

外科理论与实践 ›› 2021, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (06): 543-549.doi: 10.16139/j.1007-9610.2021.06.017
收稿日期:2020-05-09
出版日期:2021-11-25
发布日期:2022-07-27
通讯作者:
毛志海
E-mail:zhihaimao@163.com
基金资助:
LIU Shiguang, ZHAO Jingkun, LU Aiguo, MAO Zhihai( )
)
Received:2020-05-09
Online:2021-11-25
Published:2022-07-27
Contact:
MAO Zhihai
E-mail:zhihaimao@163.com
摘要:
目的:分析CXCL5(C-X-C motif ligand 5)蛋白与程序性死亡配体1(programmed death ligand 1,PD-L1)在结肠直肠癌组织中的表达,并探讨两者与临床特征的关系及预后价值。方法:收集2010年至2011年行腹腔镜切除手术的结肠直肠癌病人肿瘤组织及癌旁正常组织标本,共78例。同时对所有病例进行临床资料收集及预后随访。标本制备组织芯片,行免疫组织化学染色。采用免疫危险评分标准对CXCL5、PD-L1表达进行评分,分析其表达与各项临床病理参数关系。最后分析CXCL5、PD-L1表达与结肠直肠癌病人预后的关系。结果:结肠直肠癌组织中CXCL5、PD-L1表达均高于癌旁正常组织,与肿瘤直径、TNM分期相关。Cox单因素回归分析显示,TNM分期、CXCL5高表达、PD-L1高表达是结肠直肠癌病人总生存率的预后危险因素。多因素回归分析显示,TNM分期和PD-L1高表达是结肠直肠癌病人总生存率的独立预后危险因素。CXCL5与PD-L1均高表达的病人预后最差。结论:CXCL5与PD-L1联合可对结肠直肠癌病人进行危险度分层,预测病人预后。
中图分类号:
刘诗光, 赵敬坤, 陆爱国, 毛志海. 趋化因子CXCL5和程序性死亡配体 1在结肠直肠癌组织的表达与病人预后的关系[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2021, 26(06): 543-549.
LIU Shiguang, ZHAO Jingkun, LU Aiguo, MAO Zhihai. Expression of chemokine CXCL5 and programme death ligand 1 in colorectal cancer tissues are associated with prognosis of patients[J]. Journal of Surgery Concepts & Practice, 2021, 26(06): 543-549.
图1
基于结肠直肠癌病人生存数据的X-tile分析显示CXCL5和PD-L1免疫组织化学染色评分的cut-off值 A、D:以cut-off值为界将队列分成两个子集;X轴表示从低到高(从左到右)的所有潜在cut-off值,定义为低表达子集,Y轴表示从高到低(从上到下)的潜在cut-off值,定义为高表达子集。红色的cut-off 值表示与生存负相关,而绿色着色表示正相关,最佳cut-off值由软件计算而得(相当于AUC曲线下最大面积时的cut-off值);B、E:以直方图显示最佳cut-off值,绿色部分表示低表达,灰色部分表示高表达;C、F:以Kaplan-Meier曲线显示最佳cut-off值。
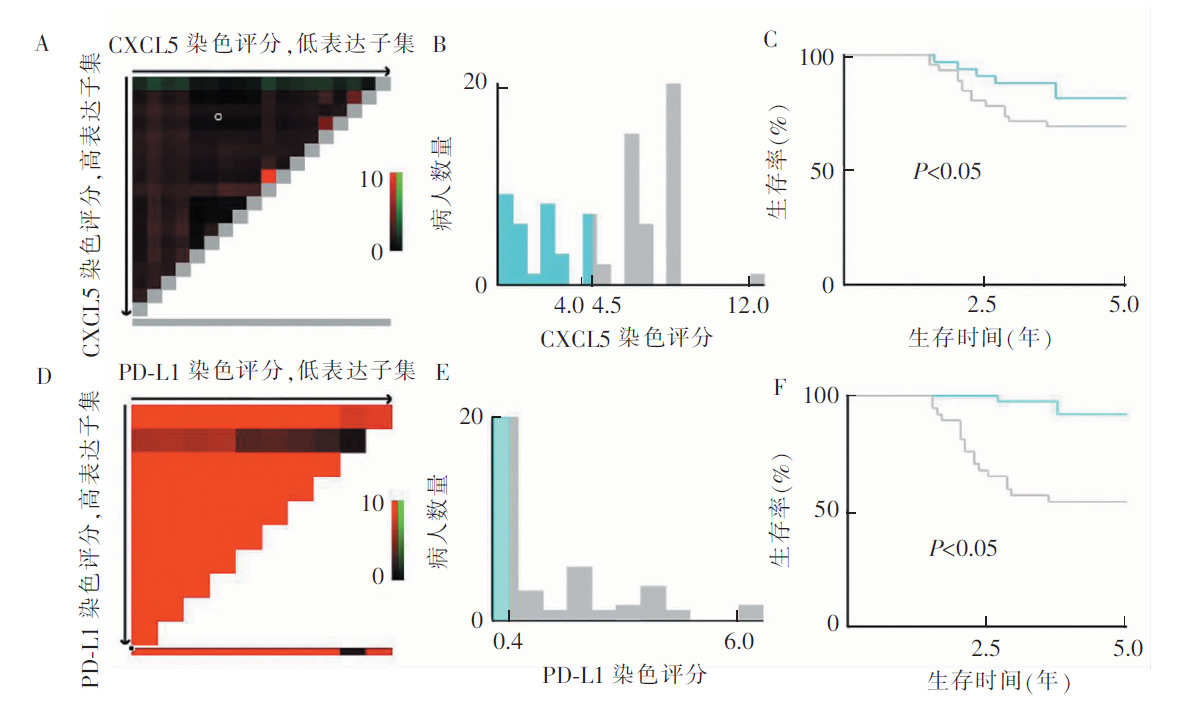
表1
结肠直肠癌组织中CXCL5、PD-L1表达与病人临床特征的关系
| 临床特征 | CXCL5表达 | 统计学数值 | P值 | PD-L1表达 | 统计学数值 | P值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高 | 低 | 高 | 低 | |||||
| 总计 | 48 | 30 | 37 | 41 | ||||
| 性别 | 1.086 | 0.297 | 1.236 | 0.266 | ||||
| 男 | 23 | 18 | 17 | 24 | ||||
| 女 | 25 | 12 | 20 | 17 | ||||
| 年龄(岁) | 0.194 | 0.660 | 0.360 | 0.549 | ||||
| <65 | 28 | 19 | 21 | 26 | ||||
| ≥65 | 20 | 11 | 16 | 15 | ||||
| 组织学 | 3.534 | 0.171 | 2.982 | 0.225 | ||||
| 管状 | 38 | 28 | 29 | 37 | ||||
| 黏液 | 9 | 2 | 7 | 4 | ||||
| 乳头状 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||
| 肿瘤直径(cm) | 3.945 | 0.047 | 4.029 | 0.045 | ||||
| ≥5 | 27 | 10 | 22 | 15 | ||||
| <5 | 21 | 20 | 15 | 26 | ||||
| TNM分期 | 2.735 | 0.003 | 11.733 | 0.008 | ||||
| Ⅰ | 5 | 10 | 4 | 10 | ||||
| Ⅱ | 21 | 12 | 11 | 16 | ||||
| Ⅲ | 16 | 8 | 16 | 15 | ||||
| Ⅳ | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 | ||||
