

Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice ›› 2024, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (01): 46-56.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2024.01.007
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
DING Jingfeng1, AO Weiqun2, ZHU Zhen1, SUN Jing1, XU Lianggen1, ZHENG Shibao1, YU Jingjing1, HU Jinwen1( )
)
Received:2023-10-30
Online:2024-02-25
Published:2024-05-30
Contact:
HU Jinwen
E-mail:hufeng678678@163.com
CLC Number:
DING Jingfeng, AO Weiqun, ZHU Zhen, SUN Jing, XU Lianggen, ZHENG Shibao, YU Jingjing, HU Jinwen. The value of radiomics based on T2WI and DWI of MRI in preoperative prediction of extramural vascular invasion in rectal cancer[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(01): 46-56.
Table 1
MRI-scanning parameters
| Equipment | Parameters Plane | T2WI | DWI Axial | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axial oblique | Sagittal | Coronal | |||
| Siemens Verio 3.0T | TR/TE,ms | 4 000/97 | 4 000/97 | 4 000/97 | 9 700/93 |
| FOV,mm | 240×240 | 220×220 | 220×220 | 280×350 | |
| Thickness,mm | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| b values | - | - | - | 0,800,1 500 | |
| Siemens Avanto 1.5T | TR/TE,ms | 4 120/97 | 3 940/85 | 4 990/96 | 4 912/95 |
| FOV,mm | 200×200 | 250×250 | 240×240 | 250×250 | |
| Thickness,mm | 2.5 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| b values | - | - | - | 50,400,800 | |
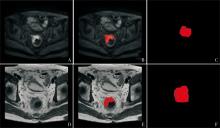
Figure 1
Segmentation of lesion A、D: DWI and T2WI original images containing lesion, respectively; B、E: Images after lesion segmentation on DWI and T2WI, respectively; The red area represents the area of the tumor that was segmented on the image;C, F: Three-dimensional masks generated by DWI and T2WI, respectively; The red area represents the three-dimensional mask automatically generated by the ITK-SNAP software after the tumor was segmented layer by layer.
Table 2
Clinical, imaging and pathological characteristics of patients in the training and validation sets
| Characteristics | Training set (n=123) | Validation set (n=45) | t/χ2 | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age(years) | 63.82±10.38 | 64.47±10.96 | 0.352 | 0.726 |
| Gender(%) | 0.164 | 0.686 | ||
| Male | 78(63.4) | 27(60.0) | ||
| Female | 45(36.6) | 18(40.0) | ||
| CEA(%) | 0.323 | 0.570 | ||
| ≤5 ng/mL | 77(62.6) | 26(57.8) | ||
| >5 ng/mL | 46(37.4) | 19(42.2) | ||
| ADC Value (×10-3mm2/s) | 0.81(0.72,0.91) | 0.78(0.71,0.87) | -1.091 | 0.275 |
| Infiltration depth (mm) | 15.34±5.73 | 16.61±8.09 | 1.130 | 0.260 |
| Length,(cm) | 43.14±15.78 | 44.50±15.56 | 0.496 | 0.621 |
| mrT stage(%) | 0.235 | 0.628 | ||
| T1~2 | 46(37.4) | 15(33.3) | ||
| T3~4 | 77(62.6) | 30(66.7) | ||
| mrEMVI(%) | 0.362 | 0.547 | ||
| Negative | 80(65.0) | 27(60.0) | ||
| Positive | 43(35.0) | 18(40.0) | ||
| pEMVI(%) | 0.016 | 0.900 | ||
| Negative | 89(72.4) | 33(73.3) | ||
| Positive | 34(27.6) | 12(26.7) | ||
| Radscore | -2.71(-3.87,-1.32) | -2.09(-3.87,-1.20) | -1.067 | 0.286 |
Table 3
Comparison of clinical and imaging characteristics between pEMVI-positive and negative groups in the training and validation sets
| Characteristics | Training set | Validation set | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMVI(-)(n=89) | EMVI(+)(n=34) | P value | EMVI(-)(n=33) | EMVI(+)(n=12) | P value | ||
| Age(years) | 64.31±10.42 | 62.53±10.30 | 0.396 | 63.7±12.1 | 66.7±6.9 | 0.423 | |
| Gender(%) | 0.814 | 0.063 | |||||
| Male | 32(36.0) | 13(38.2) | 10(30.3) | 8(66.7) | |||
| Female | 57(64.0) | 21(61.8) | 23(69.7) | 4(33.3) | |||
| CEA (%) | 0.171 | 0.097 | |||||
