

诊断学理论与实践 ›› 2024, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (01): 30-39.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2024.01.005
2030脑与类脑计划变性病痴呆多模影像诊断标准及分子影像技术研究课题组, 上海市衰老与退行性疾病学会衰老与认知障碍分会
收稿日期:2023-03-20
出版日期:2024-02-25
发布日期:2024-05-30
基金资助:Aging and Cognitive Impairment Branch of Shanghai Society of Aging and Degenerative Diseases
Received:2023-03-20
Published:2024-02-25
Online:2024-05-30
摘要:
临床医师面对以认知障碍为主要临床表现的患者,首先应完善结构MRI(或CT替代)检查,以明确其颅内病变和脑萎缩情况。对于伴有特定临床表现的患者,推荐加行特定MRI序列扫描进一步辅助诊断。对于疑似AD源性认知障碍的患者,推荐加行斜冠状位T1加权成像(T1-weighted imaging,T1W1)序列扫描,进行海马内侧颞叶萎缩评分。对于疑似血管性因素或特殊感染(朊蛋白)导致的认知障碍患者,建议加选弥散加权成像(diffusion-weighted imaging,DWI)序列。对于疑似合并锥体外系症状和(或)小血管病变患者,尤其是脑淀粉样血管病及并发糖尿病的认知障碍患者,建议加选磁敏感加权成像序列。常规MRI检查发现可疑占位时,可选用增强MRI和磁共振波谱分析。对于疑似合并肌萎缩侧索硬化的认知障碍患者,可选用弥散张量成像序列。对于怀疑神经变性病导致的痴呆,推荐完善18F-FDG PET和Aβ-PET或tau-PET检查。Aβ-PET显像和tau-PET显像可实现脑内病理蛋白沉积程度和范围的可视化,对于痴呆具有重要的预测和诊断价值,并可用于痴呆的鉴别诊断以及疾病进展评估。此外,静息态功能性MRI、近红外脑功能成像以及一些新兴的影像检查手段,如相位对比脑脊液电影MRI、类淋巴显像已经在认知障碍疾病中开展研究,期待未来能用于临床,更好地辅助认知障碍相关疾病的诊断和鉴别诊断。需要注意的是,神经影像学结果并不能代表疾病的完整诊断和临床症状,必须慎重解读和分析。
中图分类号:
2030脑与类脑计划变性病痴呆多模影像诊断标准及分子影像技术研究课题组, 上海市衰老与退行性疾病学会衰老与认知障碍分会. 痴呆及相关认知障碍的神经影像学诊断专家共识(2023年版)[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2024, 23(01): 30-39.
Aging and Cognitive Impairment Branch of Shanghai Society of Aging and Degenerative Diseases. Expert consensus on neuroimaging diagnosis of dementia and cognitive impairment (2023)[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(01): 30-39.
表1
结构性MRI扫描序列推荐方案
| 推荐加做序列 | 推荐人群 | 推荐依据 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 所有可疑认知障碍患者需完善T1WI、T2WI、FLAIR像(水平位+海马冠状位) | 斜冠状位T1W1 | 疑似AD患者 | 从认知正常人群中鉴别出AD源性痴呆的MTA界值分别是,50-64岁≥1.0(灵敏度和特异度分别为 92.3% 和 68.4%),65~74岁≥1.5(灵敏度和特异度分别为 90.4% 和 85.2%),75~84岁≥2.0(灵敏度和特异度分别为70.8%和82.3%)[ |
| 弥散加权成像 | 疑似血管性因素或特殊感染(朊蛋白)导致的认知障碍患者 | 对于朊蛋白病的诊断能力,灵敏度为90%~95%,特异度为90% 到 100%[ | |
