

Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice ›› 2025, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (03): 312-319.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2025.03.010
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
GUO Yuqing1a, WANG Changyan2, LIU Yinchun1a, PANG Yun1a, ZHU Xia1b, GE Rui1c, LI Weiping1c, ZHANG Qi2, CHEN Lin1a( )
)
Received:2025-03-28
Accepted:2025-06-05
Online:2025-06-25
Published:2025-06-25
Contact:
CHEN Lin
E-mail:hdchenlin@fudan.edu.cn
CLC Number:
GUO Yuqing, WANG Changyan, LIU Yinchun, PANG Yun, ZHU Xia, GE Rui, LI Weiping, ZHANG Qi, CHEN Lin. Application value of a deep learning model based on 3D ultrasound videos in assisting radiologists of different experience levels to differentiate benign and malignant breast masses[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2025, 24(03): 312-319.
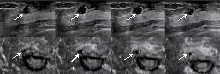
Figure 2
Multiplane images of ABVS of a tubular adenoma in right breast (arrow point) Note: DL-3DUV classified it as benign. When making independent diagnosis, all senior radiologists classified it as benign while all junior radiologists classified it as malignant. A to D are the transverse-plane images, and E to F are the coronal-plane images.
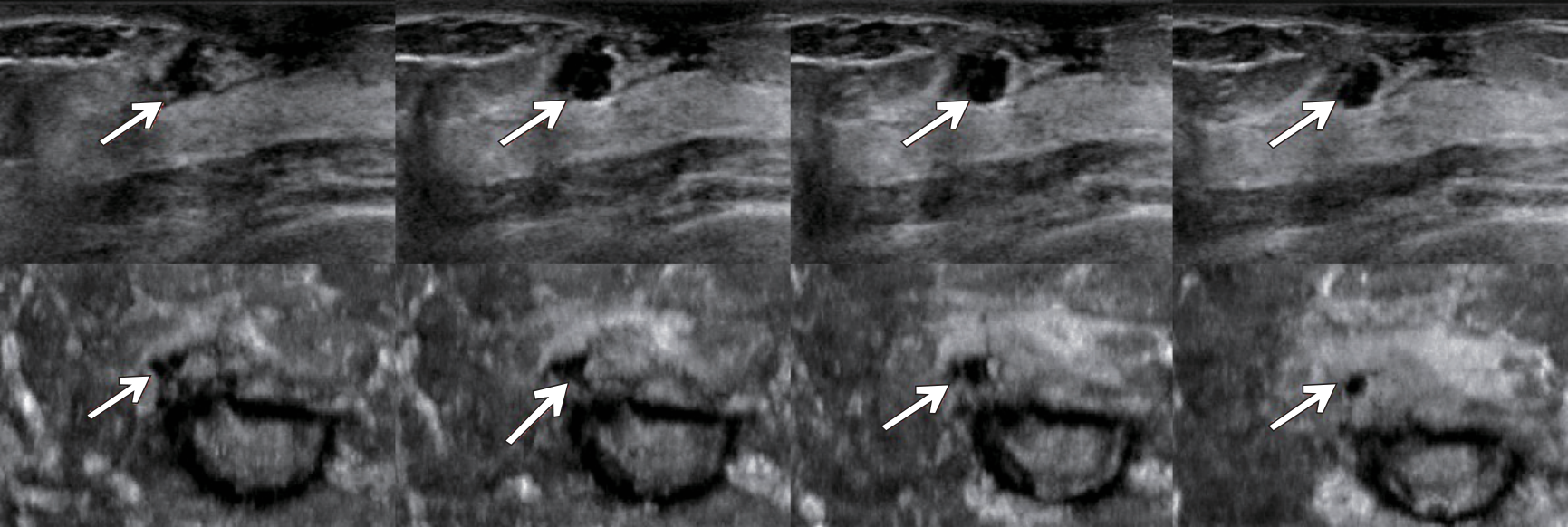
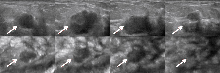
Figure 3
Multiplane images of ABVS of an invasive carcinoma in left breast (arrow point) Note: DL-3DUV classified it as malignant. When making independent diagnosis, one senior radiologist classified it as malignant, while the other two senior radiologists and all the junior radiologists classified it as benign. A to D are the transverse-plane images, and E to F are the coronal-plane images.
