

诊断学理论与实践 ›› 2024, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (05): 537-541.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2024.05.011
收稿日期:2024-04-14
接受日期:2024-08-06
出版日期:2024-10-25
发布日期:2025-02-25
通讯作者:
翁海燕 E-mail:Whaiyan1166@163.com
WANG Yurong1,2, WANG Yuanyuan1,2, WENG Haiyan1,2( )
)
Received:2024-04-14
Accepted:2024-08-06
Published:2024-10-25
Online:2025-02-25
摘要:
本文报告3例罕见的原发于胃肠道的平滑肌肉瘤(leiomyosarcoma,LMS)病例。3例患者中,男性1例,女性2例,年龄为58~68岁;肿瘤原发于胃2例,小肠1例。患者的手术切除标本,在光学显微镜下可见,肿瘤呈浸润性生长,均侵犯固有肌层,2例表面黏膜有溃疡;肿瘤细胞呈梭形,可见束状、交织状排列,细胞质丰富、嗜酸,细胞核呈中-高度异型,核分裂象易见(50~100个/50 HPF)。免疫组化染色显示,肿瘤细胞3例Desmin阳性,2例SMA、Caldesmon阳性,3例均为CD117、Dog-1、CD34阴性,Ki-67增殖指数30%~80%。3例患者随访了11~53个月,其中2例患者无瘤生存,1例患者于手术后30个月发生肿瘤胰腺转移,随访至今53个月,仍生存。LMS是一种少见的软组织肉瘤,原发于胃肠道的LMS极为罕见。该病确诊依据是术后病理检查,LMS肿瘤细胞呈梭形,细胞质嗜酸,细胞核异型明显,表达平滑肌细胞标志物,需与胃肠道间质瘤及其他梭形细胞肿瘤相鉴别。LMS以手术治疗为主,患者的预后较差,故正确诊断该病至关重要。
中图分类号:
王玉蓉, 汪元元, 翁海燕. 胃肠道平滑肌肉瘤临床病理分析3例报告[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2024, 23(05): 537-541.
WANG Yurong, WANG Yuanyuan, WENG Haiyan. Clinical and pathological analysis of gastrointestinal leiomyosarcoma:Report of three cases[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(05): 537-541.
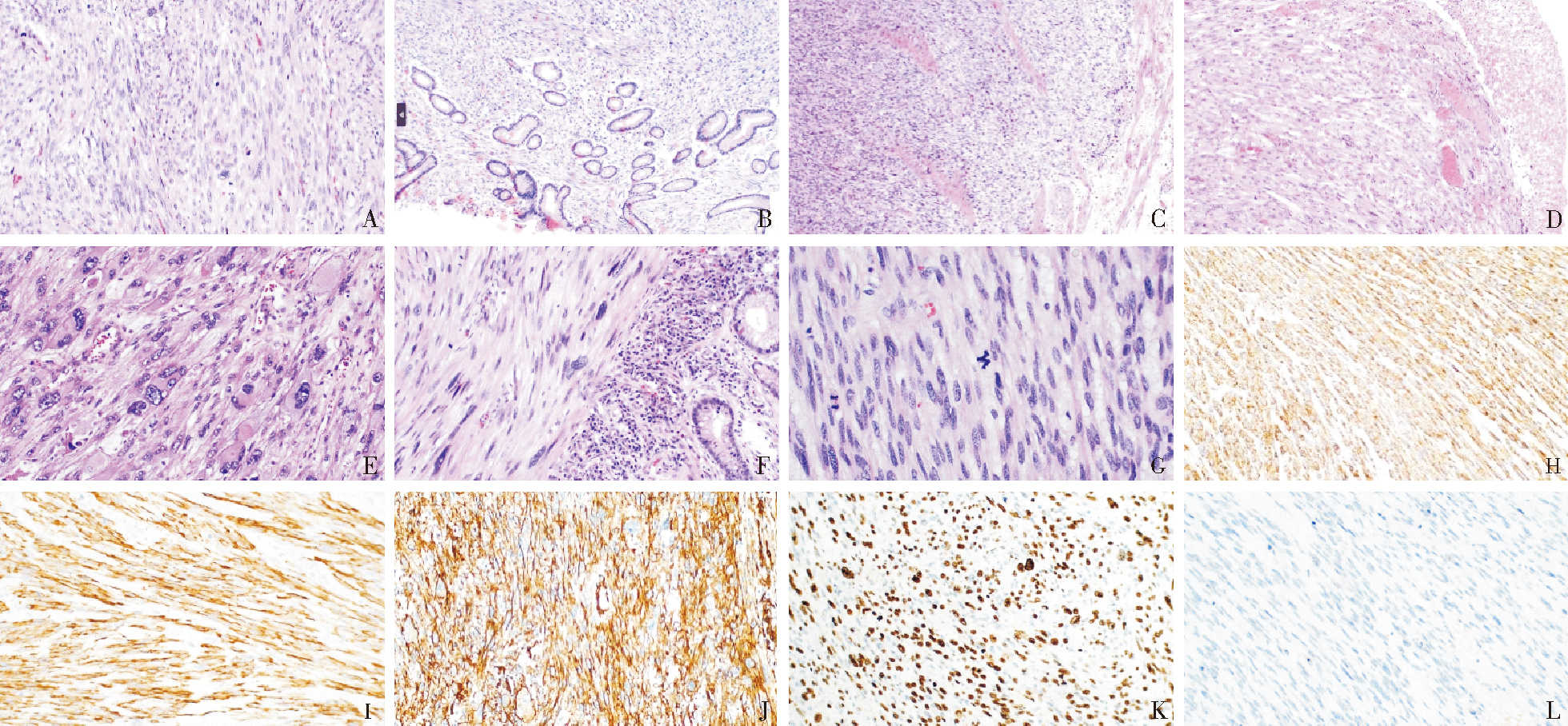
图1
