

诊断学理论与实践 ›› 2025, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (02): 212-219.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2025.02.013
收稿日期:2025-01-03
接受日期:2025-03-27
出版日期:2025-04-25
发布日期:2025-07-11
通讯作者:
贺娜英 E-mail:i@nayinghe.com
LÜ Haiying, LU Yong, HE Naying( )
)
Received:2025-01-03
Accepted:2025-03-27
Published:2025-04-25
Online:2025-07-11
摘要:
光子计数计算机断层扫描(photon-counting computed tomography, PCCT)作为新一代CT成像技术,通过光子探测器单光子逐一探测与能量分辨能力,实现了成像质量的显著提升,及辐射剂量、图像噪声的有效降低。目前,PCCT在神经系统成像领域有广阔的临床应用前景,尤其在颅内精细结构显示、颅内动脉瘤诊断和治疗监测、颅内动脉狭窄及脊髓血管病变诊疗中展现出了独特优势。头颈动脉PCCT超高分辨率(ultra-high-resolution, UHR)模式(层厚0.2 mm),在BV64~BV72卷积核重建中具有较高的信噪比;对照数字减影血管造影(digital subtraction angiography, DSA)金标准,UHR-PCCT血管成像(UHR-PCCTA)在诊断颅内动脉小动脉瘤方面的灵敏度、特异度、准确率和评估者间一致性分别约为98.0%、96.7%、97.3%和0.95(Kappa值)。此外,UHR-PCCT对动脉瘤不规则性、动脉瘤壁及其瘤内特征的识别均显著优于传统能量积分型探测器CT(energy-integrating detector CT, EID-CT)。采用UHR-PCCT有望对动脉狭窄程度进行精准评估,甚至能达到接近DSA的效果,借助其多能级虚拟单能量重建,还有望实现对颅内动脉粥样硬化斑块的定量分析和对斑块破裂风险的预测。在锐利重建核(BV72~BV80)下,PCCT对颅内动脉植入支架状态及残余动脉瘤显示清晰,为颅内动脉治疗术后替代DSA的无创监测提供新方法。PCCT在神经系统成像中的多元化应用,将为其更好地在神经系统疾病诊治中发挥作用奠定基础。然而,目前PCCT在神经系统领域的广泛应用仍受限于设备普及度、特定场景(如微小穿支动脉、重度钙化/金属植入物)下的成像优化需求以及缺乏大规模临床验证数据的支持。未来需通过硬件迭代升级、算法优化改进及多中心前瞻性研究的推动,逐步克服这些限制,充分释放PCCT的临床潜力。
中图分类号:
吕海英, 陆勇, 贺娜英. 光子计数CT在神经系统成像中的临床价值[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2025, 24(02): 212-219.
LÜ Haiying, LU Yong, HE Naying. Clinical applications of photon-counting CT in neuroimaging[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2025, 24(02): 212-219.