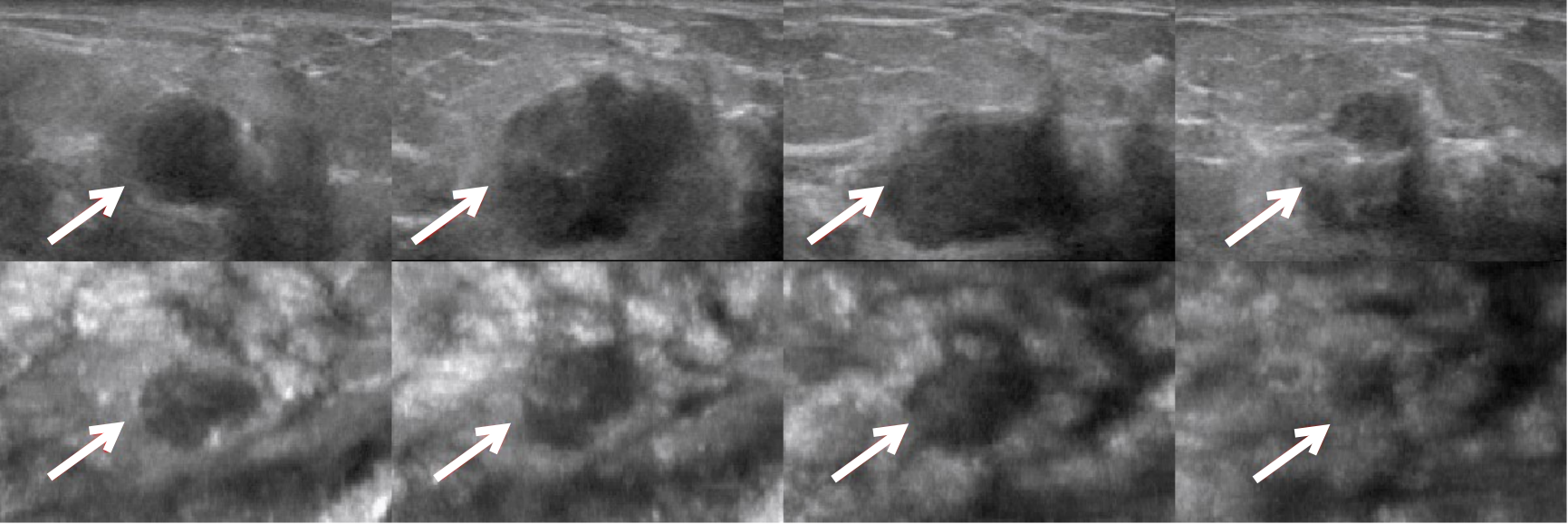
Table 1
Comparison for diagnostic performance of independent diagnosis and combined diagnosis
| Diagnostic method | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Accurcy (%) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DL-3DUV | 83.33(76.36, 95.30) | 81.58(73.09, 90.07) | 82.50(74.17, 90.83) | 0.83(0.73, 0.92) |
| Senior radiologists | 81.77(73.31, 90.23) | 87.73(80.54, 94.92) | 84.60(75.95, 93.25) | 0.85(0.80, 0.90) |
| Junior radiologists | 78.60(69.61, 87.59) | 57.00(46.15, 67.85) | 68.37(58.18, 78.56) | 0.68(0.61, 0.75) |
| Senior radiologists+ DL-3DUV | 89.70(83.04, 96.31) | 91.23(85.03, 97.43) | 89.17(82.36, 95.98) | 0.91(0.87, 0.95) |
| Junior radiologists+ DL-3DUV | 88.10(81.00, 95.20) | 82.47(74.14, 90.80) | 85.47(77.75, 93.19) | 0.85(0.80, 0.91) |
| Comparison between radiologists and DL-3DUV | ||||
| Senior radiologists vs. DL-3DUV(P) | 0.500 | 0.016 | 0.400 | 0.071 |
| Junior radiologists vs. DL-3DUV(P) | 0.031 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Senior radiologists vs. junior radiologists(P) | 0.125 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Comparison between radiologists in combination with DL-3DUV and radiologists | ||||
| Senior radiologists+ DL-3DUV vs. senior radiologists(P) | 0.001 | 0.125 | 0.118 | 0.001 |
| Junior radiologists+ DL-3DUV vs. junior radiologists(P) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.012 | <0.001 |
| Comparison between radiologists in combination with DL-3DUV and DL-3DUV | ||||
| Senior radiologists+ DL-3DUV vs. DL-3DUV(P) | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.824 | <0.001 |
| Junior radiologists+ DL-3DUV vs. DL-3DUV(P) | 0.031 | >0.99 | 0.125 | 0.007 |
| Comparison of different radiologists in combination with DL-3DUV | ||||
| Senior radiologists+ DL-3DUV vs. junior radiologists+ DL- 3DUV(P) | 0.250 | 0.002 | 0.092 | 0.001 |
| [1] | 邬昊, 吕青. 全球及中国乳腺癌的流行病学趋势及防控启示:2018-2022年《全球癌症统计报告》解读[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2024, 31(7):796-802. |
| WU H, LÜ Q. Epidemiological trends and implications of breast cancer prevention and control in China and the word: an interpretation of the global cancer statistics report 2018-2022[J]. Chin J Bases Clin Gen Surg, 2024, 31(7):796-802. | |
| [2] | 刘迎春, 陈林, 庞芸, 等. 基于自动乳腺容积扫描、乳腺X线摄影及MRI的BI-RADS分类鉴别乳腺良恶性肿[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2021, 37(3): 386-390. |
| LIU Y C, CHEN L, PANG Y, et al. BI-RADS classification based on automated breast volume scanning, X-ray mammography and MRI for differentiation of benign and malignant breast masses[J]. Chin J Med Imag Technol, 2021, 37(3):386-390. | |
| [3] | CHEN L, CHEN Y, DIAO X H, et al. Comparative study of automated breast 3D ultrasound and handheld B-mode ultrasound for differentiation of benign and malignant breast masses[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol, 2013, 39(10):1735-1742. |
