

Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice ›› 2023, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (03): 311-318.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2023.03.17
• Review articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2022-04-04
Online:2023-06-25
Published:2023-11-17
CLC Number:
LI Xiaoshi, QIN Yue. Multiple radiology imaging techniques in the diagnosis of gout[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(03): 311-318.
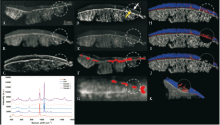
Figure 4
Visualization of calcium salt deposits by various imaging examinations (A) X-ray, (B) conventional CT, (C) ultrasound, (D) digital mammography, (E) micro-CT, (F) dual-energy CT, (G) MRI, (H-K) multi-energy photon counting detector CT. In PCD-CT, the water content of articular cartilage is marked in blue. While all imaging techniques are able to detect calcium crystal deposition within articular cartilage (yellow arrows and dashed circles), they have varying degrees of accuracy and clarity due to differences in spatial resolution. While dual-energy CT, MRI, and PCD-CT are all able to quantify calcium crystal deposition with varying accuracy, However, PCD-CT is the only technique that can determine the degree of crystal aggregation. (Figure from reference 46)
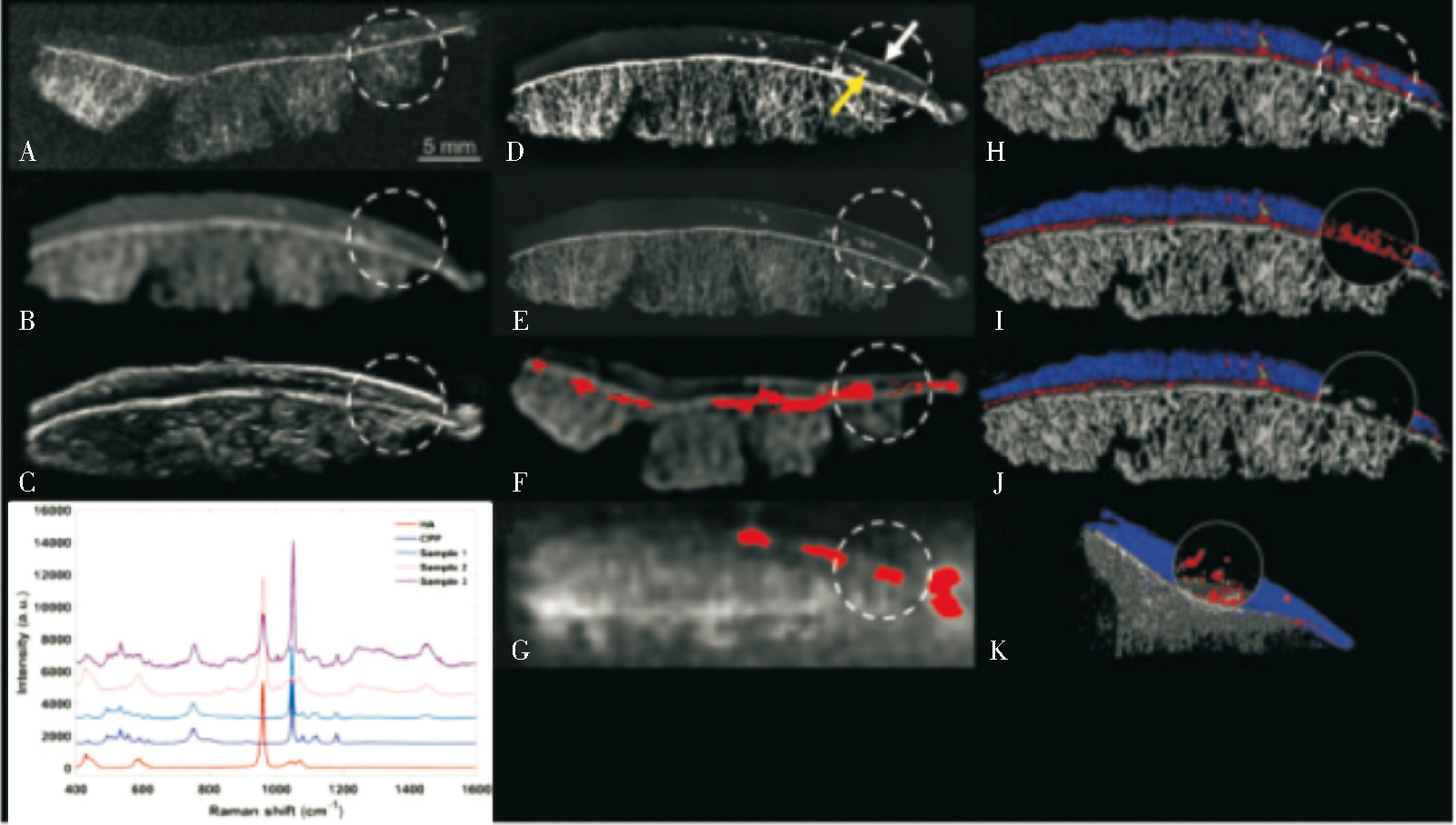
Table 1
Advantages and disadvantages of X-ray plain film, MRI and dual-energy CT in the diagnosis of gout
| 影像学检查 | 优势 | 劣势 |
|---|---|---|
| X线平片摄影 | 价格低廉 | 灵敏度低 |
| 基层医院设备充足 | 在检测骨质破坏方面不如MRI准确 | |
| 特异性高 | 特异性特征出现在疾病晚期 | |
| 无法检测其他特征,包括MSU晶体沉积 | ||
| MRI | 能够检测皮下和深层组织内的痛风石 | 检查费用昂贵 |
| 基层或社区医院缺少设备 | ||
| 无法直接可视化MSU晶体沉积 | ||
| 双能量CT | 可以直接观察到MSU晶体沉积 | 具有电离辐射 |
| 特异性及敏感性都很高 | 痛风疾病早期敏感性没有统一标准 | |
| 诊断难度较小,可以引入人工智能技术 |
| [1] | 杨丽华, 刘晓丽, 蒋雅琼, 等. 我国痛风的患病率及危险因素[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2019, 48(12):4-6. |
| YANG L H, LIU X L, JIANG Y Q, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of gout in China[J]. J Med Res, 2019, 48(12):4-6. | |
| [2] | 李燕, 陈秋志, 於一凡, 等. 痛风患者复发现状及其影响因素分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2022, 49(4):759-763. |
