Contemporary Foreign Languages Studies ›› 2020, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (6): 128-137.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8921.2020.06.014
Previous Articles Next Articles
Online:2020-11-28
Published:2021-10-13
CLC Number:
WENG Yiming, WANG Jinping. A Corpus-based Contrastive Study of Human and Machine English Translation of Chinese paratactic Sentences[J]. Contemporary Foreign Languages Studies, 2020, 20(6): 128-137.
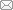
| 文本/流水句数 译文对比项 | 《骆》100 | 《狼》100 | 《围》100 | 《组》50 | 《色》20 | 总计370 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 标译/ G译 | 标译/ G译 | 标译/ G译 | 标译/ G译 | 标译/ G译 | 标译/ G译 | ||
| 句法 差异 | 主语变化(例) | 23 /0 | 12/0 | 8/0 | 2/0 | 5/0 | 50/0 |
| 非谓语动 (例) | 34 /11 | 36/8 | 37/ 8 | 7/1 | 23/ 7 | 137/35 | |
| 从句(例) | 20 /4 | 18/5 | 13/3 | 6/1 | 4/1 | 61/14 | |
| 小计 | 77/15 | 66/13 | 58/11 | 15/2 | 32/8 | 248/49 | |
| 篇章 差异 | 主观性关联词(例) | 18 / 4 | 12/1 | 15/ 2 | 8/ 0 | 6/1 | 59/8 |
| 句子语序调整(例) | 10 /0 | 2/0 | 2/0 | 1/0 | 3/0 | 18/0 | |
| 小计 | 28/4 | 14/1 | 17/2 | 9/0 | 8/1 | 77/8 | |
| 合计 | 105/19 | 80/14 | 75/13 | 24/2 | 41/9 | 325/57 | |
| [1] | Blum-Kulka S. 2000. Shifts of cohesion and coherence in translation[A]. In L. Venuti (ed.) The Translation Studies Reader[C]. London and New York: Routledge. 193-214. |
| [2] | Hutchins W. J. & H. L. Somers. 1992. An Introduction to Machine Translation[M]. San Diego: Academic Press. |
| [3] | Quirk R.,S. Greenbaum G. Leech & J.Svartvik. 1985. A Comprehensive Grammar of the English Language[M]. London: Longman. |
| [4] | 蔡子龙、杨明明、熊德意. 2018. 基于数据增强技术的神经机器翻译[J]. 中文信息学报(7):30-36. |
| [5] | 冯志伟. 2018. 机器翻译与人工智能的平行发展[J]. 外国语(上海外国语大学学报)(6):35-48. |
| [6] | 傅敬民、谢莎. 2015. 翻译技术的发展与翻译教学[J]. 外语电化教学 (6):37-41. |
| [7] | 黄荷. 2017. “英语文学最长句”中的逻辑语义关系:功能文体学视角[J]. 外语教学(6):37-41. |
| [8] | 李明. 2006. 汉英互动翻译教程[M]. 武汉: 武汉大学出版社. |
| [9] | 刘必庆. 2006. 新编汉英对比与翻译新编汉英对比与翻译[M]. 北京: 中国对外翻译出版公司. |
| [10] | 蒋跃. 2014. 人工译本与机器在线译本的语言计量特征对比——以5届韩素音翻译竞赛英译汉人工译本和在线译本为例[J]. 外语教学(5):98-102. |
| [11] | 蒋跃、张英贤、韩纪建. 2016. 英语被动句人机翻译语言计量特征对比——以《傲慢与偏见》译本为例[J]. 外语电化教学(3):46-51+63. |
| [12] | 孙茂松、周建设. 2016. 从机器翻译历程看自然语言处理研究的发展策略[J]. 语言战略研究(6):12-18. |
| [13] | 宋天锡、袁江、袁冬娥. 2000. 翻译新概念英汉互译实用教程[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社. |
| [14] | 王克非、胡显耀. 2008. 基于语料库的翻译汉语词汇特征研究[J]. 中国翻译(6):16-21+92. |
| [15] | 翁义明、王金平. 2018. 语言学视角下的译者主体性研究——以《二马》流水句的两个英译本对比为例[J]. 外国语言文学(3):276-291. |
| [16] | 张斌. 2010. 现代汉语描写语法[M]. 北京: 商务印书馆. |
| [17] | 朱德熙. 1985. 语法答问[M]. 北京: 商务印书馆. |
| [18] | 邹心胜. 2011. 基于领域本体重用的机器翻译研究[J]. 情报科学(6):935-938+956. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||