| 磁敏感加权成像 | 疑似合并锥体外系症状和(或)小血管病变,尤其是CAA及并发糖尿病的认知障碍患者 | 在CAA病例中,评估者在SWI序列上评估微出血的评估者之间的可靠性良好(组内r=0.87)[ | |
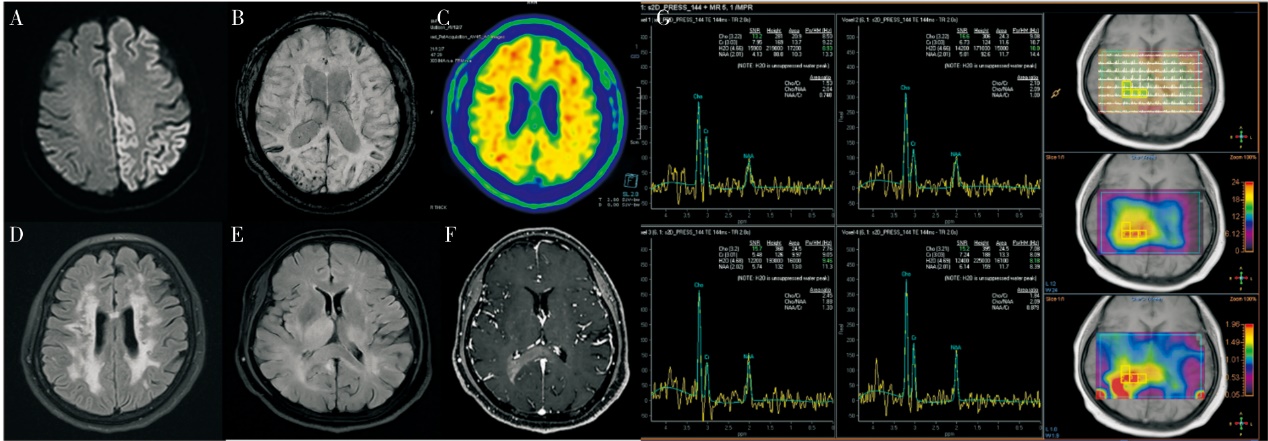
| 增强MRI和MRS | 常规MRI发现关键脑结构可疑占位的患者 | 利用Cho峰和NAA峰可将肿瘤和非肿瘤鉴别,其AUC为0.94,特异度86%,灵敏度90%[ | |
| DTI | 疑似合并ALS的认知障碍患者,如bvFTD | 一项荟萃分析纳入8项研究143例ALS患者和145名健康对照,发现ALS额叶白质,扣带回以及内囊后肢的FA减少[ |
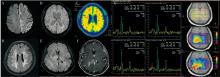
图2
MRI结构相对认知障碍的鉴别诊断 A:女,71岁,言语障碍、反应迟钝1月余,弥散加权成像序列示花边征,结合其他检查临床诊断为散发型Creutzfeldt-Jakob病;B、C:男,54岁,记忆力下降3年余,磁敏感加权成像序列示脑内多发陈旧性小出血灶,双侧额顶颞叶脑回样低信号改变,拟脑皮质表面含铁血黄素沉积(图B),18F-AV45-PET显示双侧大脑皮层广泛淀粉样蛋白沉积(图C),临床诊断为脑淀粉样血管病;D:女,60岁,记忆力减退2月余,Flair序列示广泛脑白质病变,NOTCH3基因检测到杂合变异,c.1819C>T p.R607C,该变异注释为致病/可能致病变异,结合其他检查临床诊断为CADASIL。E、G:女,58岁,记忆力下降2个月,头颅MRI检查示,右侧丘脑、右侧胼胝体压部、胼胝体体部及侧脑室后角、双侧顶叶皮层下信号异常伴局部脑回肿胀并异常强化(图E为MR Flair序列,图F为MRI增强),磁共振波谱分析提示恶性肿瘤可能,患者最终脑活检示高级别胶质瘤。
| [1] | REN R J, YIN P, WANG Z H, et al. The China alzheimer report 2021[J]. J Diagn Concepts Pract, 2021, 20(4):317-337. |
| [2] | AGRONIN M E. Alzheimer's disease and other types of dementia: Clinical Practice Guidelines[M]. 3rd Edition[J]. Shanghai Jiaotong University Press, 2015. |
| [3] |
SMITH E E, BEAUDIN A E. New insights into cerebral small vessel disease and vascular cognitive impairment from MRI[J]. Curr Opin Neurol, 2018, 31(1):36-43.
doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000513 pmid: 29084064 |
| [4] | GROUP. OLOEW, DURIEUX N, PASLEAU F, et al. OxfordThe 2011 levels of evidence. Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine[EB/OL]. (2022-08-24). |
| [5] | CHINESE SOCIETY OF RADIOLOGY. Chinese Expert Consensus on MR Detection Standards for AD[J]. 2019, 53(8). |
| [6] |
WEI M, SHI J, NI J, et al. A new age-related cutoff of medial temporal atrophy scale on MRI improving the diagnostic accuracy of neurodegeneration due to Alzheimer's disease in a Chinese population[J]. BMC Geriatr, 2019, 19(1):59.
