

Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice ›› 2025, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (03): 293-300.doi: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2025.03.008
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Rana, ZHAN Weiweia( ), LI Chenga, TANG Hailanga, BO Yulianb, LIU Kunc
), LI Chenga, TANG Hailanga, BO Yulianb, LIU Kunc
Received:2025-02-08
Accepted:2025-05-05
Online:2025-06-25
Published:2025-06-25
Contact:
ZHAN Weiwei
E-mail:shanghairuijin@126.com
CLC Number:
ZHAO Ran, ZHAN Weiwei, LI Cheng, TANG Hailang, BO Yulian, LIU Kun. Application value of transrectal contrast-enhanced ultrasound combined with magnetic resonance imaging in T staging and treatment decision-making for middle and low rectal cancer[J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2025, 24(03): 293-300.
Table 3
Sensitivity,specificity,positive and negative predictive values of three methods for T staging
| Pathologic staging | Inspection method | Sensitivity | Specificity | Positive predictive value | Negative predictive value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | CEUS MRI Joint inspection | 0.875 0.813 0.875 | 0.981 0.990 0.990 | 0.933 0.999 0.999 | 0.964 0.948 0.967 |
| T2 | CEUS MRI Joint inspection | 0.870 0.783 0.913 | 0.959 0.926 0.963 | 0.909 0.818 0.913 | 0.940 0.909 0.963 |
| T3 | CEUS MRI Joint inspection | 0.806 0.903 0.935 | 0.955 0.952 0.978 | 0.926 0.933 0.967 | 0.875 0.930 0.957 |
| T4 | CEUS MRI Joint inspection | 0.800 0.900 0.900 | 0.983 0.983 0.985 | 0.889 0.900 0.900 | 0.967 0.983 0.985 |
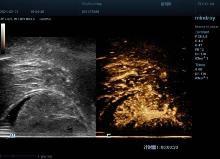
Figure 1
T1 CEUS image Note: The above image is a CEUS image of a patient with stage T1 pathology (rectal tubular villous adenoma with moderate dysplasia of superficial glandular epithelium). During the arterial phase (13 seconds after injection), contrast agent entered the mass from the pedicle and rapidly perfused internally to the edge of the mass, reaching a peak at 30 seconds. The image showed varying degrees of uniform enhancement.
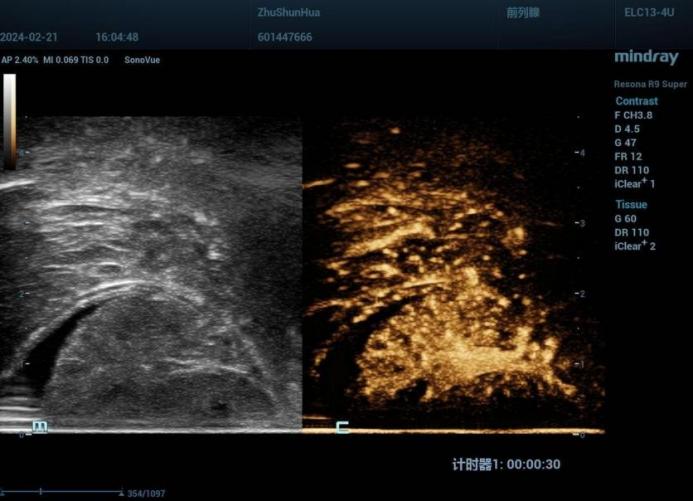
Figure 2
T2 CEUS image Note: The above image is a CEUS image of a patient with T2 stage pathology. During the arterial stage (18 seconds after injection), contrast agent appeared at the edge of the mass, rapidly perfused inward, and reached its peak at 25 seconds. The image showed uniform high enhancement.