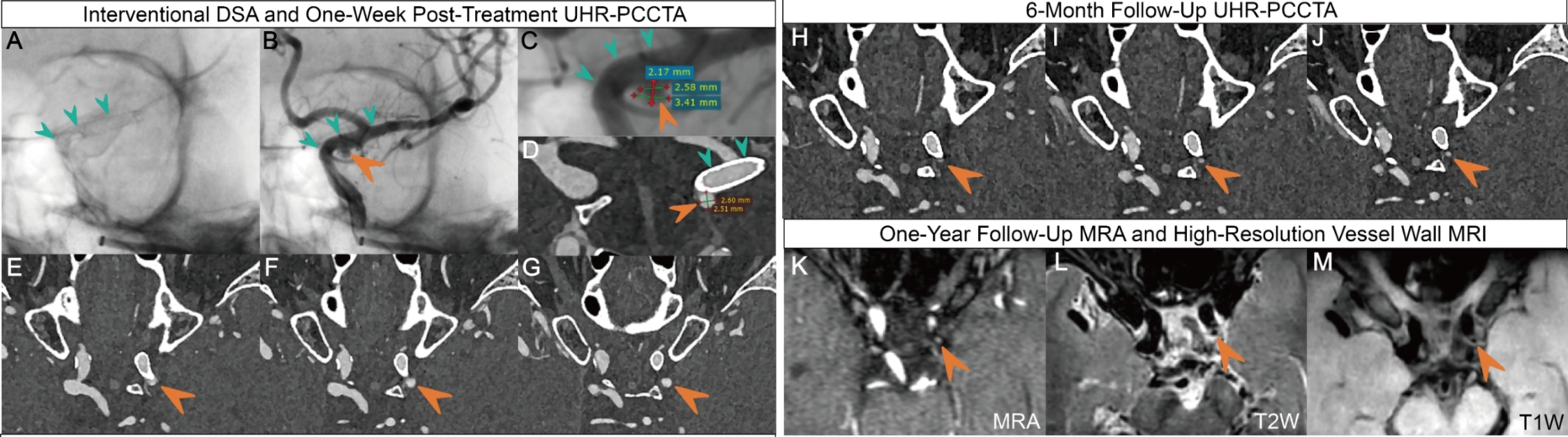
图4
64岁女性患者左侧颈内动脉眼段(C6段)血泡样动脉瘤注:患者行经DSA引导血流导向装置置入术后,随访UHR-PCCTA及MRI。A-B(术后即刻DSA):示血流导向装置在位(绿色箭头),支架释放形态良好,载瘤动脉通畅,动脉瘤腔内可见造影剂残留(橙色箭头);C-D:DSA测量的残余动脉瘤大小与术后一周UHR-PCCTA测量结果相仿;E-G(术后1周UHR-PCCTA):随访显示装置在位,残余动脉瘤清晰可见;H-J(术后6个月UHR-PCCTA):随访显示装置在位,残余动脉瘤显著缩小;K-M(术后1年MRI):头颅非增强磁共振血管成像(MRA)及高分辨率血管壁MRI随访中,MRA受支架伪影影响,术区显示欠佳,仅可隐约见少量残余动脉瘤;黑血T1W及T2W血管壁MRI示残余动脉瘤尚存在,局部瘤壁较厚,T2W等稍高信号、T1W高信号,提示可能存在附壁血栓。橙色箭头示动脉瘤的位置。
| [1] | 中华医学会放射学分会,《中华放射学杂志》光子计数CT临床应用协作组. 光子计数CT临床应用专家共识[J]. 中华放射学杂志,2025,59(4):364-383. |
| Chinese Society of Radiology Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Journal of Radiology Photon-Counting CT Clinical Application Collaborative Group. Expert consensus on clinical application of photon-counting CT[J]. Chin J Radiol,2025,59(4):364-383. | |
| [2] | 陈海燕, 杨永波, 刘璐璐, 等. 光子计数探测器CT初步临床应用的研究进展[J]. 中华放射学杂志,2022,56(2):213-216. |
| CHEN H Y, YANG Y B, LIU L L, et al. Research progress of clinical application of spectrum CT based on photon-counting detector[J]. Chin J Radiol,2022,56(2):213-216. | |
| [3] |
张龙江, 卢光明. 勇立潮头,努力提升我国光子计数CT的临床研究和应用水平[J]. 国际医学放射学杂志,2024,47(6):629-630, 635.
doi: 10.19300/j.2024.S21750 |
| ZHANG L J, LU G M. Standing at the forefront:striving to improve the clinical research and application of photon counting CT in China[J]. Int J Med Radiol,2024,47(6):629-630, 635. | |
| [4] |
ABEL F, SCHUBERT T, WINKLHOFER S. Advanced neuroimaging with photon-counting detector CT[J]. Invest Radiol,2023,58(7):472-481.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000984 pmid: 37158466 |
| [5] | CADEMARTIRI F, MELONI A, PISTOIA L, et al. Dual source photon-counting computed tomography-part Ⅱ: clinical overview of neurovascular applications[J]. J Clin Med,2023,12(11):3626. |
| [6] |
BENSON J C, CAMPEAU N G, DIEHN F E, et al. Photon-counting CT in the head and neck: current applications and future prospects[J]. Am J Neuroradiol,2024,45(8):1000-1005.
doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A8265 pmid: 38964861 |
| [7] | 中国医师协会神经介入专业委员会中国颅内动脉瘤计划研究组. 颅内动脉瘤影像学判读中国指南(2024版)[J]. 中华神经外科杂志,2024,40(8):757-773. |
| The Chinese Intracranial Aneurysm Program Research Group of the Neurointerventional Professional Committee of the Chinese Medical Association. Chinese guidelines for imaging interpretation of intracranial aneurysms (2024 edition)[J]. Chin J Neurosurg,2024,40(8):757-773. | |
| [8] |
BENDER M T, WENDT H, MONARCH T, et al. Small aneurysms account for the majority and increasing percentage of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A 25-year, single institution study[J]. Neurosurgery,2018,83(4):692-699.
doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyx484 pmid: 29029314 |
| [9] | HE N, LYU H, ZHANG Y, et al. Increased diagnostic accuracy and better morphology characterization of unruptured intracranial aneurysm by ultra-high-resolution photon-counting detector CT angiography[J/OL]. J Neurointerv Surg,2025[2025-04-05].https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40185624/. |
| [10] | HE N, ZHANG Y, LI Z, et al. Ultrahigh-resolution photon-counting detector CTA of the head and neck: image quality assessment and vascular kernel optimization[J]. Am J Roentgenol,2025,224(1):e2431763. |
| [11] | 中华医学会神经外科学分会, 中国卒中学会脑血管外科分会, 国家神经系统疾病医学中心, 等. 中国未破裂颅内动脉瘤临床管理指南(2024版)[J]. 中华医学杂志,2024,104(21):1918-1939. |
| Society of Neurosurgery of Chinese Medical Association, Society of Cerebrovascular Surgery of Chinese Stroke Association, National Center for Neurological Disorders, et al. Chinese guideline for the clinical management of patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms (2024)[J]. Natl Med J China,2024,104(21):1918-1939. | |
| [12] | BYL A, KLEIN L, SAWALL S, et al. Photon-counting normalized metal artifact reduction (NMAR) in diagnostic CT[J]. Med Phys,2021,48(7):3572-3582. |
| [13] | SCHMITT N, WUCHERPFENNIG L, ROTKOPF L T, et al. Metal artifacts and artifact reduction of neurovascular coils in photon-counting detector CT versus energy-integrating detector CT - in vitro comparison of a standard brain imaging protocol[J]. Eur Radiol,2023,33(2):803-811. |
| [14] | TÓTH A, CHO JY, WILSON E, O'DOHERTY J, et al. Photon-counting CT imaging of a patient with coiled and untreated intracranial saccular aneurysms[J/OL]. Neuroradiol J,2025[2025-04-05].https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39881477/. |
| [15] | PALLASCH F B, RAU A, REISERT M, et al. Impact of different metal artifact reduction techniques in photon-counting computed tomography head and neck scans in patients with dental hardware[J]. Eur Radiol,2024,34(6):3742-3749. |
| [16] | 中华医学会神经病学分会神经血管介入协作组, 中国医师协会神经内科医师分会神经介入专业委员会, 中国研究型医院学会介入神经病学专业委员会. 中国颅内外大动脉非急性闭塞血管内介入治疗专家共识[J]. 中华内科杂志,2020,59(12):932-941. |
| Neurovascular Intervention Group of Chinese Society of Neurology, Chinese Medical Association, Professional Committee of Neurological Intervention, Society of Neurology, Chinese Medical Doctor Association, Professional Committee of Interventional Neurology, Chinese Research Hospital Association. Expert consensus: endovascular treatment in non-acute occlusion of intracranial and extracranial large vessel in China[J]. Chin J Intern Med,2020,59(12):932-941. | |
| [17] | 刘翔宇, 王嵇, 所世腾, 等. 超高分辨率光子计数探测器CT评估颈动脉支架经皮置入术后再狭窄1例[J]. 中华放射学杂志,2025,59(1):103-104. |
| LIU X Y, WANG J, SUO S T, et al. Evaluation of in-stent restenosis after carotid artery stent implantation with ultra-high-resolution photon-counting detector CT: a case report[J]. Chin J Radiol,2025,59(1):103-104. | |
| [18] |
SHAMI A, SUN J, GIALELI C, et al. Atherosclerotic plaque features relevant to rupture-risk detected by clinical photon-counting CT ex vivo: a proof-of-concept study[J]. Eur Radiol Exp,2024,8(1):14.
