

内科理论与实践 ›› 2025, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (03): 232-241.doi: 10.16138/j.1673-6087.2025.03.08
收稿日期:2024-06-21
出版日期:2025-06-28
发布日期:2025-09-01
通讯作者:
姚玮艳
E-mail:ywy11419@rjh.com.cn
Received:2024-06-21
Online:2025-06-28
Published:2025-09-01
Contact:
YAO Weiyan
E-mail:ywy11419@rjh.com.cn
摘要:
目的:构建基于坏死性凋亡相关的长链非编码RNA(necroptosis-related long non-coding RNA,NRL)的胰腺癌预后风险模型。 方法:方法:通过TCGA和GTEx数据库获得基因表达数据和临床数据,包括171例正常胰腺组织和178例胰腺癌组织样本。使用LASSO回归及Cox回归分析筛选出与胰腺癌预后相关的NRL来构建预后风险模型。通过受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线评估模型的预测价值,并在临床蛋白质组肿瘤分析联盟(Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium,CPTAC)数据库中验证。同时进行基因富集分析、免疫浸润分析以及化疗药物的敏感性分析。 结果:共筛选出8个与胰腺癌预后有关的NRL(LINC01559、TMEM161B-AS1、AL157392.3、AC099850.3、AC136475.3、AL162274.2、MIR217HG、UNC5B-AS)用于构建预后风险模型。生存分析提示高风险组患者具有较差的预后(P<0.001),ROC曲线提示模型的风险预测能力较好。回归分析证实该模型是预测胰腺癌患者预后的独立因素(P<0.05),同时CPTAC数据集验证该模型的有效性。此外,高、低风险组中信号通路的富集、免疫细胞浸润程度、肿瘤突变负荷水平、免疫检查位点的表达以及对化疗药物的敏感性均存在差异(均P<0.05)。 结论:基于生物信息学筛选出的8个NRL构建的风险预后模型,能够有效预测胰腺癌的预后,并与胰腺癌中免疫细胞浸润水平以及免疫相关治疗药物密切相关。
中图分类号:
杨子云, 姚玮艳. 基于生物信息学构建胰腺癌坏死性凋亡相关lncRNA的预后风险评分模型[J]. 内科理论与实践, 2025, 20(03): 232-241.
YANG Ziyun, YAO Weiyan. Construction of necroptosis-related lncRNA risk model of pancreatic cancer based on bioinformatics[J]. Journal of Internal Medicine Concepts & Practice, 2025, 20(03): 232-241.
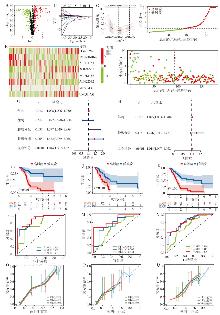
图2
坏死性凋亡相关lncRNA风险模型的构建和验证 A:387个差异表达的坏死性凋亡相关lncRNA火山图;B:OS相关蛋白的调谐参数交叉验证误差曲线;C:用于计算最低标准的垂直假想线;D:PAAD患者的风险评分分布;E.PAAD中8种lncRNA表达谱的热图;F:PAAD患者的生存状态散点图,行表示lncRNA,列表示患者;绿色到红色表示从低到高的趋势表达;G:Uni-Cox回归分析;H:Multi-Cox回归分析。I:训练集中高风险与低风险的生存分析;J:测试集;K:所有集;L:训练集中1、2和3年预后风险模型的ROC曲线;M:测试集;N:所有样本;O:测试集;P:所有集;Q:训练集1、2和3年预后风险模型的校准曲线。
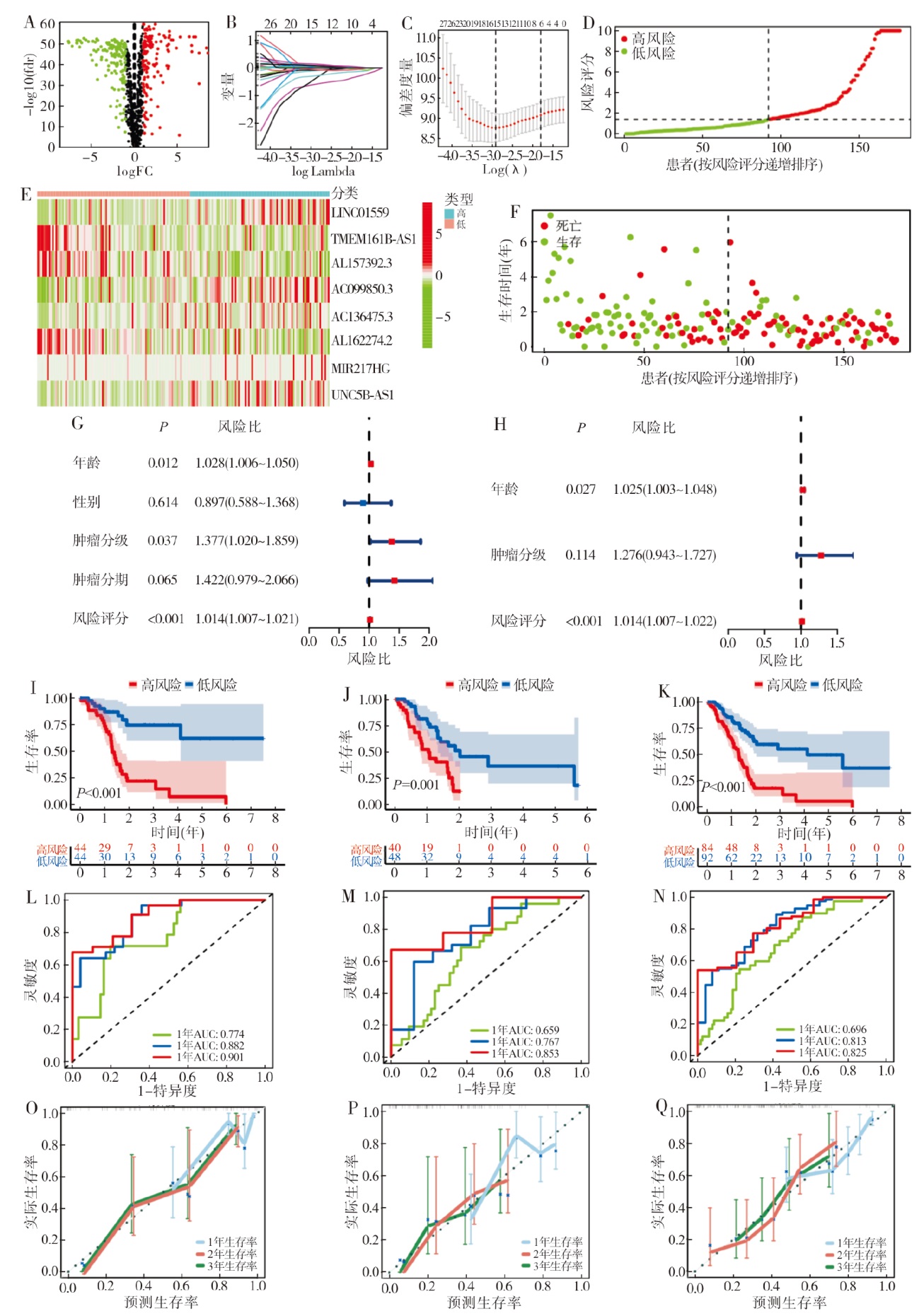
表1
不同临床特征的单因素与多因素分析
| 特征 | 例数(n) | 单因素分析 | 多因素分析 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 风险比(95% CI) | P | 风险比 (95% CI) | P | |||
| 年龄 | 178 | 1.028 (1.006 ~ 1.050) | 0.012 | 1.025 (1.003 ~ 1.048) | 0.027 | |
| 性别 | 178 | 0.897 (0.588 ~ 1.368) | 0.614 | |||
| 女性 | 80 | 基准值(Ref) | ||||
| 男性 | 98 | 0.897 (0.588 ~ 1.368) | 0.614 | |||