| ≤5 ng/mL | 59(66.3) | 18(52.9) | 22(66.7) | 4(33.3) | |||
| >5 ng/mL | 30(33.7) | 16(47.1) | 11(33.3) | 8(66.7) | |||
| ADC Value(×10-3mm2/s) | 0.85(0.74,0.99) | 0.75(0.61,0.80) | <0.001 | 0.82(0.72,0.93) | 0.75(0.68,0.79) | 0.066 | |
| Infiltration Depth(mm) | 14.63±6.03 | 17.20±4.39 | 0.011 | 14.9±5.1 | 21.4±12.3 | 0.101 | |
| Length,(cm) | 41.18±15.51 | 48.27±15.54 | 0.025 | 43.3±14.2 | 47.9±19.0 | 0.387 | |
| Location (%) | 0.683 | 0.060# | |||||
| Upper | 27(30.3) | 8(23.5) | 11(33.3) | 0(0.0) | |||
| Middle | 35(39.3) | 16(47.1) | 12(36.4) | 6(50.0) | |||
| Low | 27(30.3) | 10(29.4) | 10(30.3) | 6(50.0) | |||
| mrT stage(%) | <0.001 | 0.074 | |||||
| T1-2 | 42(47.2) | 4(11.8) | 14(42.4) | 1(8.3) | |||
| T3-4 | 47(52.8) | 30(88.2) | 19(57.6) | 11(91.7) | |||
| mrEMVI(%) | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
| Negative | 71(79.8) | 9(26.5) | 26(78.8) | 1 (8.3) | |||
| Positive | 18(20.2) | 25(73.5) | 7 (21.2) | 11(91.7) | |||
| Radscore | -3.14(-4.44,-2.08) | -1.40(-2.69,-0.69) | <0.001 | -2.46(-4.19,-1.39) | -1.25(-1.74,-0.18) | 0.004 | |
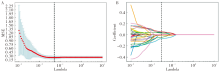
Figure 2
LASSO 10-fold cross-validation diagram A: (T2WI) The 10-fold cross-validation method was used to find the hyperparameter lambda for LASSO, with the optimal lambda value represented by a vertical dashed line; B: (DWI) Each colored line in the image represented the variation curve of the characteristic coefficient with the lambda value. The vertical dashed line represents the non-zero features obtained at the optimal lambda value.
Table 4
Results of univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis
| Variables | Univariate | Multivariate(clinical model) | Multivariate(combined model) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR(95% CI) | P value | OR(95% CI) | P value | OR(95% CI) | P value | |||
| Age | 0.983(0.946~1.022) | 0.393 | ||||||
| Gender | ||||||||
| Female | ||||||||
| Male | 0.907(0.401~2.051) | 0.814 | ||||||
| CEA | ||||||||
| ≤5 ng/mL | ||||||||
| >5 ng/mL | 1.748(0.782~3.907) | 0.173 | ||||||
| ADC | 0.000(0.000~0.012) | <0.001 | 0.000(0.000~0.016) | <0.001 | 0.000(0.000~0.016) | 0.001 | ||
| Infiltration depth | 1.085(1.008~1.167) | 0.029 | ||||||
| Length | 1.030(1.003~1.058)) | 0.029 | ||||||
| Location | ||||||||
| upper | ||||||||
| middle | 1.543(0.576~4.136) | 0.389 | ||||||
| low | 1.250(0.428~3.651) | 0.683 | ||||||
| mrT stage | ||||||||
| T1~T2 | ||||||||
| T3~T4 | 6.702(2.180~20.607) | 0.001 | 2.869(0.778~10.574) | 0.113 | 3.899(0.940~16.172) | 0.061 | ||
| mrEMVI | ||||||||
| Negative | ||||||||
| Positive | 10.957(4.363~27.518) | <0.001 | 8.643(2.886~25.886) | <0.001 | 7.928(2.397~26.221) | 0.001 | ||
| Radscore | 1.862(1.336~2.596) | <0.001 | 2.048(1.301~3.226) | 0.002 | ||||
Table 5
Predictive performance of different models in the training and validation sets
| Models | Training set | Validation set | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC(95% CI) | Sensitivity | Specificity | AUC(95% CI) | Sensitivity | Specificity | ||
| Radiomics model | 0.756(0.656~0.855) | 0.676 | 0.787 | 0.782(0.626~0.937) | 0.833 | 0.697 | |
| Clinical model | 0.888(0.829~0.948) | 0.824 | 0.865 | 0.896(0.753~1.000) | 0.917 | 0.939 | |
| Combined model | 0.926(0.879~0.973) | 0.882 | 0.865 | 0.917(0.813~1.000) | 0.917 | 0.909 | |
| [1] | XIA C, DONG X, LI H, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2022, 135(5):584-590. |
| [2] |
VAN DEN BROEK J J, VAN DER WOLF F S W, HEIJNEN L A, et al. The prognostic importance of MRI detected extramural vascular invasion (mrEMVI) in locally advanced rectal cancer[J]. Int J Colorectal Dis, 2020, 35(10):1849-1854.