doi: 10.1186/s12877-019-1072-8 pmid: 30819102 |
| [7] | ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE BRANCH OF CHINESE AGING WELL ASSOCIATION. Chinese guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer's disease dementia (2020 edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Geriatrics, 2021, 40(3). |
| [8] | BIZZI A, PASCUZZO R, BLEVINS J, et al. Evaluation of a new criterion for detecting prion disease with diffusion magnetic resonance imaging[J]. JAMA Neurol, 2020, 77(9):1141-1149. |
| [9] | CHENG A L, BATOOL S, MCCREARY C R, et al. Susceptibility-weighted imaging is more reliable than T2*-weighted gradient-recalled echo MRI for detecting microbleeds[J]. Stroke, 2013, 44(10):2782-2786. |
| [10] |
MCKNIGHT T R, VON DEM BUSSCHE M H, VIGNERON D B, et al. Histopathological validation of a three-dimensional magnetic resonance spectroscopy index as a predictor of tumor presence[J]. J Neurosurg, 2002, 97(4):794-802.
pmid: 12405365 |
| [11] |
LI J, PAN P, SONG W, et al. A meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging studies in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[J]. Neurobiol Aging, 2012, 33(8):1833-1838.
doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.04.007 pmid: 21621298 |
| [12] | ZHAO W, YIN C, YU F, et al. The value of brain structural magnetic resonance imaging combined with APOE--ε4 Genotype in early diagnosis and disease progression of senile vascular cognitive impairment no dementia[J]. Contrast Media Mol Imaging, 2022,2022:8613024. |
| [13] | GUAN H, WANG C, CHENG J, et al. A parallel attention-augmented bilinear network for early magnetic resonance imaging-based diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Hum Brain Mapp, 2022, 43(2):760-772. |
| [14] | TURHAN G, KÜÇÜK H, ISIK E O. Spatio-temporal convolution for classification of alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment[J]. Comput Methods Programs Biomed, 2022,221:106825. |
| [15] | BAE J, STOCKS J, HEYWOOD A, et al. Transfer learning for predicting conversion from mild cognitive impairment to dementia of Alzheimer's type based on a three-dimensional convolutional neural network[J]. Neurobiol Aging, 2021,99:53-64. |
| [16] |
ZAMANI J, SADR A, JAVADI A H. Diagnosis of early mild cognitive impairment using a multiobjective optimization algorithm based on T1-MRI data[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1):1020.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-04943-3 pmid: 35046444 |
| [17] | HU J, QING Z, LIU R, et al. Deep learning-based classification and voxel-based visualization of frontotemporal dementia and alzheimer's disease[J]. Front Neurosci, 2021,14:626154. |
| [18] |
NG A S L, WANG J, NG K K, et al. Distinct network topology in Alzheimer's disease and behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia[J]. Alzheimers Res Ther, 2021, 13(1):13.
doi: 10.1186/s13195-020-00752-w pmid: 33407913 |
| [19] |
BRIER M R, THOMAS J B, SNYDER A Z, et al. Loss of intranetwork and internetwork resting state functional connections with Alzheimer's disease progression[J]. J Neurosci, 2012, 32(26):8890-8899.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5698-11.2012 pmid: 22745490 |
| [20] |
WHITWELL J L, JONES D T, DUFFY J R, et al. Working memory and language network dysfunctions in logopenic aphasia: a task-free fMRI comparison with Alzheimer's dementia[J]. Neurobiol Aging, 2015, 36(3):1245-1252.
doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.12.013 pmid: 25592958 |
| [21] | GREICIUS M D, SRIVASTAVA G, REISS A L, et al. Default-mode network activity distinguishes Alzheimer's disease from healthy aging: evidence from functional MRI[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2004, 101(13):4637-4642. |
| [22] |
KHAZAEE A, EBRAHIMZADEH A, BABAJANI-FEREMI A. Identifying patients with Alzheimer's disease using resting-state fMRI and graph theory[J]. Clin Neurophysiol, 2015, 126(11):2132-2141.
doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2015.02.060 pmid: 25907414 |
| [23] |
PISTONO A, SENOUSSI M, GUERRIER L, et al. Language network connectivity increases in early alzheimer's disease[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2021, 82(1):447-460.