doi: 10.1186/s41747-023-00410-4 pmid: 38286959 |
| [19] | CAU R, SABA L, BALESTRIERI A, et al. Photon-counting computed tomography in atherosclerotic plaque characterization[J]. Diagnostics (Basel),2024,14(11):1065. |
| [20] | DAHAL S, RAJA A Y, SEARLE E, et al. Components of carotid atherosclerotic plaque in spectral photon-counting CT with histopathologic comparison[J]. Eur Radiol,2023,33(3):1612-1619. |
| [21] | MELONI A, CAU R, SABA L, et al. Photon-counting computed tomography angiography of carotid arteries: a topical narrative review with case examples[J]. Diagnostics (Basel),2024,14(18):2012. |
| [22] | FARNSWORTH P J, CAMPEAU N G, DIEHN F E, et al. High-resolution computed tomography angiography of the orbit using a photon-counting computed tomography scanner[J/OL]. Interv Neuroradiol,2023[2025-04-05].https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37401156/. |
| [23] | HARVEY E C, FENG M, JI X, et al. Impacts of photon counting CT to maximum intensity projection (MIP) images of cerebral CT angiography: theoretical and experimental studies[J]. Phys Med Biol,2019,64(18):185015. |
| [24] | 中国卒中学会神经介入分会. 症状性颅内动脉粥样硬化性狭窄血管内治疗中国专家共识2022[J]. 中国卒中杂志,2022,17(8):863-888. |
| Chinese Stroke Association, Chinese Interventional Neuroradiology Society. Chinese experts consensus on endovascular treatment for symptomatic intracranial Atherosclderotic Stenosis 2022[J]. Chin J Stroke,2022,17(8):863-888. | |
| [25] | LUDOVICHETTI R, GORUP D, KREPUSKA M, et al. Ultra-high resolution CT angiography for the assessment of intracranial stents and flow diverters using photon counting detector CT[J/OL]. J Neurointerv Surg,2025[2025-04-05].https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39438133/. |
| [26] | DACHS T M, HAUCK S R, KERN M, et al. In-stent restenosis in peripheral arterial disease: ultra-high-resolution photon-counting versus third-generation dual-source energy-integrating detector CT phantom study in seven different stent types[J]. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol,2025,48(1):65-74. |
| [27] | DECKER J A, O'DOHERTY J, SCHOEPF U J, et al. Stent imaging on a clinical dual-source photon-counting detector CT system-impact of luminal attenuation and sharp kernels on lumen visibility[J]. Eur Radiol,2023,33(4):2469-2477. |
| [28] | DE BEUKELAER F, HALAL M EL, DE BEUKELAER S, et al. Photon-counting ct-angiography to assess intracranial stents and flow diverters in comparison to digital subtraction angiography[J/OL]. Clin Neuroradiol,2025[2025-04-05].https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40343459/. |
| [29] | VERELST E, BULS N, DE MEY J, et al. Stent appeara-nce in a novel silicon-based photon-counting CT prototype: ex vivo phantom study in head-to-head comparison with conventional energy-integrating CT[J]. Eur Radiol Exp,2023,7(1):23. |
| [30] | HIGAKI F, HIRAMATSU M, YASUHARA T, et al. Cranial and spinal computed tomography (CT) angiography with photon-counting detector CT: comparison with angiographic and operative findings[J]. Jpn J Radiol,2025,43(2):143-151. |
| [31] |
HE N, LYU H, LU Y, et al. Accurate detection of spinal dural arteriovenous fistula with spinal photon-counting computed tomography angiography: a report of two cases[J]. Stroke,2025,56(2):e44-e46.
doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.124.049475 pmid: 39676653 |
| [32] |
BENSON J C, RAJENDRAN K, LANE J I, et al. A new frontier in temporal bone imaging: photon-counting detector CT demonstrates superior visualization of critical anatomic structures at reduced radiation dose[J]. Am J Neuroradiol,2022,43(4):579-584.
doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A7452 pmid: 35332019 |
| [33] | 孙钢. 光子计数CT成像技术的临床应用[J]. 中国研究型医院,2023,10(6):23-27. |
| SUN G. Clinical applications of photon counting CT ima-ging technology[J]. Chin Res Hosp,2023,10(6):23-27. |
| [1] | 蔡欣欣, 邓嵘, 徐欣欣, 许芷涵, 常蕊, 董海鹏, 林慧敏, 严福华. 基于光子计数CT的肝脏脂肪分数定量测定与磁共振质子密度脂肪分数间的一致性研究[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2025, 24(02): 146-154. |
| [2] | 王梦真, 鲍守钰, 刘鹏, 严福华, 杨文洁. 光子计数CT在心血管疾病中的应用[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2025, 24(02): 125-134. |
| [3] | 李卫侠, 严福华. 光子计数CT在肝脏疾病中的应用进展[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2025, 24(02): 118-124. |
| [4] | 黄瑞坤, 杨琰昭, 柴维敏. 光子计数CT在胰腺成像中的应用进展[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2025, 24(02): 111-117. |
| [5] | 常蕊, 李纪强, 杨琰昭, 柴维敏, 严福华, 董海鹏. 光子计数CT胰腺低剂量动态容积灌注扫描中单期图像对胰腺癌图像的评估价值[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2025, 24(02): 155-162. |
| [6] | 周山税, 秦乐, 常蕊, 杜联军, 严福华, 刘方韬. 基于光子计数探测器CT能谱定位像定量评估股骨颈骨密度的前瞻性研究[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2025, 24(02): 163-169. |
| [7] | 徐鹏宇, 迟骋, 张晓霞. 床旁肺部超声及改良方案在急诊重症监护病房患者肺部病变诊断及监测中的应用进展[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2024, 23(05): 542-549. |
| [8] | 冯原, 何钊, 孙青芳, 孙伯民, 严福华, 杨广中. 磁共振介入成像及其临床应用进展[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2024, 23(02): 108-113. |
| [9] | 王砚春, 卢仁泉. 出凝血检测在肿瘤患者中的应用价值探讨[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2023, 22(04): 341-347. |
| [10] | 游利. 重视骨转换指标的临床应用及评估[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2020, 19(03): 214-218. |
| [11] | 陈辰, 张月, 胡晓波. 尿路感染报警信息阈值设置和临床应用评价[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2020, 19(02): 168-171. |
| [12] | 余红, 王一飞, 陈佳, 陈洁, 李斌. 青蒿素及其衍生物在皮肤疾病中的作用机制研究及临床应用[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2019, 18(2): 233-236. |
| [13] | 上海市医学会分子诊断专科分会, 上海市临床检验中心, 上海东方肝胆外科医院, 中华医学会检验医学分会临床免疫学组, 中国中西医结合检验学会肝病学术委员会, 全军肝胆外科专业委员会, 上海免疫学会肿瘤免疫分会, 上海抗癌协会肿瘤标志物分会. 多学科甲胎蛋白异质体临床应用专家共识[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2018, 17(01): 19-24. |
| [14] | 朱巍巍, 万颖蕾, 刘锦燕, 张华, 陈华, 项明洁. 内毒素的检测方法与临床应用进展[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2017, 16(06): 668-671. |
| [15] | 彭奕冰, 章黎华. 免疫球蛋白游离轻链的检测与临床应用[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2017, 16(05): 468-471. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||