| [4] | 中国超声医学工程学会仪器工程开发专业委员会, 中国抗癌协会肿瘤影像专委会, 中华医学会超声医学分会浅表组织与血管学组. 自动乳腺容积超声技术专家共识(2022版)[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2022, 38(3):241-247. |
| The Instrument Engineering Development Professional Committee of the Chinese Society of Ultrasonic Medical Engineering, the Tumor Imaging Special Committee of the Chinese Anti Cancer Association, the Superficial Tissue and Vascular Group of the Ultrasound Medicine Branch of the Chinese Medical Association. Expert consensus on automated breast ultrasound technology (2022 edition)[J]. Chin J Ultrasound Med, 2022, 38(3):241-247. | |
| [5] |
BREM RF, TABAR L, DUFFY SW, et al. Assessing improvement in detection of breast cancer with three-dimensional automated breast US in women with dense breast tissue: the SomoInsight study[J]. Radiology, 2015, 274(3):663-673.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.14132832 pmid: 25329763 |
| [6] | VAN ZELST J C M, TAN T, PLATEL B, et al. Improved cancer detection in automated breast ultrasound by radio-logists using computer aided detection[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2017,89:54-59. |
| [7] | WANG Q, CHEN H, LUO G, et al. Performance of novel deep learning network with the incorporation of the automatic segmentation network for diagnosis of breast cancer in automated breast ultrasound[J]. Eur Radiol, 2022, 32(10):7163-7172. |
| [8] | WANG Y, CHOI E J, CHOI Y, et al. Breast cancer classification in automated breast ultrasound using multi-view convolutional neural network with transfer learning[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol, 2020, 46(5):1119-1132. |
| [9] | XIANG H, HUANG Y S, LEE C H, et al. 3-D Res-CapsNet convolutional neural network on automated breast ultrasound tumor diagnosis[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2021,138:109608. |
| [10] | ZHUANG Z, DING W, ZHUANG S, et al. Tumor classification in automated breast ultrasound (ABUS) based on a modified extracting feature network[J]. Comput Med Ima-ging Graph, 2021,90:101925. |
| [11] | ZHOU Y, CHEN H, LI Y, et al. Multi-task learning for segmentation and classification of tumors in 3D automated breast ultrasound images[J]. Med Image Anal, 2021,70:101918. |
| [12] | RYAN J T, HAYGOOD T M, YAMAL J M, et al. The "memory effect" for repeated radiologic observations[J]. Am J Roentgenol, 2011, 197(6):W985-W991. |
| [13] | D'ORSI C, MORRIS E, MENDELSON E. ACR BI-RADS Atlas: Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System[M]. American Collegeof Radiology, 2013. |
| [14] | WANG A, WU Y, JI X, et al. Assessing and optimizing large language models on spondyloarthritis multi-choice question answering: protocol for enhancement and assessment[J]. JMIR Res Protoc, 2024,13:e57001. |
| [15] |
XU X, BAO L, TAN Y, et al. 1000-case reader study of radiologists' performance in interpretation of automated breast volume scanner images with a computer-aided detection system[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol, 2018, 44(8):1694-1702.
