

Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice ›› 2024, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (06): 594-601.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2024.06.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Huihui, FANG Shu, WU Mengxiong, LIU Fangtao, HE Naying, DONG Haipeng( ), YAN Fuhua
), YAN Fuhua
Received:2023-02-22
Online:2024-12-25
Published:2024-12-25
Contact:
DONG Haipeng
E-mail:dhp40427@rjh.com.cn
CLC Number:
ZHANG Huihui, FANG Shu, WU Mengxiong, LIU Fangtao, HE Naying, DONG Haipeng, YAN Fuhua. Study on deep learning reconstruction technology in improving image quality of pituitary neuroendocrine tumors in coronal T1WI magnetic resonance image[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(06): 594-601.
Table 1
Consistency analysis results of subjective image quality evaluation indicators of two doctors [ICC value (95% confidence interval)]
| Subjective evaluation indicators | DL T1WI FS | OR T1WI FS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Doctor 1 | Doctor 2 | ICC | Doctor 1 | Doctor 2 | ICC | ||
| Uniformity | 4.33(3,5) | 4.35(4,5) | 0.92(0.85~0.96) | 3.73(3,4) | 3.78(3,4) | 0.88(0.76~0.93) | |
| Sharpness | 4.25(3,5) | 4.28(3,5) | 0.90(0.81~0.95) | 3.50(3,4) | 3.53(3,4) | 0.86(0.73~0.93) | |
| Artifacts | 4.35(4,5) | 4.38(4,5) | 0.84(0.71~0.91) | 2.95(2,4) | 2.93(2,4) | 0.87(0.75~0.93) | |
| Recognition of pituitary structure | 4.38(3,5) | 4.45(4,5) | 0.93(0.87~0.96) | 3.35(2,5) | 3.38(3,5) | 0.89(0.79~0.94) | |
| Recognition of the lesion | 4.6(3,5) | 4.53(3,5) | 0.85(0.71~0.92) | 3.15(2,4) | 3.18(2,4) | 0.87(0.74~0.93) | |
| Overall quality | 4.30(4,5) | 4.4(4,5) | 0.89(0.79~0.94) | 2.63(2,3) | 2.68(2,3) | 0.88(0.77~0.94) | |
Table 2
Consistency analysis results of objective image quality evaluation indicators of two doctors [ICC value (95% confidence interval)]
| Objective evaluation indicators | DL T1WI FS | OR T1WI FS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Doctor 1 | Doctor 2 | ICC | Doctor 1 | Doctor 2 | ICC | ||
| SNR adenoma | 26.34(11.42,45.55) | 28(10.45,70.66) | 0.859(0.73~0.93) | 16.76(7.8,30.26) | 17.39(8.06,34.55) | 0.912(0.83~0.95) | |
| CNR adenoma | 13.72(3.56,30.9) | 12.65(0.41,31.81) | 0.949(0.90~0.97) | 4.44(1.12,8.51) | 4.68(1.9,10.49) | 0.889(0.79~0.94) | |
| SNR pituitary | 39.92(18.76,67.79) | 39.72(21.82,75.51) | 0.934(0.88~0.97) | 18.42(11.21,28.43) | 18.2(11.64,26.41) | 0.876(0.77~0.93) | |
| CNR pituitary | 32.12(13.36,63.39) | 30.46(10.45,55.09) | 0.891(0.79~0.94) | 20.73(10.89,42.76) | 21.4(11.61,43.8) | 0.907(0.83~0.95) | |
Table 3
Comparison results of subjective evaluation of two sequences
| Subjective evaluation indicators | DL T1WI FS | OR T1WI FS | Value of Z | Value of P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uniformity | 4.33(3,5) | 3.73(3,4) | -4.69 | <0.001 |
| Sharpness | 4.25(3,5) | 3.50(3,4) | -5.04 | <0.001 |
| Artifacts | 4.35(4,5) | 2.95(2,4) | -7.96 | <0.001 |
| Recognition of pituitary structure | 4.38(3,5) | 3.35(2,5) | -6.14 | <0.001 |
| Recognition of the lesion | 4.6(3,5) | 3.15(2,4) | -7.25 | <0.001 |
| Overall quality | 4.30(4,5) | 2.63(2,3) | -8.04 | <0.001 |
Figure 1
T1WI FS coronal images of a 54-year-old female patient with a large pituitary adenoma As shown in the figure, the sella turcica was enlarged and the floor of the sella turcica was slightly sunken, and the maximum diameter of the lesion is 18 mm. A, C: DL T1WI FS coronal images; B, D: OR T1WI FS coronal images. Compared with the OR T1WI FS images, the boundary of the pituitary lesion displayed by the DL T1WI FS is clearer, the image uniformity, sharpness, recognition of pituitary structure, and recognition of the lesion are better, and the noise are significantly reduced.