| 分级 | 176 | 1.377 (1.020 ~ 1.859) | 0.037 | 1.276 (0.943 ~ 1.048) | 0.114 | |
| 1 | 31 | 基准值(Ref) | ||||
| 2 | 95 | 1.795 (0.898 ~ 3.586) | 0.098 | |||
| 3 | 48 | 2.286 (1.101 ~ 4.748) | 0.027 | |||
| 4 | 2 | 1.650 (0.210 ~ 12.995) | 0.634 | |||
| 分期 | 175 | 1.422 (0.979 ~ 2.066) | 0.065 | |||
| 2 | 147 | 基准值(Ref) | 基准值(Ref) | |||
| 4 | 4 | 0.886 (0.217 ~ 3.620) | 0.866 | 0.920 (0.225 ~ 3.762) | 0.907 | |
| 1 | 21 | 0.305 (0.123 ~ 0.761) | 0.011 | 0.348 (0.139 ~ 0.871) | 0.054 | |
| 3 | 3 | 0.668 (0.093 ~ 4.807) | 0.688 | 0.704 (0.098 ~ 5.078) | 0.728 | |
| 风险评分 | 178 | 1.014 (1.007 ~ 1.021) | < 0.001 | 1.014 (1.006 ~ 1.022) | < 0.001 | |
| [1] | Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer Statistics, 2021[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(1):7-33.. |
| [2] | Huang X, Ding L, Liu X, et al. Regulation of tumor microenvironment for pancreatic cancer therapy[J]. Biomaterials, 2021,270:120680. |
| [3] |
Gong Y, Fan Z, Luo G, et al. The role of necroptosis in cancer biology and therapy[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1):100.
doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1029-8 pmid: 31122251 |
| [4] |
Chen X, Zeh HJ, Kang R, et al. Cell death in pancreatic cancer: from pathogenesis to therapy[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 18(11):804-823.
doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00486-6 pmid: 34331036 |
| [5] | Ando Y, Ohuchida K, Otsubo Y, et al. Necroptosis in pancreatic cancer promotes cancer cell migration and invasion by release of CXCL5[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(1):e0228015. |
| [6] |
Zhang Y, Yue Q, Cao F, et al. Necroptosis-related lncRNA signatures determine prognosis in breast cancer patients[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1):11268.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15209-3 pmid: 35787661 |
| [7] | Luo J, Peng J, Xiao W, et al. A novel necroptosis-related lncRNA signature for predicting prognosis and immune response of colon cancer[J]. Front Genet, 2022,13:984696. |
