

Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice ›› 2023, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (02): 166-171.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2023.02.010
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2023-01-12
Online:2023-04-25
Published:2023-08-31
CLC Number:
XIE Yaqiong, LIN Xiaoyi. Value of serum-free light chain assay in differential diagnosis and staging of nephropathy of various etiologies[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(02): 166-171.
Table 1
The sFLC levels, sFLCκ/λ ratio and parameters of renal function in nephropathy caused by various etiologies
| Group | n | sFLCκ(mg/L) | sFLCλ(mg/L) | sFLCκ/λ | Urea(mmol/L) | Creatinine(μmol/L) | Uric acid(μmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal range | 3.3-19.4 | 5.7-26.3 | 0.26-1.65 | 2.5-7.1 | 53.0-97.0 | 160-430 | |
| Normal control | 30 | 10.6±4.7 | 11.1±4.6 | 1.12±0.63 | 3.9±1.3 | 69.3±12.5 | 268.7±88.5 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 47 | 63.4±71.3* | 60.7±54.1* | 1.06±0.94 | 13.8±9.2 | 294.1±273.5 | 435.3±96.4 |
| Diabetes | 38 | 68.6±51.9* | 74.2±51.0* | 1.13±1.19 | 15.1±7.7 | 302.1±265.2 | 390.1±100.7 |
| Primary glomerulonephritis | 56 | 62.3±100.2* | 56.8±48.3* | 0.89±0.57 | 12.8±10.1 | 257.1±309.6 | 373.4±141.2 |
| Autoimmune disease | 121 | 54.6±86.4* | 55.0±52.6* | 0.83±0.45 | 8.8±7.5 | 146.8±169.5 | 385.3±117.1 |
| IgA nephropathy | 106 | 36.6±53.8* | 49.9±67.7* | 0.72±0.33# | 8.8±6.0 | 163.3±181.4 | 376.9±89.8 |
| Monoclonal gammopathy with κ isotype | 32 | 453.0±1275.0* | 28.6±23.3* | 22.6±41.7* | 14.3±10.8 | 264.9±215.0 | 413.3±184.4 |
| Monoclonal gammopathy with λ isotype | 32 | 21.9±15.6* | 382.5±728.3* | 0.3±0.2# | 10.7±8.3 | 214.7±234.2 | 358.2±133.2 |
Figure 2
The receiver operating characteristic curves of sFLC levels and sFLCκ/λ ratio in diagnosing monoclonal gammopathy of renal significance A: The receiver operating characteristic curve of sFLCκ level in diagnosing monoclonal gammopathy with κ isotype; B: The receiver opera-ting characteristic curve of sFLCλ level in differential diagnosing monoclonal gammopathy with λ isotype; C: The receiver operating characte-ristic curve of sFLCκ/λ ratio in differential diagnosing monoclonal gammopathy with κ isotype; D: The receiver operating characteristic curve of sFLCκ/λ ratio in differential diagnosing monoclonal gammopathy with λ isotype.