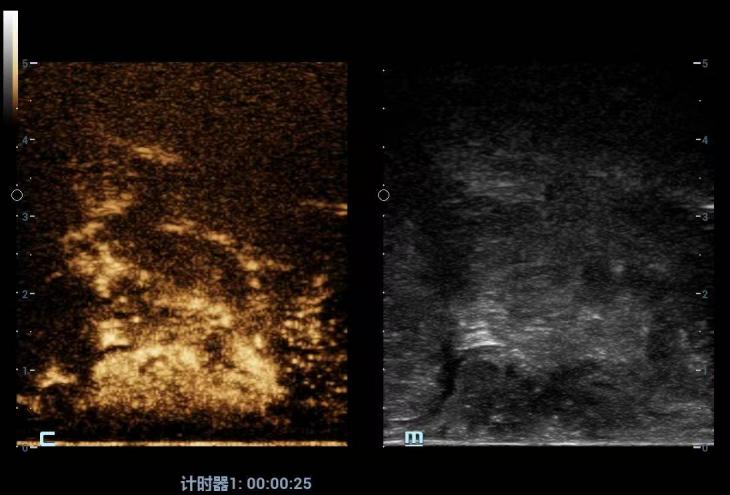

Figure 3
Combined diagnosis of CEUS and MR in T4a stage Note: The above figure shows a patient with combined diagnosis of T4a stage. TRUS shows lesions involving the serosal layer,while CEUS images show uneven high enhancement in the arterial phase. In the portal phase (40 seconds after injection of contrast agent),the tumor exhibits low enhancement characteristics. MRI showed slightly low signal intensity of T1W/T2W,high signal intensity of FS-T2W,high signal intensity of DWI,low signal intensity of ADC,and significant uneven enhancement of the lesion after enhancement. The entire intestinal wall was affected,and peritoneal retraction may be affected. Curved dilated vascular shadows were observed around the lesion with EMVI (+),and the mesorectal fascia was invaded with MRF (-). Multiple enlarged lymph nodes in the mesentery were identified with CRM (-),consistent with median rectal cancer. The combined diagnosis was considered as T4aN0. After neoadjuvant therapy,the patient underwent surgical resection after tumor regression.
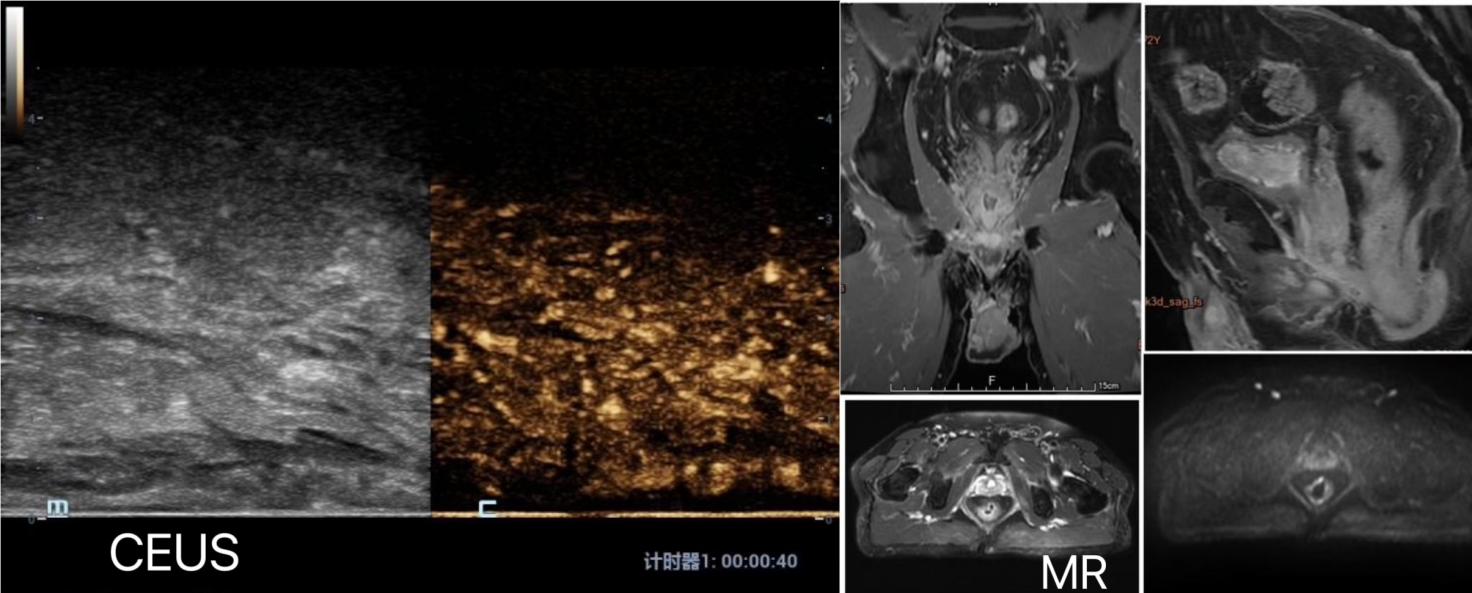
Table 4
Statistics of Missed Diagnosis and Misdiagnosis with Causes for CEUS, MRI, and Combined Examination in Mid-low Rectal Cancer
| Pathological staging | Diagnostic methods | Total number of cases | Number of correct diagnoses | Number of missed diagnoses (underestimation) | Missed diagnosis rate | Number of misdiagnoses (overestimation) | Misdiagnosis rate | Diagnostic accuracy rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pT1 | CEUS | 16 | 14 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 12.5 | 87.5 |
| MRI | 16 | 13 | 0 | 0.0 | 3 | 18.8 | 81.2 | |
| Combined examination | 16 | 14 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 12.5 | 87.5 | |
| pT2 | CEUS | 23 | 20 | 0 | 0.0 | 3 | 13.0 | 87.0 |
| MRI | 23 | 18 | 0 | 0.0 | 5 | 21.7 | 78.3 | |
| Combined examination | 23 | 21 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 8.7 | 91.3 | |
| pT3 | CEUS | 31 | 25 | 6 | 19.4 | 0 | 0.0 | 80.6 |
| MRI | 31 | 28 | 1 | 3.2 | 2 | 6.5 | 90.3 | |
| Combined examination | 31 | 29 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 6.5 | 93.5 | |
| pT4 | CEUS | 10 | 8 | 2 | 20.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 80 |
| MRI | 10 | 9 | 1 | 10.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 90 | |
| Combined examination | 10 | 9 | 1 | 10.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 90 | |
| Total | CEUS | 80 | 67 | 8 | 10.0 | 5 | 6.3 | 83.8 |
| MRI | 80 | 68 | 2 | 2.5 | 10 | 12.5 | 85 | |
| Combined examination | 80 | 73 | 1 | 1.2 | 6 | 7.5 | 91.3 |
| [1] | National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN guidelines® insights:rectal cancer,version 3.2024[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2024, 22(6):366-375. |
| [2] | SIEGEL R L, MILLER K D, JEMAL A. Cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(1):7-30. |
| [3] | 中华医学会外科学分会腹腔镜与内镜外科学组, 中华医学会外科学分会结直肠外科学组, 中国医师协会外科医师分会结直肠外科专家工作组, 等. 腹腔镜结直肠癌根治术操作指南(2023版)[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2024, 23(1):10-22. |