| [8] | Du X, Pu X, Wang X, et al. A novel necroptosis-related lncRNA based signature predicts prognosis and response to treatment in cervical cancer[J]. Front Genet, 2022,13:938250. |
| [9] | Ghafouri-Fard S, Fathi M, Zhai T, et al. LncRNAs: novel biomarkers for pancreatic cancer[J]. Biomolecules, 2021, 11(11):1665. |
| [10] | Zhao Z, Liu H, Zhou X, et al. Necroptosis-related lncRNAs: predicting prognosis and the distinction between the cold and hot tumors in gastric cancer[J]. J Oncol, 2021,2021:6718443. |
| [11] | Tang R, Xu J, Zhang B, et al. Ferroptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis in anticancer immunity[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2020, 13(1):110. |
| [12] |
Xiong Y, Kong X, Fang K, et al. Establishment of a novel signature to predict prognosis and immune characteristics of pancreatic cancer based on necroptosis-related long non-coding RNA[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2023, 50(9):7405-7419.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08663-3 pmid: 37452900 |
| [13] | Mo J, Cui Z, Wang Q, et al. Integrated analysis of necroptosis-related lncRNAs for prognosis and immunotherapy of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma[J]. Front Genet, 2022,13:940794. |
| [14] | Kumari A, Sahoo J, De M. 2D-MoS2-supported copper peroxide nanodots with enhanced nanozyme activity: application in antibacterial activity[J]. Nanoscale, 2023, 15(48):19801-19814. |
| [15] | Shi Z, Li G, Li Z, et al. TMEM161B-AS1 suppresses proliferation, invasion and glycolysis by targeting miR-23a-3p/HIF1AN signal axis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. J Cell Mol, 2023, 27(4):591-592. |
| [16] | Ho KH, Huang TW, Shih CM, et al. Glycolysis-associated lncRNAs identify a subgroup of cancer patients with poor prognoses and a high-infiltration immune microenvironment[J]. BMC Med, 2021, 19(1):59. |
| [17] |
Zhong F, Liu S, Hu D, et al. LncRNA AC099850.3 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion through PRR11/PI3K/AKT axis and is associated with patients prognosis[J]. J Cancer, 2022, 13(3):1048-1060.