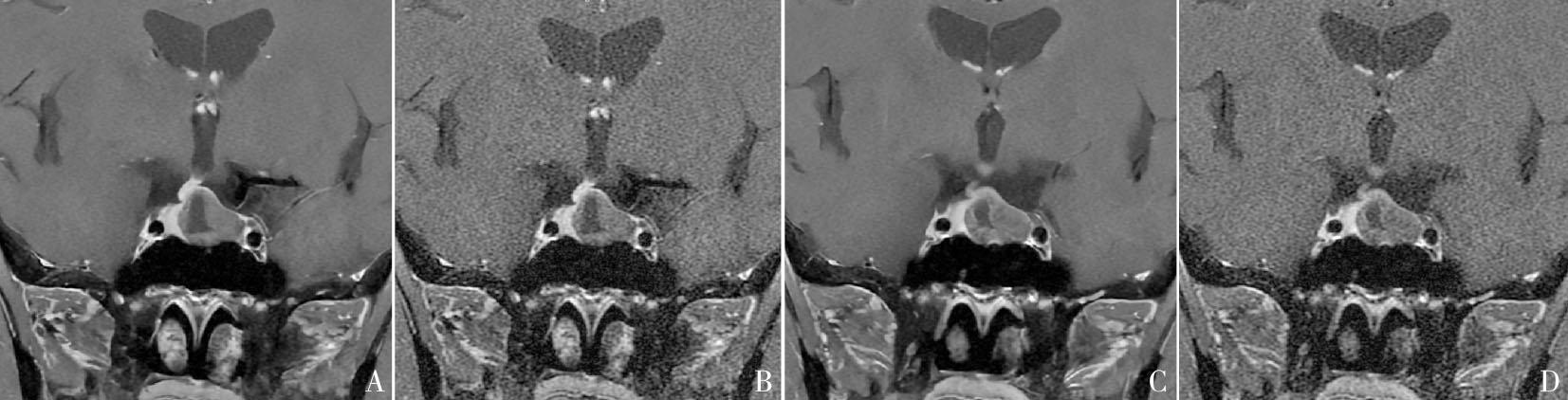

Figure 2
T1WI FS coronal images of a 23-year-old male patient with a large pituitary adenoma Nodule in the right sellar base-cavernous sinus region can be seen, the pituitary stalk is slightly left, lesions with a maximum diameter of 12 mm. A, C: DL T1WI FS coronal image; B, D: OR T1WI FS coronal image. Compared with OR T1WI FS image, DL T1WI FS showed clearer outline of lesion edges, clearer display of image details, better uniformity, sharpness, recognition of the lesion, and smaller noise.