doi: 10.3233/JAD-201584 pmid: 34024825 |
| [24] | RATHORE S, HABES M, IFTIKHAR M A, et al. A review on neuroimaging-based classification studies and associated feature extraction methods for Alzheimer's di-sease and its prodromal stages[J]. Neuroimage, 2017,155:530-548. |
| [25] |
HALLER S, ZAHARCHUK G, THOMAS D L, et al. Arterial spin labeling perfusion of the brain: emerging clinical applications[J]. Radiology, 2016, 281(2):337-356.
pmid: 27755938 |
| [26] |
BINNEWIJZEND M A, KUIJER J P, BENEDICTUS M R, et al. Cerebral blood flow measured with 3D pseudocontinuous arterial spin-labeling MR imaging in Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment: a marker for disease severity[J]. Radiology, 2013, 267(1):221-230.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.12120928 pmid: 23238159 |
| [27] |
VERFAILLIE S C, ADRIAANSE S M, BINNEWIJZEND M A, et al. Cerebral perfusion and glucose metabolism in Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal dementia: two sides of the same coin?[J] Eur Radiol, 2015, 25(10):3050-3059.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3696-1 pmid: 25899416 |
| [28] | NOBILI F, ARBIZU J, BOUWMAN F, et al. European Association of Nuclear Medicine and European Academy of Neurology recommendations for the use of brain 18 F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in neurodegenerative cognitive impairment and dementia: delphi consensus[J]. Eur J Neurol, 2018, 25(10):1201-1217. |
| [29] | ARBIZU J, FESTARI C, ALTOMARE D, et al. Clinical utility of FDG-PET for the clinical diagnosis in MCI[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2018, 45(9):1497-1508. |
| [30] |
JACK C R JR, BENNETT D A, BLENNOW K, et al. NIA-AA research framework: toward a biological definition of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2018, 14(4):535-562.
doi: S1552-5260(18)30072-4 pmid: 29653606 |
| [31] | STRIKWERDA-BROWN C, HOBBS D A, GONNEAUD J, et al. Association of elevated amyloid and tau positron emission tomography signal with near-term development of alzheimer disease symptoms in older adults without cognitive impairment[J]. JAMA Neurol, 2022, 79(10):975-985. |
| [32] | TIAN M, CIVELEK A C, CARRIO I, et al. International consensus on the use of tau PET imaging agent 18F-flortaucipir in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2022, 49(3):895-904. |
| [33] |
VALOTASSIOU V, MALAMITSI J, PAPATRIANTAF-YLLOU J, et al. SPECT and PET imaging in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Ann Nucl Med, 2018, 32(9):583-593.
doi: 10.1007/s12149-018-1292-6 pmid: 30128693 |
| [34] | REN R, QI J, LIN S, et al. The China Alzheimer report 2022[J]. Gen Psychiatr, 2022, 35(1):e100751. |
| [35] |
DOI T, MAKIZAKO H, SHIMADA H, et al. Brain activation during dual-task walking and executive function among older adults with mild cognitive impairment: a fNIRS study[J]. Aging Clin Exp Res, 2013, 25(5):539-544.
doi: 10.1007/s40520-013-0119-5 pmid: 23949972 |
| [36] | YEUNG M K, SZE SL, WOO J, et al. Altered frontal lateralization underlies the category fluency deficits in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: a near-infrared spectroscopy study[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2016,8:59. |
| [37] | YEUNG M K, SZE S L, WOO J, et al. Reduced frontal activations at high working memory load in mild cognitive impairment: near-infrared spectroscopy[J]. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord, 2016, 42(5-6):278-296. |
| [38] | YOO S H, WOO S W, SHIN M J, et al. Diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment using cognitive tasks: a functional near-infrared spectroscopy study[J]. Curr Alzheimer Res, 2020, 17(13):1145-1160. |
| [39] | NGUYEN T, KIM M, GWAK J, et al. Investigation of brain functional connectivity in patients with mild cognitive impairment: a functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) study[J]. J Biophotonics, 2019, 12(9):e201800298. |
| [40] |
KIM J, YON D K, CHOI K Y, et al. Novel diagnostic tools for identifying cognitive impairment using olfactory-stimulated functional near-infrared spectroscopy: patient-level, single-group, diagnostic trial[J]. Alzheimers Res Ther, 2022, 14(1):39.