doi: 10.7150/jca.66092 pmid: 35154469 |
| [18] | Ye J, Li H, Wei J, et al. Risk scoring system based on lncRNA expression for predicting survival in hepatocellular carcinoma with cirrhosis[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2020, 21(6):1787-1795. |
| [19] |
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation[J]. Cell, 2011, 144(5):646-674.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013 pmid: 21376230 |
| [20] |
Acloque H, Adams MS, Fishwick K et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: the importance of changing cell state in development and disease[J]. J Clin Invest, 2009, 119(6):1438-1449.
doi: 10.1172/JCI38019 pmid: 19487820 |
| [21] |
Wei D, Wang L, Kanai M, et al. KLF4α up-regulation promotes cell cycle progression and reduces survival time of patients with pancreatic cancer[J]. Gastroenterology, 2010, 139(6):2135-2145.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.08.022 pmid: 20727893 |
| [22] |
He S, Wang L, Miao L, et al. Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines cellular necrotic response to TNF-alpha[J]. Cell, 2009, 137(6):1100-1111.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.021 pmid: 19524512 |
| [23] | Yamamoto K, Venida A, Yano J, et al. Autophagy promotes immune evasion of pancreatic cancer by degrading MHC-I[J]. Nature, 2020, 581(7806):100-105. |
| [24] |
Hiraoka N, Onozato K, Kosuge T, et al. Prevalence of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells increases during the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its premalignant lesions[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2006, 12(18):5423-5434.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0369 pmid: 17000676 |
| [25] |
Chen Y, Song Y, Du W, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages: an accomplice in solid tumor progression[J]. J Biomed Sci, 2019, 26(1):78.
doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0568-z pmid: 31629410 |
| [26] | Campillo N, Falcones B, Otero J, et al. Differential oxygenation in tumor microenvironment modulates macrophage and cancer cell crosstalk: novel experimental setting and proof of concept[J]. Front Oncol, 2019,9:43. |
| [27] | Wang Z, Zhao J, Zhao H, et al. Infiltrating CD4/CD8 high T cells shows good prognostic impact in pancreatic cancer[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2017, 10(8):8820-8828. |
| [28] |
Galon J, Bruni D. Approaches to treat immune hot, altered and cold tumours with combination immunotherapies[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2019, 18(3):197-218.
doi: 10.1038/s41573-018-0007-y pmid: 30610226 |
| [29] |
Chen J, Wang S, Jia S, et al. Integrated analysis of long non-coding RNA and mRNA expression profile in pancreatic cancer derived exosomes treated dendritic cells by microarray analysis[J]. J Cancer, 2018, 9(1):21-31.