doi: S0301-5629(18)30184-4 pmid: 29853222 |
| [16] |
YANG S, GAO X, LIU L, et al. Performance and reading time of automated breast us with or without computer-aided detection[J]. Radiology, 2019, 292(3):540-549.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019181816 pmid: 31210612 |
| [17] |
HE P, CUI L G, CHEN W, et al. Subcategorization of ultrasonographic BI-RADS category 4: assessment of diagnostic accuracy in diagnosing breast lesions and influence of clinical factors on positive predictive value[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol, 2019, 45(5):1253-1258.
doi: S0301-5629(18)30555-6 pmid: 30799123 |
| [18] | 麦武平, 周美君, 胡叶, 等. AI超声辅助诊断系统在低年资医师诊断甲状腺结节良恶性中的应用[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2021, 37(3):248-251. |
| MAI W P, ZHOU M J, HU Y, et al. The application of AI ultrasound-assisted diagnosis system in diagnosing benign and malignant thyroid nodules for junior sonographers[J]. Chin J Ultrasound Med, 2021, 37(3):248-251. | |
| [19] | 刘迎春, 陈林, 庞芸, 等. 自动乳腺容积扫描冠状面特征联合超声BI-RADS诊断乳腺癌的价值[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2020, 31(11):788-792. |
| LIU Y C, CHEN L, PANG Y, et al. Values of combined coronal view features of automated breast scanning with ultrasound BI-RADS for the diagnosis of breast cancer[J]. J China Clin Med Imag, 2020, 31(11):788-792. | |
| [24] | YANG J Y, SHEN J, SHEN S P, et al. Construction and analysis of preoperative lymph node metastasis load model of breast cancer patients based on dual-mode ultrasound[J]. Chin J Gen Pract, 2024, 22(4):646-650. |
| [25] | 张杰秋, 伍棋, 王舰梅, 等. 基于机器学习的病理组学特征可预测乳腺癌患者对新辅助化疗的反应[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2023, 48(12):1483-1488. |
| ZHANG J Q, WU Q, WANG J M, et al. Pathomics signature based on machine learning can predict the response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients[J]. J Chongqing Med Univ, 2023, 48(12):1483-1488. | |
| [20] | 包凌云, 朱罗茜, 孔凡雷, 等. 自动乳腺全容积成像和常规超声对乳腺微钙化诊断的对比研究[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2012, 21(3):220-223. |
| BAO L Y, ZHU L Q, KONG F L, et al. Comparative study of automated breast volume scanner with conventional ultrasound in diagnosing of breast microcalcifications[J]. Chin J Ultrasonography, 2012, 21(3):220-223. | |
| [21] |
VAN ZELST J C M, MANN R M. Automated three-dimensional breast US for screening: technique, artifacts, and lesion characterization[J]. Radiographics, 2018, 38(3):663-683.