doi: 10.1186/s13195-022-00978-w pmid: 35260170 |
| [41] | HO T K K, KIM M, JEON Y, et al. Deep learning-based multilevel classification of alzheimer's disease using non-invasive functional near-infrared spectroscopy[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2022,14:810125. |
| [42] | BEHNKE S, PILOTTO A, LIEPELT-SCARFONE I, et al. Third ventricular width assessed by transcranial ultrasound correlates with cognitive performance in Parkinson's disease[J]. Parkinsonism Relat Disord, 2019,66:68-73. |
| [43] |
CASSINELLI PETERSEN G, ROYTMAN M, CHIANG G C, et al. Overview of tau PET molecular imaging[J]. Curr Opin Neurol, 2022, 35(2):230-239.
doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000001035 pmid: 35191407 |
| [44] | WEIGAND A J, MAASS A, EGLIT G L, et al. What's the cut-point?: a systematic investigation of tau PET thres-holding methods[J]. Alzheimers Res Ther, 2022, 14(1):49. |
| [45] | KIM J, JEONG M, STILES W R, et al. Neuroimaging modalities in Alzheimer's disease: diagnosis and clinical features[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(11):6079. |
| [46] | MARTÍ-JUAN G, SANROMA-GUELL G, PIELLA G. A survey on machine and statistical learning for longitudinal analysis of neuroimaging data in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Comput Methods Programs Biomed, 2020,189:105348. |
| [47] | DING Y, SOHN J H, KAWCZYNSKI M G, et al. A deep learning model to predict a diagnosis of Alzheimer di-sease by using 18F-FDG PET of the brain[J]. Radiology, 2019, 290(2):456-464. |
| [1] | 武冬冬, 陈玉辉, 刘芳, 刘银红, 蒋景文. 脑小血管疾病合并中枢神经系统退行性疾病机制的研究进展[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2022, 21(05): 644-649. |
| [2] | 唐静仪, 余群, 刘军. 结合人工智能的结构影像分析对阿尔茨海默病的早期预测及精准诊断研究进展[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2022, 21(01): 12-17. |
| [3] | 李建平, 任汝静, 王刚. 阿尔茨海默病的临床诊治进展[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2022, 21(01): 18-21. |
| [4] | 马少辰, 郭昕, 王铭维, 王惠君, 余启军, 苏文月, 王华龙, 马芹颖. 基于游戏的脑电神经反馈训练对认知功能改善作用的研究[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2022, 21(01): 41-45. |
| [5] | 付丛会, 徐英, 苏巍, 文静, 刘志芳, 朱倩, 张静怡, 熊泽民, 陈兰兰, 贾杰. 新型冠状病毒性肺炎疫情封闭管理期间正念减压疗法对阿尔茨海默病患者情绪障碍及睡眠状况的影响分析[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2022, 21(01): 46-51. |
| [6] | 付朝伟. 阿尔茨海默病重在预防——《中国阿尔茨海默病报告2021》解读[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2022, 21(01): 8-11. |
| [7] | 黄沛, 任汝静, 潘昱, 林国珍, 王刚. 早发型阿尔茨海默病合并脑淀粉样血管病一例报道[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2022, 21(01): 86-89. |
| [8] | 魏文石. 直面我国阿尔茨海默病诊治的挑战——《中国阿尔茨海默病报告2021》解读[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2022, 21(01): 5-7. |
| [9] | 张旻, 张雪, 周新. 2017年《重症哮喘诊断与处理中国专家共识》解读[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2018, 17(06): 630-634. |
| [10] | 孟洁, 崔诗爽, 孟云霞, 王刚. 2005年路易体痴呆诊断标准与2017年新版诊断标准的临床比较分析[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2018, 17(04): 414-418. |
| [11] | 孙家兰, 黄澍, 来小音, 朱玮, 胡荣郭, 李龙宣. 阿尔茨海默病患者外周血淋巴细胞中G蛋白偶联受体激酶5水平与疾病及程度间相关性探讨[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2018, 17(04): 419-422. |
| [12] | 许晶晶, 张敏鸣. 人工智能机器学习方法在阿尔茨海默病中的应用现状[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2018, 17(04): 466-470. |
| [13] | 赵丹丹, 张翼飞, 马勤耘, 洪洁, 王卫庆,. 糖代谢异常在阿尔茨海默病发病机制中的作用[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2016, 15(02): 185-189. |
| [14] | 张月琪, 任汝静, 王刚,. 尿液生物标志物对痴呆诊断价值的研究进展[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2016, 15(02): 190-194. |
| [15] | 乔园, 王刚, 任汝静, 陈生弟,. 阿尔茨海默病的语言障碍研究进展[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2014, 13(04): 433-436. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||