doi: 10.1007/s00384-020-03632-9 pmid: 32488420 |
| [3] | SCHAAP D P, VOOGT E L K, BURGER J W A, et al. Prognostic implications of mri-detected emvi and tumor deposits and their response to neoadjuvant therapy in cT3 and cT4 rectal cancer[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2021, 111(3):816-825. |
| [4] | TAN J J, CARTEN R V, BABIKER A, et al. Prognostic importance of MRI-detected extramural venous invasion in rectal cancer: a literature review and systematic meta-analysis[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2021, 111(2):385-394. |
| [5] | 杨鋆, 辛城霖, 张忠涛. 中低位直肠癌的精准诊断与规范治疗[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2024, 23(1):85-90. |
| YANG Y, XIN C L, ZHANG Z T. Precision diagnosis and standardized treatment of mid-low rectal cancer[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2024, 23(1):85-90. | |
| [6] | 中华医学会外科学分会腹腔镜与内镜外科学组, 中华医学会外科学分会结直肠外科学组, 中国医师协会外科医师分会结直肠外科专家工作组, 等. 腹腔镜结直肠癌根治术操作指南(2023版)[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2024, 23(1):10-22. |
| Laparoscopic & Endoscopic Surgery Group, Branch of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association; Colorectal Surgery Group, Branch of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons, Chinese Medical Doctor Association, et al. Guideline for ope-rative procedure of laparoscopic radical surgery for colorectal cancer (2023 edition)[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2024, 23(1):10-22. | |
| [7] | 肖体先, 侯文运, 梅世文, 等. 早发性结直肠癌的临床病理特征[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2023, 22(12):1476-1483. |
| XIAO T X, HOU W Y, MEI S W, et al. Clinical characteristics of early-onset colorectal cancer[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2023, 22(12):1476-1483. | |
| [8] | 应俊, 孙亚煌, 王安琪, 等. 基于SEER数据库直肠癌肝转移预后列线图预测模型的构建及其应用价值[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2023, 22(S1):51-57. |
| YING J, SUN Y H, WANG A Q, et al. Construction and application value of nomogram predictive model for the prognosis of rectal cancer liver metastases based on SEER database[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2023, 22(S1):51-57. | |
| [9] |
SMITH N J, BARBACHANO Y, NORMAN A R, et al. Prognostic significance of magnetic resonance imaging-detected extramural vascular invasion in rectal cancer[J]. Br J Surg, 2008, 95(2):229-236.