| LI Y, CHEN Q Z, YU Y F, et al. Analysis of recurrence status and influencing factors of gout patients[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2022, 49(4):759-763. | |
| [3] | 李志军. 痛风及高尿酸血症的诊断与治疗[J]. 中华全科医学, 2020, 18(1):5-6. |
| LI Z J. Diagnosis and treatment of gout and hyperuricemia[J]. Chin General Prac, 2020, 18(1):5-6. | |
| [4] | 胡有元. 血尿酸正常痛风的机制研究进展[J]. 甘肃医药, 2021, 40(4):299-301. |
| HU Y Y. Research progress on the mechanism of normal blood uric acid gout[J]. J Gansu Med, 2021, 40(4):299-301. | |
| [5] | 赵敏, 陈婷, 黄振光, 等. 1990—2019年中国痛风疾病负担研究[J]. 现代预防医学, 2021, 48(21):3974-3978. |
| ZHAO M, CHEN T, HUANG Z G, et al. Disease burden of gout in China,1990-2019[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2021, 48(21):3974-3978. | |
| [6] | 陆群群, 张永, 李琳, 等. 启动急性痛风发作炎性细胞因子的研究[J]. 医学理论与实践, 2021, 34(12):2002-2004,2001. |
| LU Q Q, ZHANG Y, LI L, et al. Study on inflammatory cytokines that triggering the onset of gout[J]. J Med Theory Pract, 2021,(12):2002-2004,2001. | |
| [7] | NEOGI T, JANSEN T L, DALBETH N, et al. 2015 Gout classification criteria: an American College of Rheumato-logy/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2015, 67(10):1789-1798. |
| [8] | ABHISHEK A, RODDY E, DOHERTY M. Gout-a guide for the general and acute physicians[J]. Clin Med (Lond), 2017, 17(1):54-59. |
| [9] | HuberN. Zur Verwertung der Röntgenstrahlen. Gebiete der inneren Medizin[J]. Deutsche Med Wochnschr, 1896, 22:182-184. |
| [10] | SUDOŁ-SZOPIŃSKA I, AFONSO P D, JACOBSON J A, et al. Imaging of gout: findings and pitfalls. A pictorial review[J]. Acta Reumatol Port, 2020, 45(1):20-25. |
| [11] | 朱忠军, 卜秀彦. X线诊断痛风性关节炎患者的临床诊断价值分析[J]. 影像研究与医学应用, 2021, 5(20):127-128. |
| ZHU Z J, BU X Y. Diagnostic value of X-ray in gouty arthritis patients[J]. Imaging Res Med, 2021, 5(20):127-128. | |
| [12] |
BRAIG E M, ROISER N, KIMM M A, et al. X-ray dark-field radiography: potential for visualization of monosodium urate deposition[J]. Invest Radiol, 2020, 55(8):494-498.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000671 URL |
| [13] |
MOGENSEN M A, DECONDE R P, SARIKAYA B. Spinal gout: Imaging and clinical features[J]. PM R, 2021, 13(11):1304-1306.