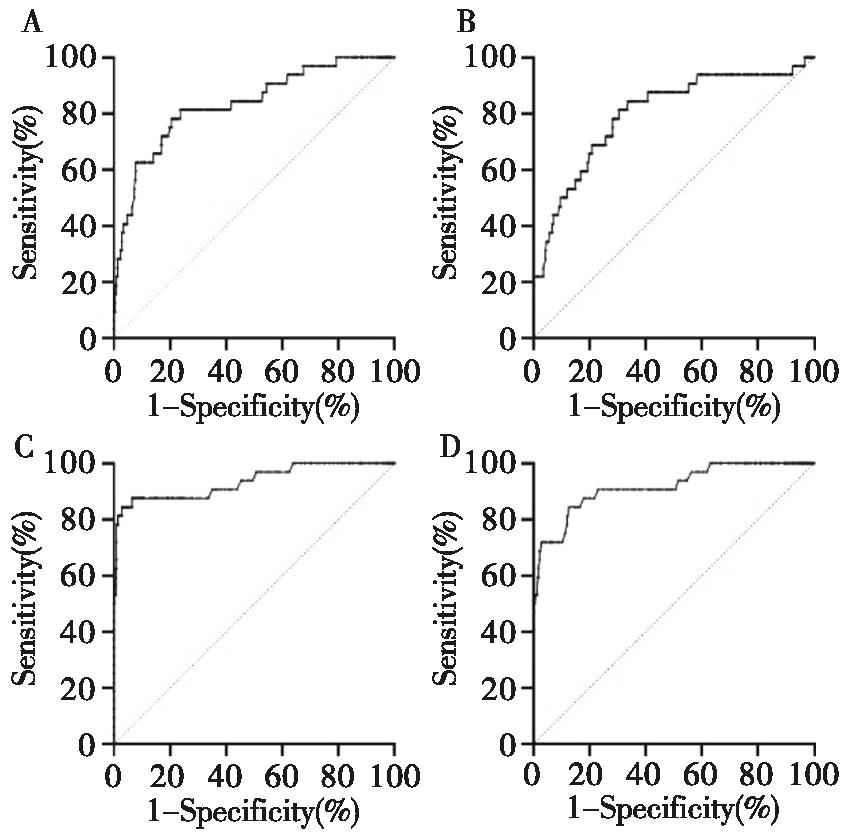
Table 2
The performance of sFLC level and sFLCκ/λ ratio in diagnosing monoclonal gammopathy of renal significance
| Disease | Parameter | Cut-off value | Sensitivity(%) | Specificity(%) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monoclonal gammopathy with κ isotype | sFLCκ | >176.5 mg/L | 62.5 | 92.1 | 0.832 6 |
| sFLCκ/λ | >1.925 | 84.4 | 97.0 | 0.933 9 | |
| Monoclonal gammopathy with λ isotype | sFLCλ | >82.3 mg/L | 68.8 | 79.1 | 0.797 6 |
| sFLCκ/λ | <0.455 | 84.4 | 87.2 | 0.915 9 |
Table 3
The correlation of sFLC levels and sFLCκ/λ ratio with staging of kidney disease caused by various etiologies
| Groups | sFLCκ | sFLCλ | sFLCκ/λ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-monoclonal gammopathy | r | 0.688 7 | 0.661 2 | 0.300 0 |
| P | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 | |
| Cardiovascular disease | r | 0.835 5 | 0.894 2 | / |
| P | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 | ns | |
| Diabetes | r | 0.767 2 | 0.727 1 | / |
| P | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 | ns | |
| Primary glomerulonephritis | r | 0.772 8 | 0.721 7 | 0.501 0 |
| P | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 | |
| Autoimmune disease | r | 0.516 8 | 0.537 9 | / |
| P | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 | ns | |
| IgA nephropathy | r | 0.689 8 | 0.687 5 | 0.211 0 |
| P | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 | 0.029 9 | |
| P | 0.003 9 | 0.006 8 | ns | |
| Monoclonal gammopathy with | r | / | 0.524 4 | / |
| κ isotype | P | ns | 0.002 1 | ns |
| Monoclonal gammopathy with | r | 0.478 0 | 0.610 1 | -0.371 9 |
| λ isotype | P | 0.005 7 | 0.000 2 | 0.036 1 |
| [1] |
DISPENZIERI A, KYLE R, MERLINI G, et al. International Myeloma Working Group guidelines for serum-free light chain analysis in multiple myeloma and related disor-ders[J]. Leukemia, 2009, 23(2):215-224.
doi: 10.1038/leu.2008.307 |
| [2] |
GRAN C, AFRAM G, LIWING J, et al. Involved free light chain: an early independent predictor of response and progression in multiple myeloma[J]. Leuk Lymphoma, 2021, 62(9):2227-2234.