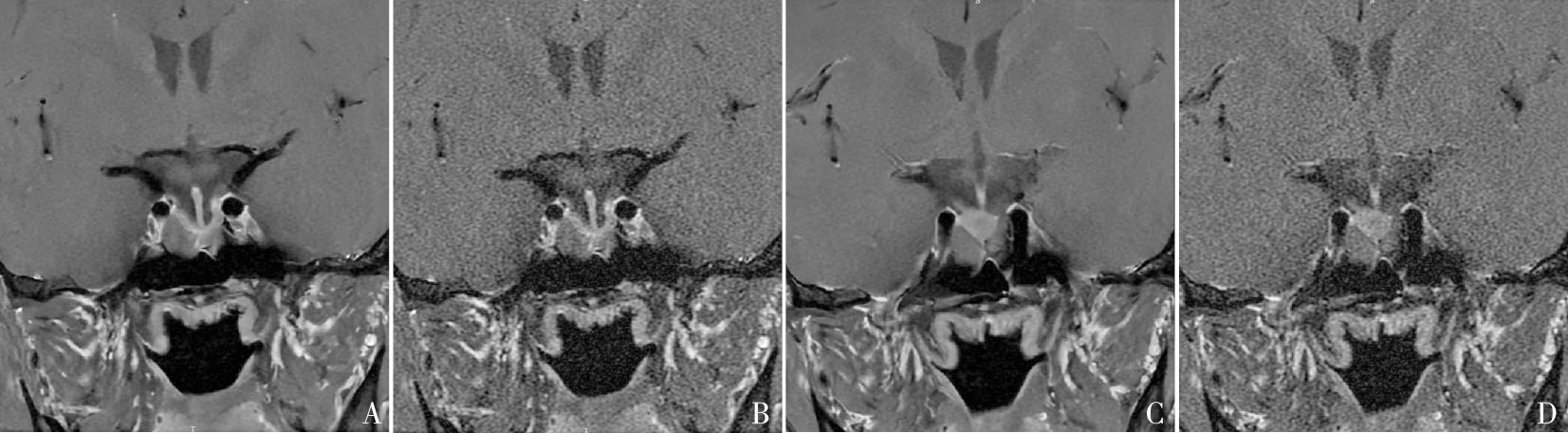
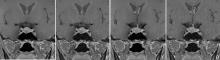
Figure 3
T1WI FS coronal images of a 38-year-old male patient with a microadenoma of the pituitary gland The right-wing nodule of pituitary gland can be seen, the pituitary gland is full in shape, and the pituitary stalk slightly deviates to the left. The largest diameter of the lesion is 8 mm., A, C: DL T1WI FS coronal image; B, D: OR T1WI FS coronal image. Compared with OR T1WI FS images, DL T1WI FS showed clear outline of pituitary lesions, better image uniformity, sharpness, recognition of pituitary structure, and recognition of the lesion, and less noise.
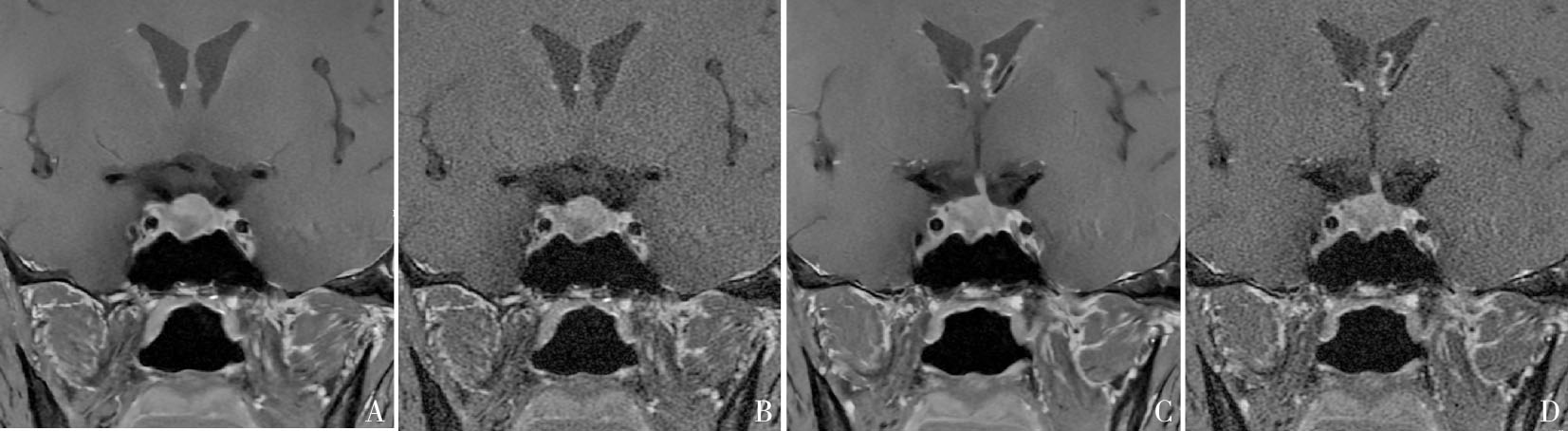
Table 4
Comparison results of objective evaluation of two sequences
| Objective evaluation indicators | DL T1WI FS | OR T1WI FS | Value of Z | Value of P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR adenoma | 26.96(18.10,34.15) | 16.51(11.24,20.65) | -4.44 | <0.000 1 |
| CNR adenoma | 11.30(6.74,19.72) | 4.34(3.07,6.00) | -5.55 | <0.000 1 |
| SNR pituitary | 38.36(31.93,47.03) | 17.02(15.49,20.51) | -5.44 | <0.000 1 |
| CNR pituitary | 29.89(23.28,39.75) | 18.44(16.61,24.56) | -4.27 | <0.000 1 |
| [1] |
DI IEVA A, ROTONDO F, SYRO L V, et al. Aggressive pituitary adenomas--diagnosis and emerging treatments[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2014, 10(7):423-435.
doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2014.64 pmid: 24821329 |
| [2] |
WANG X, DAI Y, LIN H, et al. Shape and texture analyses based on conventional MRI for the preoperative prediction of the aggressiveness of pituitary adenomas[J]. Eur Radiol, 2023, 33(5):3312-3321.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09412-7 pmid: 36738323 |
| [3] | 林绍坚, 吴隽宸, 吴哲褒. 加强垂体神经内分泌肿瘤的免疫治疗研究[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2024, 40(11):920-922. |
| LIN S J, WU J C, WU Z B, et al. Enhancing resreach on immunotherapy for pitutiary neuroendocrine tumors[J]. Chin J Endocrinol Metab, 2024, 40(11): 920-922. | |
| [4] | LEE D H, PARK J E, NAM Y K, et al. Deep learning-based thin-section MRI reconstruction improves tumour detection and delineation in pre- and post-treatment pitui-tary adenoma[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1):21302. |
| [5] |
TRITOS N A, MILLER K K. Diagnosis and management of pituitary adenomas: A review[J]. JAMA, 2023, 329(16):1386-1398.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.5444 pmid: 37097352 |
| [6] | BONNEVILLE J F, POTORAC J, BECKERS A. Neuroimaging of aggressive pituitary tumors[J]. Rev Endocr Metab Disord, 2020, 21(2):235-242. |
| [7] |
KIM M, KIM H S, KIM H J, et al. Thin-slice pituitary MRI with deep learning-based reconstruction: diagnostic performance in a postoperative setting[J]. Radiology, 2021, 298(1):114-122.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020200723 pmid: 33141001 |
| [8] | KIM M, KIM H S, PARK J E, et al. Thin-slice pituitary MRI with deep learning-based reconstruction for preo-perative prediction of cavernous sinus invasion by pitui-tary adenoma: a prospective study[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2022, 43(2):280-285. |
| [9] | RASTOGI A, BRUGNARA G, FOLTYN-DUMITRU M, et al. Deep-learning-based reconstruction of under-sampled MRI to reduce scan times: a multicentre, retrospective, cohort study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2024, 25(3):400-410. |
| [10] | 严福华. 深度学习图像重建算法的临床应用和发展前景[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2022, 56(11):1165-1167. |
| YAN F H. The clinical application and development prospect of deep learning reconstruction algorithm[J]. Chin J Radiol, 2022, 56(11):1165-1167. | |
| [11] |
VAN DER VELDE N, HASSING H C, BAKKER B J, et al. Improvement of late gadolinium enhancement image quality using a deep learning-based reconstruction algorithm and its influence on myocardial scar quantification[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(6):3846-3855.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07461-w pmid: 33219845 |
| [12] | DUBLJEVIC N, MOORE S, LAUZON M L, et al. Effect of MR head coil geometry on deep-learning-based MR image reconstruction[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2024, 92(4):1404-1420. |
| [13] | SHIRAISHI K, NAKAURA T, UETANI H, et al. Deep learning-based reconstruction and 3D hybrid profile order technique for MRCP at 3T: evaluation of image qua-lity and acquisition time[J]. Eur Radiol, 2023, 33(11):7585-7594. |
| [14] | ICHINOHE F, OYAMA K, YAMADA A, et al. Usefulness of breath-hold fat-suppressed T2-weighted images with deep learning-based reconstruction of the liver: comparison to conventional free-breathing turbo spin echo[J]. Invest Radiol, 2023, 58(6):373-379. |
| [15] | 方姝, 吴梦雄, 陈乾, 等. 深度学习在肝脏屏气T2加权成像图像质量评价中的应用研究[J]. 磁共振成像, 2023, 14(5):31-35,40. |
| FANG S, WU M X, CHEN Q, et al. Clinical feasibility of breath-hold fat-suppressed T2-weighted sequence with deep learning reconstruction for liver imaging[J]. Chin J Magn Reson Imaging, 2023, 14(5): 31-35+40. | |
| [16] | CHAIKA M, AFAT S, WESSLING D, et al. Deep learning-based super-resolution gradient echo imaging of the pancreas: Improvement of image quality and reduction of acquisition time[J]. Diagn Interv Imaging, 2023, 104(2):53-59. |
| [17] |
ALMANSOUR H, GASSENMAIER S, NICKEL D, et al. Deep learning-based superresolution reconstruction for upper abdominal magnetic resonance imaging: An analysis of image quality, diagnostic confidence, and lesion conspicuity[J]. Invest Radiol, 2021, 56(8):509-516.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000769 pmid: 33625063 |