doi: 10.1002/pmrj.v13.11 URL |
| [14] | 陈凯然. X线诊断在痛风性关节炎患者中的临床应用[J]. 医疗装备, 2018, 31(5):114-116. |
| CHEN K R. Clinical application of X-ray diagnosis in gouty arthritis patients[J]. Med Equip, 2018, 31(5):114-116. | |
| [15] |
RICHETTE P, DOHERTY M, PASCUAL E, et al. 2018 updated European League Against Rheumatism evidence-based recommendations for the diagnosis of gout[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2020, 79(1):31-38.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215315 pmid: 31167758 |
| [16] |
CALVI M, GNESUTTA A, ZABETTA L C, et al. Case report of a tibial fracture in a patient suffering from gout: An atypical site, the importance of differential diagnosis[J]. Radiol Case Rep, 2022, 17(4):1180-1184.
doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2022.01.005 URL |
| [17] |
XIE Y, LI L, LUO R, et al. Diagnostic efficacy of joint ultrasonography, dual-energy computed tomography and minimally invasive arthroscopy on knee gouty arthritis, a comparative study[J]. Br J Radiol, 2021, 94(1121):20200493.
doi: 10.1259/bjr.20200493 URL |
| [18] | 蒋洪涛, 杜益文. X线、CT和MRI在痛风性关节炎诊断上的应用价值比较[J]. 吉林医学, 2020, 41(12):2973-2974. |
| JIANG H T, DU Y W. Comparison of X-ray, CT and MRI in diagnosis of gouty arthritis[J]. Jilin Med J, 2020, 41(12):2973-2974. | |
| [19] | 林仁杰, 郑道练, 陈深远. X线CT和磁共振成像诊断痛风性关节炎价值对比[J]. 实用医学影像杂志, 2021, 22(06):638-640. |
| LIN R J, ZHENG D L, CHEN S Y. X-ray computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of gouty arthritis value contrast[J]. J Pract Med Imaging, 2021, 22(6):638-640. | |
| [20] |
LI S, XU G, LIANG J, et al. The role of advanced imaging in gout management[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 12:811323.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.811323 URL |
| [21] |
WEAVER J S, VINA E R, MUNK P L, et al. Gouty arthropathy: review of clinical manifestations and treatment, with emphasis on imaging[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 11(1):166.
doi: 10.3390/jcm11010166 URL |
| [22] |
MATEEN S, KWAADU K Y, ALI S. Diagnosis, imaging, and potential morbidities of the hallux interphalangeal joint os interphalangeus[J]. Skeletal Radiol, 2022, 51(6):1143-1151.
doi: 10.1007/s00256-021-03946-x |
| [23] |
MOGENSEN M A, DECONDE R P, SARIKAYA B. Spinal gout: Imaging and clinical features[J]. PM R, 2021, 13(11):1304-1306.