胃肠道平滑肌肉瘤 A. 肿瘤细胞呈梭形,可见束状、交织状排列 HE,×200;B. 肿瘤细胞侵犯至粘膜固有层 HE,×100;C. 肿瘤细胞穿插于固有肌层之间 HE,×100;D. 粘膜表面可见出血、坏死、肉芽组织增生 HE,×100;E. 瘤巨细胞 HE,×200;F. 奇异形核 HE,×200;G. 核分裂象 HE,×400;H. SMA弥漫阳性表达(EnVision两步法,×200);I. Desmin弥漫阳性表达(EnVision两步法,×200);J. Caldesmon弥漫阳性表达(EnVision两步法,×200);K. Ki-67增殖指数表达EnVision两步法,×200;L. CD117阴性表达 EnVision两步法,×200
| [1] | SERRANO C, GEORGE S. Leiomyosarcoma[J]. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am, 2013, 27(5):957-974. |
| [2] |
GEORGE S, SERRANO C, HENSLEY M L, et al. Soft tissue and uterine leiomyosarcoma[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2018, 36(2):144-150.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.75.9845 pmid: 29220301 |
| [3] | KANG W Z, XUE L Y, TIAN Y T. Leiomyosarcoma of the stomach: A case report[J]. World J Clin Cases, 2019, 7 (21):3575-3582. |
| [4] |
AGGARWAL G, SHARMA S, ZHENG M, et al. Primary leiomyosarcomas of the gastrointestinal tract in the post-gastrointestinal stromal tumor era[J]. Ann Diagn Pathol, 2012, 16(6):532-540.
doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2012.07.005 pmid: 22917807 |
| [5] |
TAKAGI T, SAITO S, YOKOTA S, et al. Laparoscopic and endoscopic cooperative surgery for leiomyosarcoma of the stomach: a case report with a review of the literature[J]. Surg Case Rep, 2021, 7(1):146.