| [18] | SAUER S T, CHRISTNER S A, LOIS A M, et al. Deep learning k-space-to-image reconstruction facilitates high spatial resolution and scan time reduction in diffusion-weighted imaging breast MRI[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2024, 60(3):1190-1200. |
| [19] | LEE K L, KESSLER D A, DEZONIE S, et al. Assessment of deep learning-based reconstruction on T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted prostate MRI image quality[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2023, 166:111017. |
| [20] |
FEUERRIEGEL G C, WEISS K, KRONTHALER S, et al. Evaluation of a deep learning-based reconstruction method for denoising and image enhancement of shoulder MRI in patients with shoulder pain[J]. Eur Radiol, 2023, 33(7):4875-4884.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09472-9 pmid: 36806569 |
| [21] |
ESTLER A, HAUSER T K, BRUNNÉE M, et al. Deep learning-accelerated image reconstruction in back pain-MRI imaging: reduction of acquisition time and improvement of image quality[J]. Radiol Med, 2024, 129(3):478-487.
doi: 10.1007/s11547-024-01787-x pmid: 38349416 |
| [22] | KANIEWSKA M, DEININGER-CZERMAK E, GETZMANN J M, et al. Application of deep learning-based image reconstruction in MR imaging of the shoulder joint to improve image quality and reduce scan time[J]. Eur Radiol, 2023, 33(3):1513-1525. |
| [23] |
YOO H, YOO R E, CHOI S H, et al. Deep learning-based reconstruction for acceleration of lumbar spine MRI: a prospective comparison with standard MRI[J]. Eur Radiol, 2023, 33(12):8656-8668.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09918-0 pmid: 37498386 |
| [24] | XIE Y, LI X, HU Y, et al. Deep learning reconstruction for turbo spin echo to prospectively accelerate ankle MRI: A multi-reader study[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2024, 175:111451. |
| [25] |
SUH P S, PARK J E, ROH Y H, et al. Improving diagnostic performance of MRI for temporal lobe epilepsy with deep learning-based image reconstruction in patients with suspected focal epilepsy[J]. Korean J Radiol, 2024, 25(4):374-383.
doi: 10.3348/kjr.2023.0842 pmid: 38528695 |
| [26] | CHAIKA M, BRENDEL J M, URSPRUNG S, et al. Deep learning reconstruction of prospectively accelerated MRI of the pancreas: clinical evaluation of shortened breath-hold examinations with dixon fat suppression[J/OL]. Invest Radiol, 2024-07-23. https://journals.lww.com/investigativeradiology/abstract/9900/deep_learning_reconstruction_of_prospectively.235.aspx. |
| [27] | SHANBHOGUE K, TONG A, SMEREKA P, et al. Accele-rated single-shot T2-weighted fat-suppressed (FS) MRI of the liver with deep learning-based image reconstruction: qualitative and quantitative comparison of image quality with conventional T2-weighted FS sequence[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(11):8447-8457. |
| [28] | PARK H, NAM Y K, KIM H S, et al. Deep learning-based image reconstruction improves radiologic evaluation of pituitary axis and cavernous sinus invasion in pitui-tary adenoma[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2023, 158:110647. |
| [29] | GONG K, HAN P, EL FAKHRI G, et al. Arterial spin labeling MR image denoising and reconstruction using unsupervised deep learning[J]. NMR Biomed, 2022, 35(4):e4224. |
| [30] |
KAKIGI T, SAKAMOTO R, TAGAWA H, et al. Diagnostic advantage of thin slice 2D MRI and multiplanar reconstruction of the knee joint using deep learning based denoising approach[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1):10362.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14190-1 pmid: 35725760 |
| [31] | DALY A F, BECKERS A. The epidemiology of pituitary adenomas[J]. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am, 2020, 49(3):347-355. |
| [32] | LIU Z, WEN B, WANG Z, et al. Deep learning-based reconstruction enhances image quality and improves diagnosis in magnetic resonance imaging of the shoulder joint[J]. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 2024, 14(4):2840-2856. |
| [33] |
WANG X, MA J, BHOSALE P, et al. Novel deep learning-based noise reduction technique for prostate magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Abdom Radiol (NY), 2021, 46(7):3378-3386.