| Laparoscopic & Endoscopic Surgery Group, Branch of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association, Colorectal Surgery Group, Branch of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons, Chinese Medical Doctor Association, et al. Guideline for operative procedure of laparoscopic radical surgery for colorectal cancer (2023 edition)[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2024, 23(1): 10-22. | |
| [4] | EDGE S B, BYRD D R, COMPTON C C, et al. AJCC cancer staging manual[M]. 7th ed. New York: Springer, 2010. |
| [5] | SARGENT D J, MARSON R P, MONGA J, et al. Preope-rative chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer: Long-term results of RTOG 98-11 trial[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2012, 30(13):1491-1497. |
| [6] | van HAGEN P, HULSHOF M C, van LANSCHOT J J, et al. Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer: A systematic review[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2012, 13(6):e270-e277. |
| [7] | MAAS M, BEETS-TAN R, LAMBIN P, et al. Preoperative MRI in rectal cancer: A systematic review[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2010, 11(9):817-826. |
| [8] | CUI X W, TANG Y L, LIANG P, et al. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound for colorectal cancer diagnosis: A meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2018,108:142-150. |
| [9] | ZHANG X, LIANG P, WANG Y, et al. Diagnostic values of 3D transrectal ultrasound and MRI in T substaging of rectal cancer[J]. Abdom Radiol, 2019, 44(10):3616-3624. |
| [10] | KANG X, ZHANG X, LIANG P, et al. Double contrast-enhanced ultrasonography vs MRI in rectal cancer staging[J]. Eur Radiol, 2018, 28(11):4655-4663. |
| [11] | SIDDIQUI F, BROWN G, TEKKIS P, et al. Multidisciplinary team management of rectal cancer:A systematic review[J]. Br J Surg, 2017, 104(13):1732-1743. |
| [12] | 多中心直肠癌真实世界数据库建设与数据质量控制策略[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2025, 24(1):77-81. |
| Multicenter rectal cancer real-world database construction and data quality control strategies[J]. J Chin Dig Surg, 2025, 24(1):77-81. | |
| [13] | BROWN G, SIDDIQUI F, TEKKIS P, et al. Impact of multidisciplinary team meetings on colorectal cancer management[J]. Clin Oncol, 2018, 30(11):697-707. |
| [14] | MAAS M, BEETS-TAN R, LAMBIN P, et al. Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging of rectal cancer:a systematic review[J]. Lancet Oncology, 2010, 11(9):817-826. |
| [15] | 舒国亮, 肖耀成, 唐贤朋, 等. 腔内超声及磁共振对局部进展期直肠癌诊断准确性的研究[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2022, 38(22):2850-2854. |
| SHU G L, XIAO Y C, TANG X P, et al. Study on diagnostic accuracy of intracavitary ultrasound and MRI for locally advanced rectal cancer[J]. J Pract Med, 2022, 38(22):2850-2854. | |
| [16] | 刘丽娟, 袁倩, 徐晓红, 等. 超声双重造影在结直肠癌诊断及分期评估中的应用进展[J]. 山东医药, 2024, 64(1):111-114. |
| LIU L J, YUAN Q, XU X H, et al. Application progress of dual-contrast ultrasound in diagnosis and staging of colorectal cancer[J]. Shandong Med J, 2024, 64(1):111-114. | |
| [17] | 李陶, 任安平, 程伟, 等. 双平面经直肠腔内超声联合超微血流成像在中低位直肠癌术前T分期中的应用价值[J]. 中华普通外科杂志, 2023, 38(9):662-668. |
| LI T, REN A P, CHENG W, et al. Value of dual-plane transrectal ultrasound with microflow imaging in preope-rative T staging of mid-low rectal cancer[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2023, 38(9):662-668. | |
