MAAs: anti-SSA,anti-SSB,anti-PM-Scl75 and anti-Ku antibody
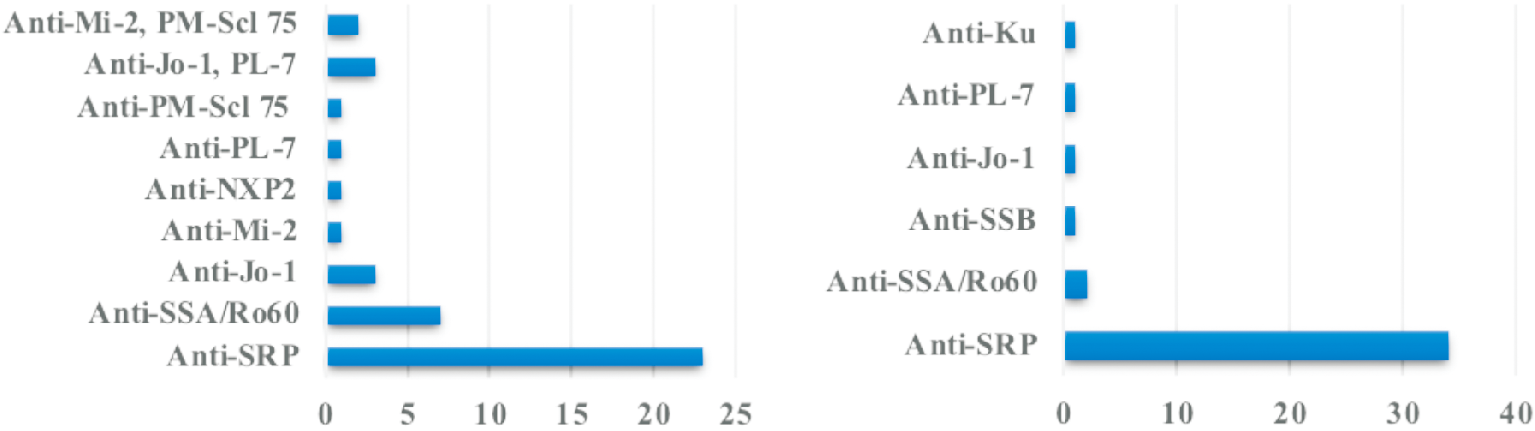
Table 2
Correlation of anti-Ro52 antibody expression with clinical characters in IMNM patients
| Indice | Anti-Ro52 antibody | High titer ANA |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-Ro52 antibody | - | 0.351 (0.008) |
| Creatine kinase | 0.098 (0.487) | 0.381 (0.005) |
| WBC count | 0.274 (0.043) | 0.018 (0.894) |
| Neutro count | 0.29 (0.035) | -0.027 (0.847) |
| High titer ANA | 0.351 (0.008) | - |
| ILD | 0.312 (0.019) | 0.141 (0.301) |
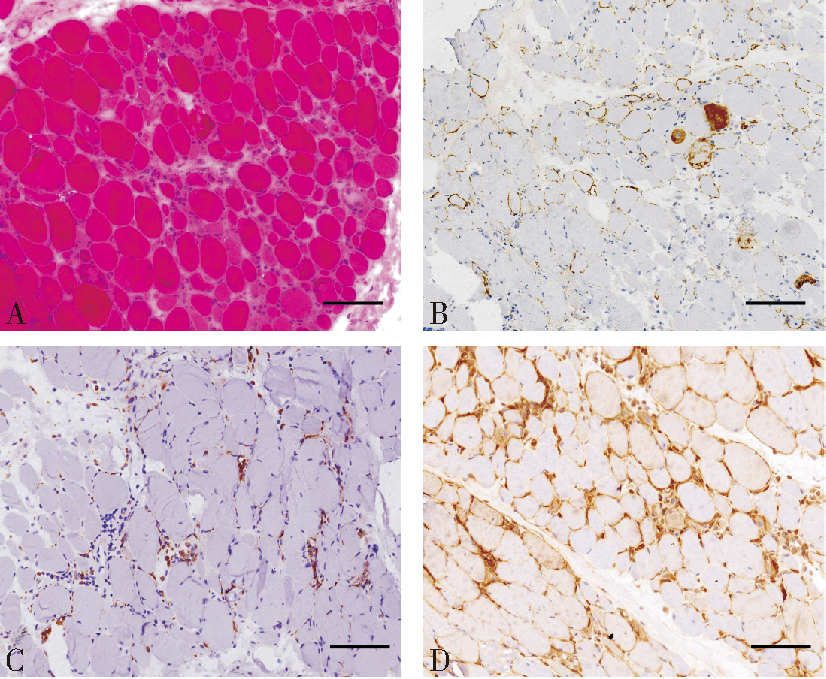
Figure 2
Representative images of anti-TRIM21 /Ro52 antibody positive anti-SRP (+) IMNM patients(×200) A: Representative images of hematoxylin-eosin (HE)-stained sections showing numerous necrotic, atrophy and degenerating fibers; B: Representative images of sarcolemma and sarcoplasmic MAC deposition on fibers in biopsied samples of anti-TRIM21 /Ro52 antibody positive anti-SRP (+) IMNM patients; C: Representative images of CD68 in necrotic and normal fibres with a diffusely staining pattern; D: Representative images of upregulation of MHC-I. Original magnification: ×200.