doi: 10.1002/bjs.5917 pmid: 17932879 |
| [10] |
BAE J S, KIM S H, HUR B Y, et al. Prognostic value of MRI in assessing extramural venous invasion in rectal cancer: multi-readers' diagnostic performance[J]. Eur Radiol, 2019, 29(8):4379-4388.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5926-9 pmid: 30617483 |
| [11] | BROWN G, RADCLIFFE A G, NEWCOMBE R G, et al. Preoperative assessment of prognostic factors in rectal cancer using high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Br J Surg, 2003, 90(3):355-364. |
| [12] | LAMBIN P, LEIJENAAR R T H, DEIST T M, et al. Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and persona-lized medicine[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2017, 14(12):749-762. |
| [13] | YU X, SONG W, GUO D, et al. Preoperative prediction of extramural venous invasion in rectal cancer: comparison of the diagnostic efficacy of radiomics models and quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Front Oncol, 2020,10:459. |
| [14] | LIU S, YU X, YANG S, et al. Machine learning-based radiomics nomogram for detecting extramural venous invasion in rectal cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2021,11:610338. |
| [15] | SHU Z, MAO D, SONG Q, et al. Multiparameter MRI-based radiomics for preoperative prediction of extramural venous invasion in rectal cancer[J]. Eur Radiol, 2022, 32(2):1002-1013. |
| [16] | KANDA T, MATSUDA M, OBA H, et al. Gadolinium deposition after contrast-enhanced MR imaging[J]. Radio-logy, 2015, 277(3):924-925. |
| [17] |
DUAN C, KALLEHAUGE J F, BRETTHORST G L, et al. Are complex DCE-MRI models supported by clinical data?[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2017, 77(3):1329-1339.
doi: 10.1002/mrm.26189 pmid: 26946317 |
| [18] | 国家卫生健康委员会医政司, 中华医学会肿瘤学分会. 国家卫健委中国结直肠癌诊疗规范(2023版)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2023, 43(6):602-630. |
| Hospital Authority of National Health Commission ofthe People's Republic of China; Chinese Society ofOncology, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese protocol of diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer of the National Health Commission(2023 edition)[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2023, 43(6):602-630. | |
| [19] |
TALBOT I C, RITCHIE S, LEIGHTON M, et al. Invasion of veins by carcinoma of rectum: method of detection, histological features and significance[J]. Histopathology, 1981, 5(2):141-163.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1981.tb01774.x pmid: 7216178 |
| [20] | BATES D D B, HOMSI M E, CHANG K J, et al. MRI for rectal cancer: staging, mrCRM, EMVI, lymph node staging and post-treatment response[J]. Clin Colorectal Cancer, 2022, 21(1):10-18. |
| [21] | GLYNNE-JONES R, WYRWICZ L, TIRET E, et al. Rectal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up[J]. Ann Oncol, 2017, 28(suppl_4):iv22-iv40. |
| [22] |
ZHAO L, LIANG M, WANG S, et al. Preoperative evaluation of extramural venous invasion in rectal cancer using radiomics analysis of relaxation maps from synthetic MRI[J]. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021 Aug; 46(8):3815-3825.
doi: 10.1007/s00261-021-03021-y pmid: 33743017 |
| [23] | WANG H, CHEN X, DING J, et al. Novel multiparametric MRI-based radiomics in preoperative prediction of perirectal fat invasion in rectal cancer[J]. Abdom Radiol (NY), 2023, 48(2):471-485. |
| [24] | ROY S, MAJI P. Multispectral co-occurrence of wavelet coefficients for malignancy assessment of brain tumors[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(6):e0250964. |
| [25] | PENG Y, LUO Y, HU X, et al. Quantitative T2*-weighted imaging and reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted imaging of rectal cancer: correlation of R2* and apparent diffusion coefficient with histopathological prognostic factors[J]. Front Oncol, 2021,11:670156. |
| [26] |
AO W, ZHANG X, YAO X, et al. Preoperative prediction of extramural venous invasion in rectal cancer by dynamic contrast-enhanced and diffusion weighted MRI: a preliminary study[J]. BMC Med Imaging, 2022, 22(1):78.