| [18] | 郭碧萍. 直肠超声双重造影与介入活检检查对直肠癌分型及TN分期的评估[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2022, 51(8):57-60. |
| GUO B P. Evaluation of rectal cancer classification and TN staging by dual-contrast rectal ultrasound and biopsy[J]. J Med Res, 2022, 51(8):57-60. | |
| [19] | 李观远. 经直肠超声造影参数与直肠癌患者临床病理特征及生存预后的相关性[J]. 生命科学仪器, 2023, 21(3):97-100. |
| LI G Y. Correlation between parameters of transrectal contrast-enhanced ultrasound and clinical pathological characteristics in rectal cancer[J]. Life Sci Instrum, 2023, 21(3):97-100. | |
| [20] | 邓旦, 李茜, 孙丽娟. 术前经直肠三维超声及盆腔MRI检查在中低位直肠癌TN分期评估中的应用[J]. 山东医药, 2018, 58(27):75-78. |
| DENG D, LI Q, SUN L J. Application of preoperative 3D transrectal ultrasound and pelvic MRI in TN staging of mid-low rectal cancer[J]. Shandong Med J, 2018, 58(27):75-78. | |
| [21] | 宋天彬, 卢洁. 磁共振扩散加权成像在直肠癌新辅助放化疗中的应用价值[J]. 协和医学杂志, 2017, 8(2-3):100-105. |
| SONG T B, LU J. Application value of diffusion-weighted MRI in neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer[J]. Med J Peking Union Med Coll, 2017, 8(2-3):100-105. | |
| [22] | 赵任, 蒋奕枚. 直肠癌外科手术治疗进展[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2016, 21(6):468-471. |
| ZHAO R, JIANG Y M. Progress in surgical treatment of rectal cancer[J]. J Surg Theory Pract, 2016, 21(6):468-471. | |
| [23] | 孙跃明, 张冬生. 重视结直肠癌外科手术的进步[J]. 中国肿瘤外科杂志, 2022, 4(6):521-526. |
| SUN Y M, ZHANG D S. Advances in colorectal cancer surgery[J]. Chin J Surg Oncol, 2022, 14(6):521-526. | |
| [24] | 李珂璇, 肖体先, 汪晓东, 等. 中低位直肠癌初诊及新辅助治疗后评估完成度分析:全国多中心真实世界研究[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2025, 24(1): 113-119. |
| LI K X, XIAO T X, WANG X D, et al. Analysis of completion rate of tumor evaluation at initial assessment and after neoadjuvant therapy for mid and low rectal cancer : a national multicenter real-world study[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2025, 24(1):113-119. | |
| [25] | 马韬, 冯波. 局部进展期直肠癌全程新辅助治疗的发展与挑战[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2023, 43(7):744-751. |
| MA T, FENG B. Development and challenges of total neoadjuvant therapy for locally advanced rectal cancer[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2023, 43(7):744-751. | |
| [26] | 徐远, 曲智锋, 原翔. Ⅲb期直肠癌术前短程放疗与术前长程放疗分别联合化疗疗效的随机对照研究[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2021, 29(11):1923-1928. |
| XU Y, QU Z F, YUAN X. Randomized controlled study of preoperative short-course vs long-course radiotherapy combined with chemotherapy for stage Ⅲb rectal cancer[J]. Mod Oncol, 2021, 29(11):1923-1928. |
| [1] | CAI Xinxin, DENG Rong, XU Xinxin, XU Zhihan, CHANG Rui, DONG Haipeng, LIN Huimin, YAN Fuhua. Study on consistency between liver fat fraction quantification based on photon-counting CT and MRI proton density fat fraction [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2025, 24(02): 146-154. |
| [2] | WANG Kangning, ZHU Lan, FENG Weiming, XIA Yihan, SHI Bowen, ZHANG Huan. Value of synthetic MRI in predicting treatment response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2025, 24(02): 170-177. |