| [1] |
ALLENBACH Y, MAMMEN A L, BENVENISTE O, et al. 224th ENMC International Workshop: Clinico-sero-pathological classification of immune-mediated necrotizing myopathies Zandvoort, The Netherlands, 14-16 October 2016[J]. Neuromuscular Disorders, 2018, 28(1):87-99.
doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2017.09.016 URL |
| [2] | MA X, BU B-T. Anti-SRP immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy: a critical review of current concepts[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2022, 13. |
| [3] |
ALLENBACH Y, BENVENISTE O, STENZEL W, et al. Immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy: clinical features and pathogenesis[J]. Nature Reviews Rheumatology, 2020, 16(12):689-701.
doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-00515-9 pmid: 33093664 |
| [4] | SUZUKI S, NISHIKAWA A, KUWANA M, et al. Inflammatory myopathy with anti-signal recognition particle antibodies: case series of 100 patients[J]. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 2015, 10. |
| [5] | GHIRARDELLO A, BORELLA E, BEGGIO M, et al. Myositis autoantibodies and clinical phenotypes[J]. Auto- immunity highlights, 2014, 5(3):69-75. |
| [6] | 严婷婷, 薛静. 抗Ro52/TRIM21抗体在结缔组织病中临床作用的研究进展[J]. 基础医学与临床, 2021, 41(9):1360-5. |
| YAN Ting-ting, XUE Jing. Research progress of clinical effects of anti-Ro52 /TRIM21 antibody in connective tissue diseases[J]. Basic & Clinical Medicine. 2021, 41(9):1360-1365. | |
| [7] |
NAKKEN B, JONSSON R, BOLSTAD A I. Polymorphisms of the Ro52 gene associated with anti-Ro 52-kd autoantibodies in patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome[J]. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 2001, 44(3):638-46.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1529-0131 URL |
| [8] | ZAMPELI E, MAVROMMATI M, MOUTSOPOULOS H M, et al. Anti-Ro52 and/or anti-Ro60 immune reactivity: autoantibody and disease associations[J]. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology, 2020, 38(4):S134-S41. |
| [9] |
CAVAZZANA I, FRANCESCHINI F, QUINZANINI M, et al. Anti-Ro/SSA antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: Clinical and immunologic associations[J]. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology, 2006, 24(1):59-64.
pmid: 16539820 |
| [10] |
OKE V, WAHREN-HERLENIUS M. The immunobiology of Ro52 (TRIM21) in autoimmunity: a critical review[J]. Journal of Autoimmunity, 2012, 39(1-2):77-82.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2012.01.014 pmid: 22402340 |
| [11] | FERREIRA J P, ALMEIDA I, MARINHO A, et al. Anti-ro52 antibodies and interstitial lung disease in connective tissue diseases excluding scleroderma[J]. ISRN rheumatology, 2012:415272. |
| [12] |
SABBAGH S, PINAL-FERNANDEZ I, KISHI T, et al. Anti-Ro52 autoantibodies are associated with interstitial lung disease and more severe disease in patients with juvenile myositis[J]. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 2019, 78(7):988-95.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-215004 pmid: 31018961 |
| [13] |
RUTJES S A, EGBERTS W, JONGEN P, et al. Anti-Ro52 antibodies frequently co-occur with anti-Jo-1 antibodies in sera from patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathy[J]. Clinical and Experimental Immunology, 1997, 109(1):32-40.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1997.4081308.x pmid: 9218821 |
| [14] |
PATERNOSTRO-SLUGA T, GRIM-STIEGER M, POSCH M, et al. Reliability and validity of the Medical Research Council (MRC) scale and a modified scale for testing muscle strength in patients with radial palsy[J]. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 2008, 40(8):665-671.