doi: 10.1080/10428194.2021.1907370 URL |
| [3] |
HUTCHISON C A, BASNAYAKE K, COCKWELL P. Serum free light chain assessment in monoclonal gammopathy and kidney disease[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2009, 5(11):621-628.
doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2009.151 pmid: 19786994 |
| [4] |
YADAV P, SATHICK I J, LEUNG N, et al. Serum free light chain level at diagnosis in myeloma cast nephropathy-a multicentre study[J]. Blood Cancer J, 2020, 10(3):28.
doi: 10.1038/s41408-020-0295-4 pmid: 32127527 |
| [5] |
OLSEN E, VAN GALEN G. Chronic renal failure-causes, clinical findings, treatments and prognosis[J]. Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract, 2022, 38(1):25-46.
doi: 10.1016/j.cveq.2021.11.003 URL |
| [6] |
PATTRAPORNPISUT P, AVILA-CASADO C, REICH H N. IgA Nephropathy: Core Curriculum 2021[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2021, 78(3):429-441.
doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.01.024 pmid: 34247883 |
| [7] | 中国医师协会血液科医师分会,中华医学会血液学分会. 中国多发性骨髓瘤诊治指南(2022年修订)[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2022, 61(5):480-487. |
| Chinese Hematlology Association, Chinese Society of Hematology. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of multiple myeloma in China (2022 revision)[J]. Chin J Intern Med, 2022, 61(5):480-487. | |
| [8] |
LEVEY A S, ECKARDT K U, TSUKAMOTO Y, et al. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: a position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO)[J]. Kidney Int, 2005, 67(6):2089-2100.
doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00365.x pmid: 15882252 |
| [9] | CÁRDENAS M C, IÑIGO B, ORTEGA I, et al. Can urine studies be replaced by serum free light chains measurements to assign responses in multiple myeloma patients?[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12:1056293. |
| [10] | 陈海飞, 侯健, 袁振刚, 等. 血清游离轻链的检测及其在不分泌型多发性骨髓瘤中的临床意义[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2008, 29(2):113-116. |
| CHEN H F, HOU J, YUAN Z G, et al. Detection of serum free light chain and its clinical significance in nonsecretory multiple myeloma[J]. Chin J Hematol, 2008, 29(2):113-116. | |
| [11] | 宋萍, 安志明, 周小钢, 等. 血清游离轻链的检测及其在轻链型多发性骨髓瘤中的临床意义[J]. 中国实验血液学杂志, 2015, 23(5):1357-1361. |
| SONG P, AN Z M, YUAN Z G, et al. Test of serum free light chain and its clinical significance in light chain multiple myeloma[J]. J Exp Hematol, 2015, 23(5):1357-1361. | |
| [12] | 彭奕冰, 章黎华. 免疫球蛋白游离轻链的检测与临床应用[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2017, 16(5):468-471. |
| PENG Y B, ZHANG L H. Detection of immunoglobulin free light chain and its clinical application[J]. J Diagn Concepts Pract, 2017, 16(5):468-471. | |
| [13] | 陈文明. 我如何治疗伴肾功能不全的多发性骨髓瘤[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2021, 42(2):97-100. |
| CHEN W M. How I treat multiple myeloma with renal impairment[J]. Chin J Hematol, 2021, 42(2):97-100. | |
| [14] |
SINGH G. Serum free light chain assay and κ/λ ratio performance in patients without monoclonal gammopathies: high false-positive Rate[J]. Am J Clin Pathol, 2016, 146(2):207-214.
doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqw099 URL |
| [15] |
SINGH G. Serum free light chain assay and κ/λ ratio: performance in patients with monoclonal gammopathy-high false negative rate for κ/λ ratio[J]. J Clin Med Res, 2017, 9(1):46-57.
doi: 10.14740/jocmr2802w pmid: 27924175 |
| [16] |
LONG T E, INDRIDASON O S, PALSSON R, et al. Defining new reference intervals for serum free light chains in individuals with chronic kidney disease: results of the iStopMM study[J]. Blood Cancer J, 2022, 12(9):133.