| [3] | ZHANG Huihui, FANG Shu, WU Mengxiong, LIU Fangtao, HE Naying, DONG Haipeng, YAN Fuhua. Study on deep learning reconstruction technology in improving image quality of pituitary neuroendocrine tumors in coronal T1WI magnetic resonance image [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(06): 594-601. |
| [4] | FENG Yuan, HE Zhao, SUN Qingfang, SUN Bomin, YAN Fuhua, YANG Guangzhong. Advances in interventional magnetic resonance imaging and its clinical applications [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(02): 108-113. |
| [5] | ZHA Yunfei, WU Xiaxia. Application and research progress of MRI deep learning image reconstruction technology in clinical diagnosis of musculoskeletal system diseases [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(02): 114-118. |
| [6] | GAO Meng, CHAI Weimin, YAN Fuhua. Advance in study on diagnosis of pancreatic cystic tumors on CT/MRI imaging [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(02): 184-191. |
| [7] | LI Ming, CHEN Kemin, PAN Zilai, LUO Yu. Research progress on the value of CT and MRI in predicting hemorrhagic transformation after acute ischemic stroke [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(01): 83-89. |
| [8] | DING Jingfeng, AO Weiqun, ZHU Zhen, SUN Jing, XU Lianggen, ZHENG Shibao, YU Jingjing, HU Jinwen. The value of radiomics based on T2WI and DWI of MRI in preoperative prediction of extramural vascular invasion in rectal cancer [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2024, 23(01): 46-56. |
| [9] | ZHOU Yilei, ZHANG Miao, GUO Rui, ZHOU Jinxin, LI Biao, LI Xiang. Value of 18F-PSMA PET/MRI for early diagnosis of recurrence and metastasis in prostate cancer patients after radical prostatectomy [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(06): 567-572. |
| [10] | FENG Li, REN Gang, CAI Rong, WANG Xinyun, WANG Hui, ZHU Mingjie. Clinical features study of perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) in genitourinary system [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(05): 460-465. |
| [11] | LI Xiaoshi, QIN Yue. Multiple radiology imaging techniques in the diagnosis of gout [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(03): 311-318. |
| [12] | CHEN Qian, LIN Huimin, YAN Fuhua. Advances in the evaluation of hepatic function by magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2023, 22(02): 190-196. |
| [13] | HUANG Juan, ZHU Xiaolei, LI Xiao, CHEN Kemin, YAN Fuhua, XU Xueqin. Study on blood oxygen level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of early renal hypoxia in chronic kidney disease [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2022, 21(03): 385-389. |
| [14] | ZHU Naiyi, JIANG Yixin, CHAI Li, CHAI Weimin. Diagnostic values of magnetic resonance imaging in mammography detected BI-RADS≥4 category calcifications with negative ultrasound results [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2021, 20(05): 439-444. |
| [15] | ZHANG Xuekun, LI Yan, YAN Fuhua, ZHAO Hongfei, SONG Qi. Application value of new accelerating technology based on constellation shuttling imaging in brain MRI [J]. Journal of Diagnostics Concepts & Practice, 2021, 20(04): 378-383. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||