doi: 10.1186/s12880-022-00810-9 pmid: 35484509 |
| [27] | 吴德生, 梁烨鑫, 陈秀婵, 等. 高分辨T2WI在直肠癌壁外血管侵犯诊断中的应用价值[J]. 中国中西医结合影像学杂志, 2020, 18(6):548-551. |
| WU D S, LIANG Y X, CHEN X C, et al. Application value of high-resolution MRI T2WI in extramural vascular invasion of rectal cancer[J]. Chin Imag J Integr Tradit West Med, 2020, 18(6):548-551. | |
| [28] | 张益飞, 李月玥, 杨彦松, 等. 基于高分辨率T2WI的影像组学列线图预测直肠癌脉管侵袭的研究[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2021, 32(7):500-505. |
| ZHANG Y F, LI Y Y, YANG Y S, et al. High resolution T2WI-based radiomics nomogram for prediction of lymphovascular invasion in rectal cancer[J]. J China Clin Med Imag, 2021, 32(7):500-505. | |
| [29] | 王可欣, 余静, 徐青. 基于RESOLVE ADC的影像组学列线图在预测直肠癌壁外血管侵犯中的应用价值[J]. 肿瘤影像学, 2023, 32(2):138-147. |
| WANG K X, YU J, XU Q. Radiomics based on RESOLVE ADC in identification of extramural venous invasion in rectal cancer[J]. Oncoradiol, 2023, 32(2):138-147. |
| [1] | LI Ming, CHEN Kemin, PAN Zilai, LUO Yu. Research progress on the value of CT and MRI in predicting hemorrhagic transformation after acute ischemic stroke [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(01): 83-89. |
| [2] | QIAN Danye, MENG Xiangjun, ZHU Liming. Value of Kyoto gastritis score and modified prediction model in diagnosing Helicobacter pylori infection status under gastroscopy in Chinese population [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(06): 555-561. |
| [3] | ZHOU Yilei, ZHANG Miao, GUO Rui, ZHOU Jinxin, LI Biao, LI Xiang. Value of 18F-PSMA PET/MRI for early diagnosis of recurrence and metastasis in prostate cancer patients after radical prostatectomy [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(06): 567-572. |
| [4] | FENG Li, REN Gang, CAI Rong, WANG Xinyun, WANG Hui, ZHU Mingjie. Clinical features study of perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) in genitourinary system [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(05): 460-465. |
| [5] | QIN Xiaodan, SUN Huiling, PAN Bei, PAN Yuqin, WANG Shukui. miR-1229-3p inhibits the malignant progression of colorectal cancer and serves as a potential biomarker [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(05): 429-440. |
| [6] | WEI Jian, SUN Jie, CUI Shishuang. Development of a Nomogram model for early diagnosis of Parkinson disease [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(03): 277-282. |
| [7] | LI Xiaoshi, QIN Yue. Multiple radiology imaging techniques in the diagnosis of gout [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(03): 311-318. |
| [8] | CHEN Qian, LIN Huimin, YAN Fuhua. Advances in the evaluation of hepatic function by magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(02): 190-196. |
| [9] | WANG Han, LU Haidi, WANG Lei, CONG Wenming, ZHENG Jianming, BAI Chenguang. Clinicopathological features of 2 cases of squamous cell carcinoma and 2 cases of adenosquamous carcinoma [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(01): 44-49. |
| [10] | LI Jiaxi, WANG Jinjiang, YU Liping, YUAN Ying, QIAO Guanglei, MA Lijun. Effect of RAB25 knockdown on ferroptosis of colorectal cancer cells [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2022, 21(06): 710-718. |
| [11] | YANG Ruixin, DU Yutong, YAN Ranlin, ZHU Zhenggang, LI Chen, YU Yingyan. Improving exploration of biological sample pretreatment in single-cell transcriptome sequencing of gastrointestinal tumors [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2022, 21(05): 567-574. |
| [12] | HUANG Juan, ZHU Xiaolei, LI Xiao, CHEN Kemin, YAN Fuhua, XU Xueqin. Study on blood oxygen level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of early renal hypoxia in chronic kidney disease [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2022, 21(03): 385-389. |
| [13] | DU Yanran, JIAO Jing, REN Yunyun, ZHOU Jianqiao. Application of ultrasound-based radiomics technology in the evaluation of fetal lung maturity [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2022, 21(03): 326-330. |
| [14] | ZHU Naiyi, JIANG Yixin, CHAI Li, CHAI Weimin. Diagnostic values of magnetic resonance imaging in mammography detected BI-RADS≥4 category calcifications with negative ultrasound results [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2021, 20(05): 439-444. |
| [15] | ZHANG Hua, LU Wei, YANG Chengyi, XIANG Mingjie. Value of serum FBLN1 detection in diagnosis and prognosis prediction of colorectal cancer [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2021, 20(05): 462-465. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||