doi: 10.7150/jca.21749 pmid: 29290766 |
| [30] | Lawlor RT, Mattiolo P, Mafficini A, et al. Tumor mutational burden as a potential biomarker for immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer: systematic review and still-open questions[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2021, 13(13):3119. |
| [31] | Cullis J, Das S, Bar-Sagi D. Kras and tumor immunity: friend or foe?[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med, 2018, 8(9):a031849. |
| [32] | Blagih J, Buck MD, Vousden KH. p53, cancer and the immune response[J]. J Cell Sci, 2020, 133(5):jcs237453. |
| [33] | Abu Samaan TM, Samec M, Liskova A, et al. Paclitaxel’s mechanistic and clinical effects on breast cancer[J]. Biomolecules, 2019, 9(12):789. |
| [34] | Bacherikov VA. Total synthesis, mechanism of action, and antitumor efficacy of camptothecin and some of its analogues[J]. Anticancer Agents Med Chem, 2022, 22(20):3438-3465. |
| [35] | Bongiovanni A, Liverani C, Recine F, et al. Phase-Ⅱ trials of pazopanib in metastatic neuroendocrine neoplasia (mNEN)[J]. Front Oncol, 2020,10:414. |
| [36] | Yuan R, Kay A, Berg WJ, et al. Targeting tumorigenesis: development and use of mTOR inhibitors in cancer therapy[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2009,2:45. |
| [1] | 郭根宇, 张楚乔, 许尹梅, 等. 通过整合生物信息学分析与机器学习揭示糖尿病足溃疡缺氧相关生物标志物[J]. 组织工程与重建外科杂志, 2025, 21(3): 238-. |
| [2] | 金佳斌, 马君俊, 叶枫, 马诗瑜, 陈敬贤. 基于网络药理学、分子对接和双样本孟德尔随机化分析探讨槐耳抗胰腺癌的作用机制[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2025, 30(03): 247-255. |
| [3] | 徐荆庶, 施建华, 顾海雁, 陈蕾, 钱孝琳, 陆璐, 钮登. 1992—2021年上海市徐汇区户籍居民胰腺癌死亡率趋势分析[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2025, 30(01): 34-40. |
| [4] | 雷朝闻尉, 饶佳玲, 周梦雪, 杨虹. 胰腺脂肪沉积的危险因素及相关疾病的研究进展[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2025, 24(01): 72-79. |
| [5] | 张珂, 张唯一, 孙海天, 曹铭峰, 张新焕. 细胞失巢相关基因PDK4与2型糖尿病发病相关——基于生物信息的研究[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2025, 24(01): 27-34. |
| [6] | 盛兆晴, 刘晓红. 阿尔茨海默病自噬相关基因的筛选及其通路分析[J]. 内科理论与实践, 2024, 19(04): 236-242. |
| [7] | 汪卓鑫, 黄昕洋, 金依洵, 王立夫. 通过机器学习识别急性胰腺炎的铜死亡特征基因[J]. 内科理论与实践, 2024, 19(04): 224-230. |
| [8] | 欧丹, 蔡钢, 陈佳艺. RAD51AP1基因表达在三阴性乳腺癌脑转移中的生物信息分析[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2024, 23(02): 146-154. |
| [9] | 胡彬蔚, 沈柏用. 胰腺癌新辅助治疗的优势和进展[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2024, 29(01): 74-80. |
| [10] | 任加强, 武帅, 莫建涛, 周灿灿, 韩亮, 仵正. 磁性氧化铁纳米粒子应用于胰腺癌靶向诊疗的研究进展[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2024, 29(01): 61-66. |
| [11] | 王美文, 傅宁稹, 王伟珅, 任新平. 胰十二指肠联合静脉切除重建术后早期血管栓塞的床旁超声诊断及危险因素分析[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2024, 29(01): 54-60. |
| [12] | 齐中, 邢颖, 程石. 人工智能技术在当前生物学获益为主的胰腺癌诊疗模式中的发展方向[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2024, 29(01): 5-9. |
| [13] | 陆忠晓, 汤杰, 黄文海. 以SEER为基础的列线图构建和胰腺癌病人生存预测[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2024, 29(01): 46-53. |
| [14] | 陈佳浩, 姜翀弋. 2023年第2版《NCCN胰腺癌临床实践指南》更新解读[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2024, 29(01): 10-13. |
| [15] | 张太平, 翁桂湖, 刘悦泽. 可切除胰腺癌新辅助治疗的研究及指南解读,肯定还是否定?[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2024, 29(01): 1-4. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