表2
结肠直肠癌病人单因素与多因素Cox回归分析
| 参数 | 总生存率 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | P值 | |
| 单因素分析 | |||
| 年龄(岁)(<65比≥65) | 1.003 | 0.410~2.454 | 0.995 |
| 性别(女比男) | 1.812 | 0.740~4.433 | 0.193 |
| 组织学 | |||
| 乳头状 | 1.000 | .. | 0.222 |
| 管状比乳头状 | 0.164 | 0.021~1.272 | 0.084 |
| 黏液比乳头状 | 0.198 | 0.020~1.948 | 0.165 |
| TNM分期 | |||
| Ⅲ+Ⅳ比Ⅰ+Ⅱ | 0.181 | 0.060~0.541 | 0.002 |
| 肿瘤直径(<5 cm比≥5 cm) | 0.537 | 0.219~1.314 | 0.173 |
| CXCL5(低表达比高表达) | 0.229 | 0.067~0.783 | 0.019 |
| PD-L1(低表达比高表达) | 0.397 | 0.164~0.958 | 0.040 |
| 多因素分析 | |||
| TNM分期 | |||
| Ⅲ+Ⅳ比Ⅰ+Ⅱ | 0.235 | 0.075~0.734 | 0.013 |
| CXCL5(低表达比高表达) | 0.786 | 0.202~3.063 | 0.728 |
| PD-L1(低表达比高表达) | 0.156 | 0.042~0.584 | 0.006 |
| TNM分期 | |||
| Ⅲ+Ⅳ比Ⅰ+Ⅱ | 0.234 | 0.076~0.721 | 0.011 |
| CXCL5(低表达比高表达) | 0.345 | 0.098~1.215 | 0.098 |
| [1] | Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2002[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2005, 55(2):74-108. |
| [2] | 陈万青, 孙可欣, 郑荣寿, 等. 2014年中国分地区恶性肿瘤发病和死亡分析[J]. 中国肿瘤, 2018, 27(1):1-14. |
| [3] | Hegde PS, Chen DS. Top 10 challenges in cancer immunotherapy[J]. Immunity, 2020, 52(1):17-35. |
| [4] | Borsig L, Wolf MJ, Roblek M, et al. Inflammatory chemokines and metastasis-tracing the accessory[J]. Oncogene, 2014, 33(25):3217-3224. |
| [5] | Stillie R, Farooq SM, Gordon JR, et al. The functional significance behind expressing two IL-8 receptor types on PMN[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2009, 86(3):529-543. |
| [6] | Arenberg DA, Keane MP, DiGiovine B, et al. Epithelial- neutrophil activating peptide (ENA-78) is an important angiogenic factor in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. J Clin Invest, 1998, 102(3):465-472. |
| [7] | Begley LA, Kasina S, Mehra R, et al. CXCL 5 promotes prostate cancer progression[J]. Neoplasia, 2008, 10(3):244-254. |
| [8] | Atanackovic D, Luetkens T, Kröger N. Coinhibitory molecule PD-1 as a potential target for the immunotherapy of multiple myeloma[J]. Leukemia, 2014, 28(5):993-1000. |
| [9] | Zhao J, Ou B, Han D, et al. Tumor-derived CXCL5 promotes human colorectal cancer metastasis through activation of the ERK/Elk-1/Snail and AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathways[J]. Mol Cancer, 2017, 16(1):70. |
| [10] | Hsu YL, Hou MF, Kuo PL, et al. Breast tumor-associated osteoblast-derived CXCL5 increases cancer progression by ERK/MSK1/Elk-1/snail signaling pathway[J]. Oncogene, 2013, 32(37):4436-4447. |