doi: 10.1186/s40792-021-01218-3 pmid: 34143361 |
| [6] | BANANZADEH A, MOKHTARI M, SOHOOLI M, et al. Two cases of primary leiomyosarcoma of sigmoid colon treated with laparoscopic surgery: A case report and a review of literature[J]. Int J Surg Case Rep, 2021, 87:106420. |
| [7] | WANG T, ZREIK R, LENG B. The landscape of primary gastric leiomyosarcoma in texas population: analysis of texas cancer registry data[J]. Cureus, 2023, 15(11):e49403. |
| [8] | ANNICCHIARICO A, MONTALI F, BALDINU M, et al. Leiomyosarcoma of the rectum: A systematic review of recent literature[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2024, 129(2):365-380. |
| [9] |
ARTS R, BOSSCHA K, RANSCHAERT E, et al. Small bowel leiomyosarcoma: a case report and literature review[J]. Turk J Gastroenterol, 2012, 23(4):381-384.
pmid: 22965511 |
| [10] |
MIETTINEN M, LASOTA J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: review on morphology, molecular pathology, prognosis, and differential diagnosis[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2006, 130(10):1466-1478.
doi: 10.5858/2006-130-1466-GSTROM pmid: 17090188 |
| [11] | BASU I, LEMONAS P. Leiomyosarcoma of the rectum following pelvic irradiation: a difficult histological diagnosis[J]. Ann R Coll Surg Engl, 2012, 94(1):e44-e45 |
| [12] | CRYSTAL J S, KORDERAS K, SCHWARTZBERG D, et al. Primary leiomyosarcoma of the colon: a report of two cases, review of the literature, and association with immunosuppression for IBD and rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Case Rep Surg, 2018, 2018:6824643. |
| [13] |
MARUZZO M, BRUNELLO A, DIMINUTTO A, et al. Long-term response to first-line trabectedin in an elderly female patient with a metastatic leiomyosarcoma unfit for anthracycline[J]. Anticancer Drugs, 2016, 27(3):264-267.
doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000326 pmid: 26629769 |
| [14] | COCO C, RIZZO G, MANNO A, et al. Surgical treatment of small bowel neoplasms[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2010, 14(4):327-333. |
| [15] | ÖZTEKIN M, YILMAZ B, AĞAGÜNDÜZ D, et al. Overview of helicobacter pylori infection: clinical features, treatment, and nutritional aspects. diseases[J]. 2021, 9(4):66. |
| [16] | GARCIA-ORTEGA D Y, REYES-GARCIA N, MARTINEZ-SAID H, et al. Radiation-induced leiomyosarcoma of the rectum after cervical cancer treatment[J]. Rev Gastroenterol Mex (Engl Ed), 2018, 83(4):465-467. |
| [17] |
ANDERSON N D, BABICHEV Y, FULIGNI F, et al. Lineage-defined leiomyosarcoma subtypes emerge years before diagnosis and determine patient survival[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1):4496.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24677-6 pmid: 34301934 |
| [18] |
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Electronic address: elizabeth.demicco@sinaihealthsystem.ca; Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive and Integrated Genomic Characterization of Adult Soft Tissue Sarcomas[J]. Cell, 2017, 171(4):950-965.e28.
doi: S0092-8674(17)31203-5 pmid: 29100075 |
| [19] | COPE B M, TRAWEEK R S, LAZCANO R, et al. Targe-ting the molecular and immunologic features of leiomyosarcoma[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2023, 15(7):2099. |
| [20] |
HILAL L, BARADA K, MUKHERJI D, et al. Gastrointestinal (GI) leiomyosarcoma (LMS) case series and review on diagnosis, management, and prognosis[J]. Med Oncol, 2016, 33(2):20.
doi: 10.1007/s12032-016-0730-3 pmid: 26786155 |
| [21] | YANG J. Primary leiomyosarcoma in the colon: A case report[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2018, 97(7):e9923. |
| [22] |
YAHAGI M, ISHII Y, HARA A, et al. Laparoscopic surgery to treat leiomyosarcomas of the sigmoid colon:a case report and literature review[J]. Surg Case Rep, 2019, 5(1):20.