doi: 10.1148/rg.2018170162 pmid: 29624482 |
| [22] | 吴佩佩, 张刚, 李倩, 等. 基于超声构建乳腺癌腋下淋巴结良恶性的预测模型[J]. 安徽医学, 2024, 45(11):1417-1423. |
| WU P P, ZHANG G, LI Q, et al. Prediction model for benign and malignant axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer based on ultrasound[J]. Anhui Med, 2024, 45(11): 1417-1423. | |
| [23] | 安林林, 马芳, 沈莉莉, 等. 乳腺癌超声征象与免疫组化指标表达关系的研究进展[J]. 中国临床研究, 2024, 37(10):1489-1493. |
| AN L L, MA F, SHEN L L, et al. Research progress on the relationship between ultrasound signs and expression of immunohistechemical indicators in breast cancer[J]. Chin Clin Res, 2024, 37(10):1489-1493. | |
| [24] | 杨骏宇, 沈吉, 沈思平, 等. 基于双模态超声的乳腺癌患者术前淋巴结转移负荷模型构建分析[J]. 中华全科医学, 2024, 22(4):646-650. |
| [1] | ZHANG Huihui, FANG Shu, WU Mengxiong, LIU Fangtao, HE Naying, DONG Haipeng, YAN Fuhua. Study on deep learning reconstruction technology in improving image quality of pituitary neuroendocrine tumors in coronal T1WI magnetic resonance image [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(06): 594-601. |
| [2] | RUAN Miao, DA Qian, XU Haimin, DONG Lei, FEI Xiaochun. Study on clinicopathological features and prognosis of HER2 low expression breast cancer [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(05): 500-508. |
| [3] | ZHA Yunfei, WU Xiaxia. Application and research progress of MRI deep learning image reconstruction technology in clinical diagnosis of musculoskeletal system diseases [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(02): 114-118. |
| [4] | LÜ Xiaoyu, FENG Weiming, ZHOU Huiyun, LI Jiqiang, DONG Haipeng, HUANG Juan. Feasibility of reducing scan time based on deep learning reconstruction in magnetic resonance imaging: a phantom study [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(02): 131-138. |
| [5] | QIAN Jiale, FAN Jing, ZHU Hong, WANG Luotong, KONG Deyan. The application of deep learning image reconstruction in dual-energy CT virtual non-contrast CT urography [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(02): 139-145. |
| [6] | LIU Juan, YIN Lijuan, FAN Desheng. The clinicopathologic significance of AR, SKP2, SOX10, PD-L1 and TILs expression in triple-negative breast cancer [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(02): 162-172. |
| [7] | OU Dan, CAI Gang, CHEN Jiayi. Bioinformatics analysis for expression of RAD51AP1 in triple negative breast cancer with brain metastasis [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(02): 146-154. |
| [8] | YAN Ling, WANG Lingyun, CHEN Yong, DU Lianjun. Application of deep learning image reconstruction algorithm in dual-energy CT scanning for preoperative T sta-ging of gastric cancer [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(02): 154-159. |
| [9] | FAN Jing, YANG Wenjie, WANG Mengzhen, LU Wei, SHI Xiaomeng, ZHU Hong. The application of deep learning algorithm reconstruction in low tube voltage coronary CT angiography [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2022, 21(03): 374-379. |
| [10] | HOU Xiaosa, YANG Zhenjiang. Risk factors of non-sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients with positive sentinel lymph nodes [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2021, 20(03): 284-289. |
| [11] | LU Yejun, CHEN Hui, ZHANG Jian, XU Bin, WANG Chong, HE Ye. Superb microvascular imaging in combination with ultrasonic elastography and high-frequency ultrasound in micro breast cancer:an assessment on the diagnostic efficacy and screening for high-risk features on ultrasound [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2020, 19(04): 391-396. |
| [12] | ZHONG Ming, ZHAO Feng, WU Yan, PEI Wenjiang, GAO Hang, GUO Shanyu, DAI Qiancheng, ZHANG Wei. Establishment of a detection method for tumor suppressor gene HIC-1 methylation in cell-free DNA and its significance in diagnosis of breast diseases [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2019, 18(2): 144-148. |
| [13] | WANG Zhiwei, ZHANG Xiaoxiao, WANG Jie, WEI Min, SHAO Yuguo, JI Min, YANG Li, HE Qi. Influencing factors of axillary lymph node metastasis in patients with locally advanced breast cancer [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2019, 18(2): 189-192. |
| [14] | YAO Jiejie, ZHU Ying, ZHAN Weiwei, CHEN Xiaosong, FEI Xiaochun. Correlation of sonographic features of non-mass ductal carcinoma in situ with clinicopathological findings and biomarkers [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2018, 17(06): 676-681. |
| [15] | PEI Wenjiang, ZHAO Feng, WU Yan, ZHONG Ming, GAO Hang, LI Yousheng, GU Yan, GUO Shanyu, DAI Qiancheng, ZHANG Wei. Effect of hypermethylated in cancer 1-downstream-regulated gene HMMR on cell migration and invasion in breast cancer: an in vitro study on breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2018, 17(01): 70-75. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||