| [11] | Sanchez-Lopez E, Flashner-Abramson E, Shalapour S, et al. Targeting colorectal cancer via its microenvironment by inhibiting IGF-1 receptor-insulin receptor substrate and STAT3 signaling[J]. Oncogene, 2016, 35(20):2634-2644. |
| [12] | Chang MS, Mcninch J, Basu R, et al. Cloning and cha-racterization of the human neutrophil-activating peptide (ENA-78) gene[J]. J Biol Chem, 1994, 269(41):25277-25282. |
| [13] | Walz A, Burgener R, Car B, et al. Structure and neutrophil-activating properties of a novel inflammatory peptide (ENA-78) with homology to interleukin 8[J]. J Exp Med, 1991, 174(6):1355-1362. |
| [14] | Z′Graggen K, Walz A, Mazzucchelli L, et al. The C-X-C chemokine ENA-78 is preferentially expressed in intestinal epithelium in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Gastroenterology, 1997, 113(3):808-816. |
| [15] | Lu B, Chen L, Liu L, et al. T-cell-mediated tumor immune surveillance and expression of B7 co-inhibitory molecules in cancers of the upper gastrointestinal tract[J]. Immunol Res, 2011, 50(2-3):269-275. |
| [16] | Hino R, Kabashima K, Kato Y, et al. Tumor cell expression of programmed cell death ligand-1 is a prognostic factor for malignant melanoma[J]. Cancer, 2010, 116(7):1757-1766. |
| [17] | Hou J, Yu Z, Xiang R, et al. Correlation between infiltration of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells and expression of B7-H1 in the tumor tissues of gastric cancer[J]. Exp Mol Pathol, 2014, 96(3):284-291. |
| [18] | Qin T, Zeng YD, Qin G, et al. High PD-L 1 expression was associated with poor prognosis in 870 Chinese patients with breast cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(32):33972-33981. |
| [19] | Shi SJ, Wang LJ, Wang GD, et al. B7-H1 expression is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal carcinoma and regulates the proliferation and invasion of HCT116 colorectal cancer cells[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(10):e76012. |
| [20] | Droeser RA, Hirt C, Viehl CT, et al. Clinical impact of programmed cell death ligand 1 expression in colorectal cancer[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2013, 49(9):2233-2242. |
| [21] | Li Z, Zhou J, Zhang J, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote PD-L1 expression in mice cancer cells via secreting CXCL5[J]. Int J Cancer, 2019, 145(7):1946-1957. |
| [22] | Wang Y, Zhuang Q, Zhou S, et al. Costimulatory molecule B7-H1 on the immune escape of bladder cancer and its clinical significance[J]. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci, 2009, 29(1):77-79. |