doi: 10.1002/pmrj.v13.11 URL |
| [24] | 李慧. 痛风性膝关节炎的MR征象分析[J]. 现代医用影像学, 2020, 29(11):2070-2072. |
| LI H. Analysis of MR Signs of gouty knee arthritis[J]. Modern Medical Imaging, 20, 29(11):2070-2072. | |
| [25] |
CIMMINO M A, ZAMPOGNA G, PARODI M, et al. MRI synovitis and bone lesions are common in acute gouty arthritis of the wrist even during the first attack[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2011, 70(12):2238-2239.
doi: 10.1136/ard.2011.153353 pmid: 21791451 |
| [26] |
CURD E D, RAVICHANDIRAN K, ABOUALI J. Gouty tophus presenting as an anterior cruciate ligament mass in the knee: case report and brief review of relevant literature[J]. Int J Surg Case Rep, 2021, 82:105920.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2021.105920 URL |
| [27] | 刘欣, 杨海涛, 王琪琪, 等. MR T2WI单序列纹理分析对类风湿性关节炎和痛风性关节炎的鉴别诊断价值[J]. 磁共振成像, 2021, 12(5):50-54. |
| LIU X, YANG H T, WANG Q Q, et al. Texture analysis based on MR T2WI single sequence for differentiating rheumatoid arthritis from gouty arthritis[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2021, 12(5):50-54. | |
| [28] |
刘敏, 孟娟. 基于全科医生视角的《2020年美国风湿病学会痛风治疗指南》解读[J]. 中国全科医学, 2021, 24(25):3148-3153.
doi: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.133 |
| LIU M, MENG J. Interpretation of 2020 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Management of Gout from the Perspective of General Practitioners[J]. Chin J Gen Pract, 2021, 24(25):3148-3153. | |
| [29] |
POH Y J, DALBETH N, DOYLE A, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging bone edema is not a major feature of gout unless there is concomitant osteomyelitis: 10-year findi-ngs from a high-prevalence population[J]. J Rheumatol, 2011, 38(11):2475-2481.
doi: 10.3899/jrheum.110477 URL |
| [30] |
SCHUMACHER H R JR, BECKER M A, EDWARDS N L, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging in the quantitative assessment of gouty tophi[J]. Int J Clin Pract, 2006, 60:408-414.
pmid: 16620352 |
| [31] |
GERSTER J C, LANDRY M, DUVOISIN B, et al. Computed tomography of the knee joint as an indicator of intraarticular tophi in gout[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1996, 39(8):1406-1409.
doi: 10.1002/art.v39:8 URL |
| [32] | 沈中梅, 卫荣. 双能量CT对急性痛风结晶的评估及相关因素分析[J]. 影像研究与医学应用, 2022, 6(3):20-22,25. |
| SHEN Z M, WEI R. Evaluation of urate crystallization in acute gouty arthritis by dual energy CT and analysis of related factors[J]. Imaging Res Med, 2002, 6(3):20-22,25. | |
| [33] | 欧阳建龙, 王涛, 兰小文, 等. 能谱CT对痛风性关节炎的诊断价值[J]. 当代医学, 2021, 27(35):69-70. |
| OU YANG J L, WANG T, LAN X W, et al. The value of energy spectrum CT in the diagnosis of gouty arthritis[J]. Contemp Med, 2021, 27(35):69-70. | |
| [34] | STAUDER S K, PELOSO P M. Dual-energy computed tomography has additional prognostic value over clinical measures in gout including tophi: a systematic literature review[J]. J Rheumatol, 2022, 49(11):1256-1268. |
| [35] | 陆伟锋, 张丽卿. 新型影像学检查在痛风性关节炎早期诊断中的作用[J]. 医学综述, 2021, 27(3):571-575. |
| LU W F, ZHANG L Q. Function of Novel Imaging Techniques in Early Diagnosis of Gouty Arthritis[J]. Med Rev, 2021, 27(3):571-575. | |
| [36] | 骆秋霞, 李远辉. 光谱CT对痛风患者尿酸盐沉积的诊断价值[J]. 影像研究与医学应用, 2021, 5(8):80-81,84. |
| LUO Q X, LI Y H. Diagnostic value of spectral CT for urate deposition in gout patients[J]. Imaging Res Med, 2021, 5(8):80-81,84. | |
| [37] | 尚瑾. 足踝痛风:基于能谱成像技术的单源DECT对不同病程中疑似痛风性关节炎患者的价值[D]. 安徽医科大学, 2021. |
| SHANG J. Foot and ankle gout: Value of single source DECT based on energy spectrum imaging in patients with suspected gouty arthritis in different course of disease[D]. Anhui Med Univ, 2021. | |
| [38] | 鬲洋院, 李双, 张锦娟, 等. 内分泌代谢科就诊高尿酸血症患者痛风患病现状及其影响因素[J]. 华南预防医学, 2022, 48(02):241-243. |
| LI Y Y, LI S, ZHANG J J, et al. Prevalence and influen-cing factors of gout in patients with hyperuricemia in Endocrine Metabolism Department[J]. S Chin Prev Med, 2022, 48(2):241-243. | |
| [39] | WEAVER J S, OMAR I, MAR W, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of rheumatological diseases[J]. Pol J Radiol, 2022, 87:e93-e112. |
| [40] |
TOPROVER M, MECHLIN M, FIELDS T, et al. Monosodium urate deposition in the lumbosacral spine of patients with gout compared with non-gout controls: A dual-energy CT study[J]. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2022, 56:152064.
doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2022.152064 URL |
| [41] |
DALBETH N, KALLURU R, AATI O, et al. Tendon involvement in the feet of patients with gout: a dual-energy CT study[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2013, 72(9):1545-1548.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202786 pmid: 23334212 |
| [42] |
ZHANG J, KNOPP M I, KNOPP M V. Sparse detector configuration in sipm digital photon counting PET: a feasibility study[J]. Mol Imaging Biol, 2019, 21(3):447-453.
doi: 10.1007/s11307-018-1250-7 pmid: 30094653 |
| [43] |
RAJBHANDARY P L, PERSSON M, PELC N J. Detective efficiency of photon counting detectors with spectral degradation and crosstalk[J]. Med Phys, 2020, 47(1):27-36.
doi: 10.1002/mp.13889 pmid: 31665541 |
| [44] |
MARCUS R P, FLETCHER J G, FERRERO A, et al. Detection and Characterization of Renal Stones by Using Photon-Counting-based CT[J]. Radiology, 2018, 289(2):436-442.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018180126 pmid: 30084728 |
| [45] |
GRUNZ J P, HUFLAGE H, HEIDENREICH J F, et al. Image quality assessment for clinical cadmium telluride-based photon-counting computed tomography detector in cadaveric wrist imaging[J]. Invest Radiol, 2021, 56(12):785-790.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000789 URL |
| [46] |
EULER A, NOWAK T, BUCHER B, et al. Assessment of bone mineral density from a computed tomography topogram of photon-counting detector computed tomography-effect of phantom size and tube voltage[J]. Invest Radiol, 2021, 56(10):614-620.
doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000781 URL |
| [47] |
NOWAK T, EBERHARD M, SCHMIDT B, et al. Bone mineral density quantification from localizer radiographs: accuracy and precision of energy-integrating detector CT and photon-counting detector CT[J]. Radiology, 2021, 298(1):147-152.
doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020202767 pmid: 33141002 |
| [48] |
VENTURA-RÍOS L, SÁNCHEZ-BRINGAS G, PINEDA C, et al. Tendon involvement in patients with gout: an ultrasound study of prevalence[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2016, 35(8):2039-2044.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-016-3309-7 URL |
| [49] | 禤璇, 韦翠美, 许赤多, 等. 关节超声与双源CT对痛风性关节炎诊断效能的影像学比较[J]. 深圳中西医结合杂志, 2021, 31(13):91-93. |
| XUAN X, WEI C M, XU C D, et al. Comparison of imaging findings and effects between joint ultrasound and dual-energy CT in the diagnosis of gouty arthritis[J]. Shenzhen Comb Traditional Chin West Med, 2021, 31(13):91-93. | |
| [50] | 高金妹, 袁宇. 肌骨超声在痛风诊疗中的应用与研究进展[J]. 国际医学放射学杂志, 2021, 44(4):451-455. |
| HIGH J M, YUAN Y. Applications and research progresses of musculoskeletal ultrasound in gout[J]. Int J Med Radiol, 2021, 44(4):451-455. | |
| [51] |
ITO K, MINAMIMOTO R, MOROOKA M, et al. A case of gouty arthritis to tophi on 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging[J]. Clin Nucl Med, 2012, 37(6):614-617.