doi: 10.2340/16501977-0235 URL |
| [15] |
TATEBE N, SADA K-E, ASANO Y, et al. Anti-SS-A/Ro antibody positivity as a risk factor for relapse in patients with polymyositis/dermatomyositis[J]. Modern Rheumatology, 2018, 28(1):141-6.
doi: 10.1080/14397595.2017.1317377 pmid: 28463039 |
| [16] |
SHAO C, SUN Y, HUANG H, et al. Myositis specific antibodies are associated with isolated anti-Ro-52 associated interstitial lung disease[J]. Rheumatology, 2022, 61(3):1083-91.
doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab488 URL |
| [17] |
BRAUNER S, ZHOU W, BACKLIN C, et al. Reduced expression of TRIM21/Ro52 predicts poor prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients with and without rheumatic disease[J]. Journal of Internal Medicine, 2015, 278(3):323-32.
doi: 10.1111/joim.12375 pmid: 25880119 |
| [18] |
KONG H J, ANDERSON D E, LEE C H, et al. Cutting edge: Autoantigen Ro52 is an interferon inducible E3 ligase that ubiquitinates IRF-8 and enhances cytokine expression in macrophages[J]. Journal of Immunology, 2007, 179(1):26-30.
pmid: 17579016 |
| [19] |
STRANDBERG L, ARNBROSI A, ESPINOSA A, et al. Interferon-alpha induces up-regulation and nuclear translocation of the Ro52 autoantigen as detected by a panel of novel Ro52-specific monoclonal antibodies[J]. Journal of Clinical Immunology, 2008, 28(3):220-31.
doi: 10.1007/s10875-007-9157-0 pmid: 18071879 |
| [20] | 郑艺明, 郝洪军, 刘怡琳, 等. Ro52抗体与其他肌炎抗体共阳性的相关性研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2020, 52(06):1088-92. |
| ZHENG Yi-ming, HAO Hong-jun, LIU Yi-lin et al. Correlation study on anti-Ro52 antibodies frequently co-occur with other myositis- specific and myositis-associated autoantibodies[J]. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences). 2020, 52(6):1088-1092. | |
| [21] | 徐莉, 杨梦歌, 张清, 等. 免疫介导的坏死性肌病重叠综合征患者的临床特点分析[J]. 国际神经病学神经外科学杂志, 2022, 49(5):7-12. |
| XU Li, YANG Meng-Ge, ZHANG Qing, et al. Clinical features of immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy overlap syndrome[J]. Journal of International Neurology and Neurosurgery. 2022, 49(5):7-12. | |
| [22] | 赵婷, 王玉粦, 张少军, 等. 结缔组织病相关间质性肺病发生疾病进展的危险因素及血清铁蛋白对其预测价值[J]. 中外医学研究, 2022, 20(14):8-12. |
| ZHAO Ting, WANG Yulin, ZHANG Shaojun, et al. Risk factors for progression of connective tissue disease associated interstitial lung disease and the predictive value of serum ferritin[J]. Chinese and Foreign Medical Research, 2022, 20(14):8-12 | |
| [23] | VOJINOVIC T, CAVAZZANA I, CERUTI P, et al. Predictive features and clinical presentation of interstitial lung disease in inflammatory myositis[J]. Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology, 2021, 60(1):87-94. |
| [24] |
BAUHAMMER J, BLANK N, MAX R, et al. Rituximab in the treatment of jo1 antibody-associated antisynthetase syndrome: anti-Ro52 positivity as a marker for severity and treatment response[J]. Journal of Rheumatology, 2016, 43(8):1566-74.
doi: 10.3899/jrheum.150844 pmid: 27252419 |
| [25] | XING X, LI A, LI C. Anti-Ro52 antibody is an independent risk factor for interstitial lung disease in dermatomyositis[J]. Respiratory Medicine, 2020, 172. |
| [26] |
GE Y, YANG H, XIAO X, et al. Interstitial lung disease is not rare in immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy with anti-signal recognition particle antibodies[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2022, 22(1):14.
doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01802-1 pmid: 35000598 |
| [27] |
KAO A H, LACOMIS D, LUCAS M, et al. Anti-signal recognition particle autoantibody in patients with and patients without idiopathic inflammatory myopathy[J]. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 2004, 50(1):209-15.
pmid: 14730618 |
| [28] | SCHNEIDER-GOLD C, HARTUNG H-P, GOLD R. Mycophenolate mofetil and tacrolimus: New therapeutic options in neuroimmunological diseases[J]. Muscle & Nerve, 2006, 34(3):284-91. |
| [29] | CHEN B, WU Q, KE G T, et al. Efficacy and safety of tacrolimus treatment for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7. |
| [30] |
LIU C C, GUI M C, CAO Y Y, et al. Tacrolimus improves symptoms of children with myasthenia gravis refractory to prednisone[J]. Pediatric Neurology, 2017, 77:42-7.