| [23] | Speetjens FM, Kuppen PJ, Sandel MH, et al. Disrupted expression of CXCL5 in colorectal cancer is associated with rapid tumor formation in rats and poor prognosis in patients[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2008, 14(8):2276-2284. |
| [24] | 李芮. 综合护理干预对烧伤患者趋势因子及创面愈合的影响[J]. 实用临床护理学杂志, 2017, 2(45):56-59. |
| [25] | 焦海良, 朱斌, 苏瑞洋. 多学科协作诊治模式下结直肠癌术前辅助检查系统的临床应用初步探索[J]. 当代医学, 2017, 23(22):42-44. |
| [1] | 殷剑光, 宗雅萍, 沈晓卉, 赵敬坤, 陆爱国. 同时性多原发结肠直肠癌治疗与预后分析(附39例报告)[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2022, 27(06): 540-544. |
| [2] | 包全, 邢宝才. 复杂双叶多发性结肠直肠癌肝转移外科治疗策略[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2022, 27(02): 128-130. |
| [3] | 张华, 陆炜, 杨承翌, 项明洁. 血清人衰老关键蛋白1检测对结肠直肠癌的诊断和预后价值[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2021, 20(05): 462-465. |
| [4] | 蔡三军. 结肠直肠癌诊治的思考[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2021, 26(04): 297-299. |
| [5] | 张弢, 叶枫, 赵任. 结肠直肠癌的微创手术——在工具和价值间的不断平衡优化[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2021, 26(04): 300-304. |
| [6] | 杨飖, 傅传刚. NOSES在结肠直肠癌手术中的应用现状与展望[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2021, 26(04): 305-311. |
| [7] | 王常刚, 刘坤, 冯浩然, 蒋奕玫, 施毅卿, 陈献则, 宋子甲, 李军, 李佑, 蔡东莉, 赵任. 结肠直肠癌B7S1表达与免疫浸润的关系[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2021, 26(04): 336-342. |
| [8] | 茅届齐, 徐多刚, 张米粒, 肖蕴誉, 明旭, 李雨哲, 曹灿, 于亮, 李继坤. 结肠直肠癌病人D-二聚体升高的研究[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2021, 26(04): 361-366. |
| [9] | 杨盈赤, 宋建宁, 张忠涛. 中国腹腔镜结肠直肠手术的回顾与展望——基于手术病例登记研究和数据库建立的思考[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2021, 26(04): 277-280. |
| [10] | 顾晋. 局部晚期结肠直肠癌治疗和联合脏器切除[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2021, 26(04): 290-296. |
| [11] | 吴春晓, 龚杨明, 顾凯, 庞怡, 鲍萍萍, 王春芳, 施亮, 向詠梅, 窦剑明, 付晨, 施燕. 2016年上海市结肠直肠癌发病和死亡情况与2002—2016年间的变化趋势分析[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2021, 26(04): 325-335. |
| [12] | 程国柱, 蔡国响. 结肠直肠癌腹膜转移的腹腔药物治疗研究[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2021, 26(01): 34-37. |
| [13] | 林松斌, 冯青阳, 许剑民. KRAS基因突变类型预测结肠直肠癌根治术后异时性远处转移[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2021, 26(01): 66-71. |
| [14] | 关天培, 雷子颖, 崔书中. 结肠直肠癌腹膜转移防治临床研究[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2021, 26(01): 7-10. |
| [15] | 邹兴, 赵敬坤, 宗雅萍, 陆爱国. 腹腔镜结肠直肠癌手术吻合口出血的防治[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2021, 26(01): 87-91. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||