doi: 10.1038/s41408-022-00732-3 pmid: 36100605 |
| [17] |
HUTCHISON C A, HARDING S, HEWINS P, et al. Quantitative assessment of serum and urinary polyclonal free light chains in patients with chronic kidney disease[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2008, 3(6):1684-1690.
doi: 10.2215/CJN.02290508 URL |
| [18] |
ERDEM B K, DAVRAN F, YILMAZ V T, et al. The association of serum-free light-chain levels with markers of renal function[J]. Ren Fail, 2015, 37(6):1057-1060.
doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2015.1052980 pmid: 26056734 |
| [19] |
CAO D, SHOU L, WU Y, et al. The role of serum-free light chain ratios in the prediction of poor prognosis in multiple myeloma patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hematology, 2022, 27(1):1130-1139.
doi: 10.1080/16078454.2022.2127460 pmid: 36165782 |
| [20] |
TACCHETTI P, ROCCHI S, ZAMAGNI E, et al. Role of serum-free light chain assay for defining response and progression in immunoglobulin secretory multiple myeloma[J]. Am J Hematol, 2022, 97(12):1607-1615.
doi: 10.1002/ajh.26747 pmid: 36198076 |
| [1] | HAO Jiaqi, WANG Xinlu, HU Xiaofan, PAN Xiaoxia, XU Jing, MA Jun. Clinical differential diagnosis of acute tubulointerstitial nephritis and acute tubular necrosis [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(02): 127-133. |
| [2] | WANG Zhaohui, WU Haibo. Clinicopathological analysis of 31 cases of gastric schwannoma [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2021, 20(06): 552-556. |
| [3] | WU Lin, ZHENG Ge, TAO Ting. Angiotensin-converting enzyme gene insertion/deletion polymorphism and decline of renal function in elderly [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2019, 18(2): 204-208. |
| [4] | WANG Jianjun, CHEN Ya, FAN Xiangshan, NIU Fengnan. Sclerosing angiomatoid nodular transformation of spleen: clinicopathological analysis and literature review [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2019, 18(05): 560-564. |
| [5] | CHANG Rui, XU Jiaxu, DONG Haipeng, WU Mengxiong, ZHAO Xuesong, MIAO Fei, YAN Fuhua. Value of CT spectral imaging in the evaluation of Crohn's disease activity [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2019, 18(04): 432-435. |
| [6] | YANG Ruxue, LI Nan, ZHOU Ting, ZHAO Yan, CHEN Shaohua, ZHU Qing, FENG Zhenzhong. Clinicopathologic analysis of skin melanocyte lesions [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2018, 17(05): 566-571. |
| [7] | LIU Yiping, TANG Yuanyuan, XU Kui, TENG Xiaoming. Correlation between sperm DNA fragmentation index and sperm morphology [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2018, 17(01): 98-101. |
| [8] | WU Xinyang, ZHANG Huan, PAN Zilai, TAN Jingwen, GAO Xiaoyuan. The diagnostic value of dual-source CT in differentiating primary gastric lymphoma from advanced gastric cancer [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2018, 17(01): 60-65. |
| [9] | ZHU Peipei, ZOU Jue, CHEN Jun, XU Rongrong, YAN Hongzhu. Intracranial solitary fibrous tumor/hemangiopericytoma: a clinicopathologic study of 20 cases with review of literature [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2017, 16(06): 622-626. |
| [10] | YI Lin, XIAO Li, CHEN Yan, YIN Yulei. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma: a clinicopathological study and review of literature [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2017, 16(03): 313-319. |
| [11] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2016, 15(04): 354-359. |
| [12] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2015, 14(04): 308-312. |
| [13] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2014, 13(05): 501-504. |
| [14] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2014, 13(05): 491-494. |
| [15] | . [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2013, 12(02): 170-174. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