doi: 10.1007/s00261-021-02964-6 pmid: 33580348 |
| [34] | TAO Q, WANG K, WEN B, et al. Assessment of image quality and diagnostic accuracy for cervical spondylosis using T2W-STIR sequence with a deep learning-based reconstruction approach[J]. Eur Spine J, 2024, 33(8):2982-2996. |
| [1] | ZHOU Henghua, LIN Lan, ZHU Guixiang, LIU Min, HUANG Wentao. Pure epithelial neuroendocrine neoplasms of the bladder: clinicopathological characteristics of 2 cases and literature review [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(06): 602-611. |
| [2] | FENG Yuan, HE Zhao, SUN Qingfang, SUN Bomin, YAN Fuhua, YANG Guangzhong. Advances in interventional magnetic resonance imaging and its clinical applications [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(02): 108-113. |
| [3] | ZHA Yunfei, WU Xiaxia. Application and research progress of MRI deep learning image reconstruction technology in clinical diagnosis of musculoskeletal system diseases [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(02): 114-118. |
| [4] | LÜ Xiaoyu, FENG Weiming, ZHOU Huiyun, LI Jiqiang, DONG Haipeng, HUANG Juan. Feasibility of reducing scan time based on deep learning reconstruction in magnetic resonance imaging: a phantom study [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(02): 131-138. |
| [5] | QIAN Jiale, FAN Jing, ZHU Hong, WANG Luotong, KONG Deyan. The application of deep learning image reconstruction in dual-energy CT virtual non-contrast CT urography [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(02): 139-145. |
| [6] | GAO Meng, CHAI Weimin, YAN Fuhua. Advance in study on diagnosis of pancreatic cystic tumors on CT/MRI imaging [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(02): 184-191. |
| [7] | LI Ming, CHEN Kemin, PAN Zilai, LUO Yu. Research progress on the value of CT and MRI in predicting hemorrhagic transformation after acute ischemic stroke [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(01): 83-89. |
| [8] | DING Jingfeng, AO Weiqun, ZHU Zhen, SUN Jing, XU Lianggen, ZHENG Shibao, YU Jingjing, HU Jinwen. The value of radiomics based on T2WI and DWI of MRI in preoperative prediction of extramural vascular invasion in rectal cancer [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(01): 46-56. |
| [9] | ZHOU Yilei, ZHANG Miao, GUO Rui, ZHOU Jinxin, LI Biao, LI Xiang. Value of 18F-PSMA PET/MRI for early diagnosis of recurrence and metastasis in prostate cancer patients after radical prostatectomy [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(06): 567-572. |
| [10] | FENG Li, REN Gang, CAI Rong, WANG Xinyun, WANG Hui, ZHU Mingjie. Clinical features study of perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) in genitourinary system [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(05): 460-465. |
| [11] | LI Xiaoshi, QIN Yue. Multiple radiology imaging techniques in the diagnosis of gout [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(03): 311-318. |
| [12] | YAN Ling, WANG Lingyun, CHEN Yong, DU Lianjun. Application of deep learning image reconstruction algorithm in dual-energy CT scanning for preoperative T sta-ging of gastric cancer [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(02): 154-159. |
| [13] | CHEN Qian, LIN Huimin, YAN Fuhua. Advances in the evaluation of hepatic function by magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(02): 190-196. |
| [14] | FAN Jing, YANG Wenjie, WANG Mengzhen, LU Wei, SHI Xiaomeng, ZHU Hong. The application of deep learning algorithm reconstruction in low tube voltage coronary CT angiography [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2022, 21(03): 374-379. |
| [15] | HUANG Juan, ZHU Xiaolei, LI Xiao, CHEN Kemin, YAN Fuhua, XU Xueqin. Study on blood oxygen level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of early renal hypoxia in chronic kidney disease [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2022, 21(03): 385-389. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||