doi: S0887-8994(17)30315-6 pmid: 29074055 |
| [31] |
GE Y, ZHOU H, SHI J, et al. The efficacy of tacrolimus in patients with refractory dermatomyositis/polymyositis: a systematic review[J]. Clinical Rheumatology, 2015, 34(12):2097-103.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-3065-0 pmid: 26328518 |
| [1] | ZHOU Xiaodie, CHEN Weiwei, YU Bo, WANG Xuan, WANG Jianjun, SHI Qunli, RAO Qiu, BAO Wei. Clinicopathological features of urothelial carcinoma [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(03): 292-299. |
| [2] | SONG Luqian, CHANG Chunkang. Interpretation of clinical practice guidelines for myelodysplastic syndrome (version 1, 2023) of National Comprehensive Cancer Nerwork(NCCN) [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(02): 116-120. |
| [3] | XU Jiankun, ZHOU Luting, ZHANG Wenjing, XU Haimin, WANG Chaofu. The prognostic value of CA9 expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(01): 37-43. |
| [4] | WANG Han, LU Haidi, WANG Lei, CONG Wenming, ZHENG Jianming, BAI Chenguang. Clinicopathological features of 2 cases of squamous cell carcinoma and 2 cases of adenosquamous carcinoma [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(01): 44-49. |
| [5] | WANG Jin, GUO Rui, LI Biao, ZHANG Xiaozhe. Prognostic evaluation of extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type(ENKTL) with 18F-FDG PET/CT [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2022, 21(06): 702-709. |
| [6] | XIE Wen, LIANG Huaiyu, DONG Lei, YUAN Fei, WANG Chaofu, GUO Yan. Analysis of genetic status of pivotal driver genes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and their correlation with clinicopathologic features [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2022, 21(05): 581-587. |
| [7] | LI Lei, YUAN Fei, WANG Chaofu, XU Haimin, WANG Ting. Ampullary adenocarcinoma: analysis of the clinicopathological features and prognostic factors [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2022, 21(03): 355-361. |
| [8] | FENG Guowei, ZHANG Xiaojuan, GUO Rui, GUAN Zhe, WANG Yue. The prognostic value of pretreatment 18F-FDG PET/CT in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2021, 20(06): 533-539. |
| [9] | LIANG Yali, ZHAO Haigang, XIANG Guangyu. The stress-induced hyperglycemia ratio in the prognosis prediction of patients with acute ischemic stroke one year after thrombolytic therapy [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2021, 20(06): 562-566. |
| [10] | FENG Mingyang, DING Yezhou, ZHAO Qingqing, ZHAO Gangde, LOU Shike, ZHENG Chao, SUN Xuehua, LIU Kehui, LIN Lanyi, XIE Qing, ZHENG Lan, WANG HUI. Relation of TCM syndrome type in traditional Chinese medicine with liver failure staging in Western medicine in patients with liver failure [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2021, 20(04): 391-395. |
| [11] | RUI Wenbin, XU Da, ZHU Yu, WU Yuxuan, WANG Haofei, WANG Chenghe, YUAN Fei. Expression of HIF-1α and its relationship with prognosis in papillary renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2021, 20(03): 265-370. |
| [12] | ZHANG Zhongwen, ZUO Xiangrong, ZHENG Xuhui, CAO Quan, Li Xinli, LI Yanxiu. Correlation between gene polymorphism of chromosome 3q26 rs12696304 and 1-year survival rate after acute heart failure in an elderly Han population in South China [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2020, 19(06): 565-571. |
| [13] | XU Zhaoping, WANG Haofei. Expression of ZNF692 gene in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its relationship with prognosis [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2020, 19(03): 292-296. |
| [14] | DU Hailei, CHEN Ling, LUO Fangxiu, LI Yong, CHENG Qijian, ZHU Lianggang, HANG Junbiao. The prognostic value of Beclin-1 and Bcl-2 and its relationship with pathological characteristics in patients with non-small cell lung cancer [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2020, 19(03): 258-263. |
| [15] | LUO Xiaoying, ZHU Xuemei, XU Yan, ZHANG Fengru, WU Liqun, QI Wenhang. Value of NT-proBNP level in predicting prognosis of hospitalized elderly pneumonia patients without heart failure history [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2019, 18(03): 319-322. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||