doi: 10.1186/s40792-019-0579-8 pmid: 30756192 |
| [24] |
FENTY M, SHAHBAZOV R, DHIR M. Primary gastric leiomyosarcoma-a rarely encountered clinical entity[J]. J Gastrointest Surg, 2021, 25(5):1340-1342.
doi: 10.1007/s11605-020-04857-3 pmid: 33169323 |
| [25] |
SATO T, AKAHOSHI K, TOMOEDA N, et al. Leiomyosarcoma of the stomach treated by endoscopic submucosal dissection[J]. Clin J Gastroenterol, 2018, 11(4):291-296.
doi: 10.1007/s12328-018-0838-4 pmid: 29500609 |
| [26] |
SMRKE A, BENSON C, STRAUSS D C, et al. Gastrointestinal leiomyosarcoma demonstrate a predilection for distant recurrence and poor response to systemic treatments[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2021, 47(10):2595-2601.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2021.04.043 pmid: 33966946 |
| [1] | 张俊花, 李一林, 谢静远, 张春丽, 徐静. C3肾病临床预后相关病理特征分析[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2024, 23(06): 587-593. |
| [2] | 阮淼, 笪倩, 许海敏, 董磊, 费晓春. HER2低表达乳腺癌临床病理学特征及预后研究[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2024, 23(05): 500-508. |
| [3] | 李卓含, 黄新韵, 郭睿, 李彪. 18F-FDG PET/CT在滤泡性淋巴瘤诊断和预后评估中的研究进展[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2024, 23(04): 439-444. |
| [4] | 朱维维, 李倩, 吴凡, 翟志敏. 100例骨髓增生异常性肿瘤患者基因突变及其与临床特征间的关系[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2024, 23(03): 305-312. |
| [5] | 王书奎, 顾心亮. tsRNA作为肿瘤诊断和预后标志物的研究进展[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2023, 22(05): 413-420. |
| [6] | 李一林, 陈杨, 李艳艳, 冯旭娇, 章程, 李健, 沈琳. 循环肿瘤细胞检测在常见恶性肿瘤精准医学中的应用和展望[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2023, 22(04): 332-340. |
| [7] | 刘英婷, 易红梅, 王雪, 杨春雪, 欧阳斌燊, 许海敏, 王朝夫. 十二指肠型滤泡性淋巴瘤17例临床病理特征及预后分析[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2023, 22(04): 362-368. |
| [8] | 张兰兰, 杨巧, 聂尊珍, 郭英. 胸膜SMARCA4缺失未分化肿瘤1例报告[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2023, 22(04): 389-392. |
| [9] | 胡静静, 沈银忠, 刘莉, 卢洪洲. 艾滋病合并播散性非结核分枝杆菌病诊治现状及研究进展[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2023, 22(04): 402-406. |
| [10] | 徐莉, 高华杰, 杨梦歌, 李悦, 季苏琼. 合并抗TRIM21/Ro52抗体阳性的抗SRP阳性坏死性肌病患者临床特点分析[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2023, 22(03): 247-254. |
| [11] | 周晓蝶, 陈巍魏, 余波, 王璇, 王建军, 石群立, 饶秋, 鲍炜. 尿路上皮癌的临床病理学特征[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2023, 22(03): 292-299. |
| [12] | 宋陆茜, 常春康. 2023年美国国立综合癌症网络(NCCN)《骨髓增生异常综合征临床实践指南》(第1版)解读[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2023, 22(02): 116-120. |
| [13] | 许建昆, 周露婷, 张文净, 许海敏, 王朝夫. CA9在透明细胞肾细胞癌预后评估中的价值[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2023, 22(01): 37-43. |
| [14] | 王瀚, 陆海迪, 王雷, 丛文铭, 郑建明, 白辰光. 结肠鳞癌2例和腺鳞癌2例临床病理学特征分析[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2023, 22(01): 44-49. |
| [15] | 王瑾, 郭睿, 李彪, 张晓哲. 18F-FDG PET/CT显像动态评估自然杀伤/T细胞淋巴瘤(鼻型)治疗预后[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2022, 21(06): 702-709. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||