doi: 10.1097/RLU.0b013e3182478a66 pmid: 22614203 |
| [52] |
王飞跃, 李长贵, 国元元, 等. 平行高特:基于ACP的平行痛风诊疗系统框架[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 2017, 30(12):1057-1068.
doi: 10.16451/j.cnki.issn1003-6059.201712001 |
| WANG F Y, LI C G, GUO Y Y, et al. Parallel gout: an acp-based system framework for gout diagnosis and treatment[J]. J Pattern Recognit Artif Intell, 2017, 30(12):1057-1068. |
| [1] | WU Nanming, LI Jun, TAO Juan. Hot spots in diagnosis of malignant melanoma [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(03): 215-220. |
| [2] | YANG Qiao, FU Xin, WANG Zhe, LIU Tantan. Cytopathologic analysis of thyroid secondary tumors [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(03): 270-276. |
| [3] | HAO Jiaqi, WANG Xinlu, HU Xiaofan, PAN Xiaoxia, XU Jing, MA Jun. Clinical differential diagnosis of acute tubulointerstitial nephritis and acute tubular necrosis [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(02): 127-133. |
| [4] | XIE Yaqiong, LIN Xiaoyi. Value of serum-free light chain assay in differential diagnosis and staging of nephropathy of various etiologies [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(02): 166-171. |
| [5] | CHEN Qian, LIN Huimin, YAN Fuhua. Advances in the evaluation of hepatic function by magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(02): 190-196. |
| [6] | DIAO Xuehong, SHEN Yan, CHEN Lin, ZHAN Jia, FANG Liang, CAI Jianfei, CHEN Yue. Application of superb microvascular imaging technology in diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis in the clinical remission stage [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2022, 21(05): 575-580. |
| [7] | HUANG Juan, ZHU Xiaolei, LI Xiao, CHEN Kemin, YAN Fuhua, XU Xueqin. Study on blood oxygen level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of early renal hypoxia in chronic kidney disease [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2022, 21(03): 385-389. |
| [8] | WANG Zhaohui, WU Haibo. Clinicopathological analysis of 31 cases of gastric schwannoma [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2021, 20(06): 552-556. |
| [9] | ZHU Naiyi, JIANG Yixin, CHAI Li, CHAI Weimin. Diagnostic values of magnetic resonance imaging in mammography detected BI-RADS≥4 category calcifications with negative ultrasound results [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2021, 20(05): 439-444. |
| [10] | ZHANG Xuekun, LI Yan, YAN Fuhua, ZHAO Hongfei, SONG Qi. Application value of new accelerating technology based on constellation shuttling imaging in brain MRI [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2021, 20(04): 378-383. |
| [11] | SUN Tiantian, YE Baoying, YANG Yu, NIU Jianmei. Color Doppler ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in prenatal diagnosis of pernicious placenta previa and pernicious placenta previa with placenta accreta: clinic value and analysis of missed diagnosis [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2021, 20(02): 173-177. |
| [12] | CAO Juntao, HU Ming, QIAN Pingkang, TU Jianchun, ZHANG Huan, SHEN Junkang. Application value of 3.0T MRI 3D-MERGE sequence in evaluating the degree of supraspinatus tendon injury [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2021, 20(01): 77-81. |
| [13] | GU Xiaohong, SUN Aimin, WANG Qian, ZHU Ming, ZHONG Yumin. The three-dimensional balanced steady state free precession magnetic resonance imaging sequence in diagnosis of anomalous origin of the coronary artery from the pulmonary artery in children [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2020, 19(02): 145-150. |
| [14] | WU Shuang, XIE Qian, GUAN Xueni, ZHANG Sufang, GAO Xinfang, LIANG Zonghui. Perfomence of MRI intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion weighted imaging parameters in diagnosing active Crohn's disease [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2020, 19(02): 157-161. |
| [15] | CHEN Jie, HU Jin, YANG Kang, FU Yi. Analysis of risk factors and prognosis of cerebral hemorrhage patients accompanied by cortical superficial siderosis [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2019, 18(2): 133-138. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
